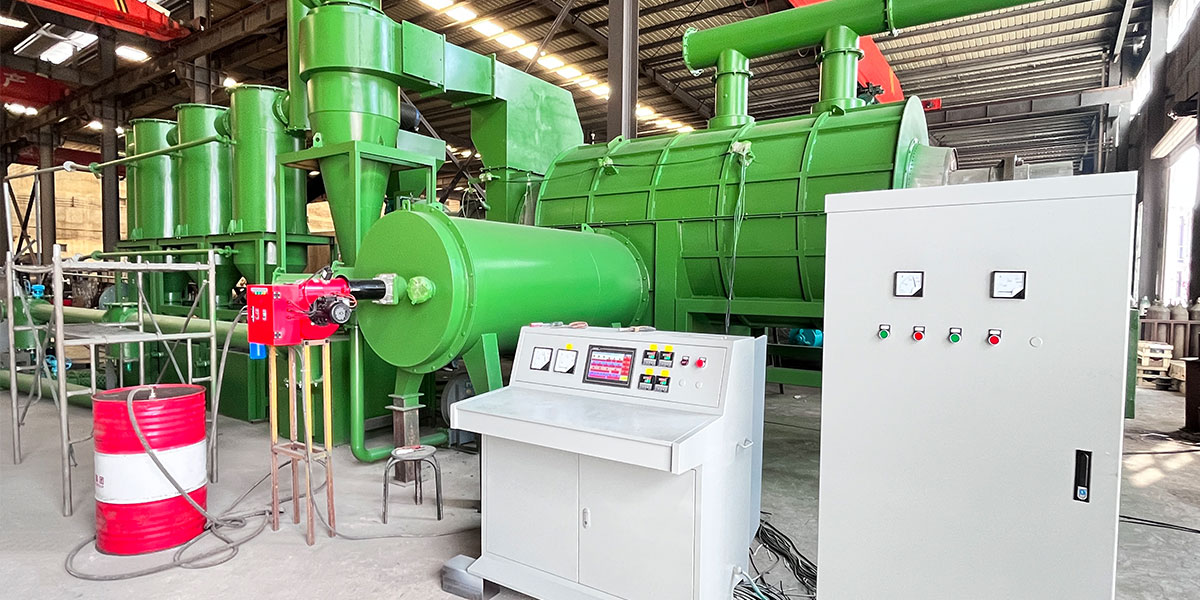
The Bio Charcoal Making Machine can process biomass (straw, wood, rice husk, coconut and animal manure) into biochar by pyrolysis technology. Bio Charcoal is produced by thermal cracking of biomass under anoxic or anaerobic conditions.
High-temperature pyrolysis technology is currently the most commonly used method for making biochar. The cost of biomass carbonization machine is low, but the biochar yield is higher.
Biochar has the characteristics of high carbon content, rich nutrients, strong stability and developed pore structure. It can promote soil health, repair ecological environmental pollution and reduce CO2 emissions.
Biochar generally has a developed pore structure and rich multivalent cations (Ca2+ and Mg2+), which can be used as a saline-alkali land conditioner. It can effectively improve the physical and chemical properties of soil and the structure of microbial communities, and improve the salt tolerance of plants. In addition, biochar with a large specific surface area can stimulate the growth of N2O reducing microorganisms, increase the abundance of nitrogen fixation, nitrification and denitrification functional genes, and thus reduce N2O emissions.
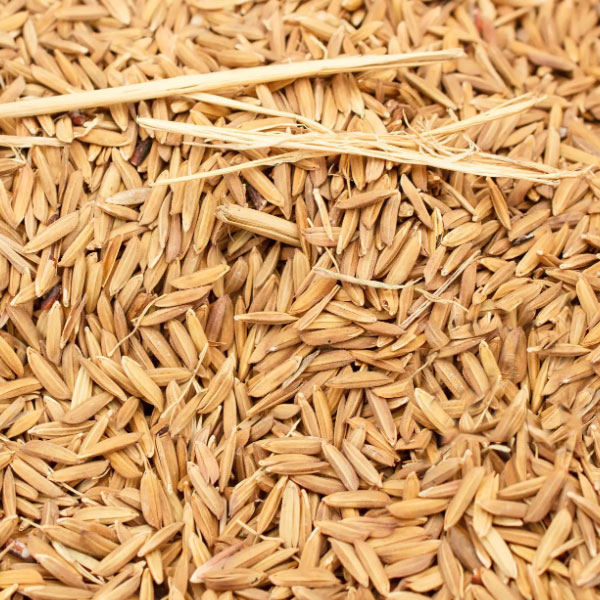
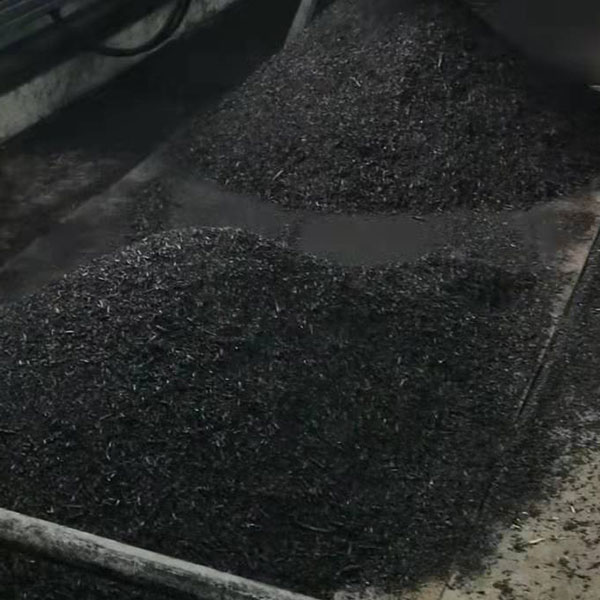
Using rice husk as biomass raw material, the Bio Charcoal Making process by biomass pyrolysis equipment is introduced below.


Bio Charcoal Making Process
The continuous biomass carbonization plant has a raw material size requirement of less than 20mm and a moisture content of less than 15%. The size and moisture content of rice husks meet the requirements of Bio Charcoal Making Equipment and no pretreatment is required.
Pyrolysis is the core link of rice husk charcoal making. Under anaerobic or oxygen-free conditions, the rice husk biomass raw material is heated to a certain temperature. The rotary pyrolysis furnace is suitable for large-scale continuous production, which allows the rice husk to be evenly heated in the rotating furnace body.
The rice husk enters the rotatable cylindrical furnace body from the feed port. As the furnace body rotates and rolls, it is fully in contact with the hot air flow and evenly heated. By adjusting parameters (furnace body speed, temperature and pyrolysis time) the quality and output of rice husk chaarcoal can be controlled.
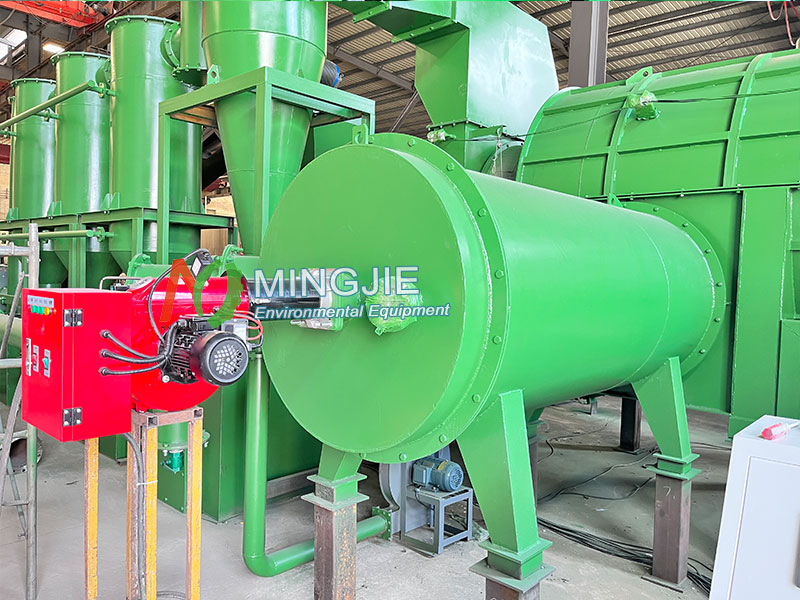

The pyrolysis temperature of rice husk is generally controlled between 400-600℃. During the biomass pyrolysis process, the cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin components in the rice husk biomass undergo dehydration, depolymerization, cracking and other reactions. Finally, the rice husk is converted into solid biochar, liquid bio-oil and gaseous pyrolysis gas.
At lower temperatures (400-500℃), it is conducive to the production of rice husk charcoal with rich pore structure and improve its adsorption performance. At higher temperatures (500-600℃), the pyrolysis gas output increases, and the hardness and stability of rice husk charcoal are improved.
Collection and Treatment of Biomass Pyrolysis Products
After biomass pyrolysis, the rice husk charcoal, bio-oil and pyrolysis gas produced need to be separated. The larger particles of rice husk charcoal can be separated from the mixed products by a cyclone separator. For fine charcoal powder, it is further filtered and collected by a bag filter.
The condenser can condense the bio-oil vapor and water vapor in the mixed gas into liquid. Then the bio-oil and pyrolysis gas are separated by a gas-liquid separation device.
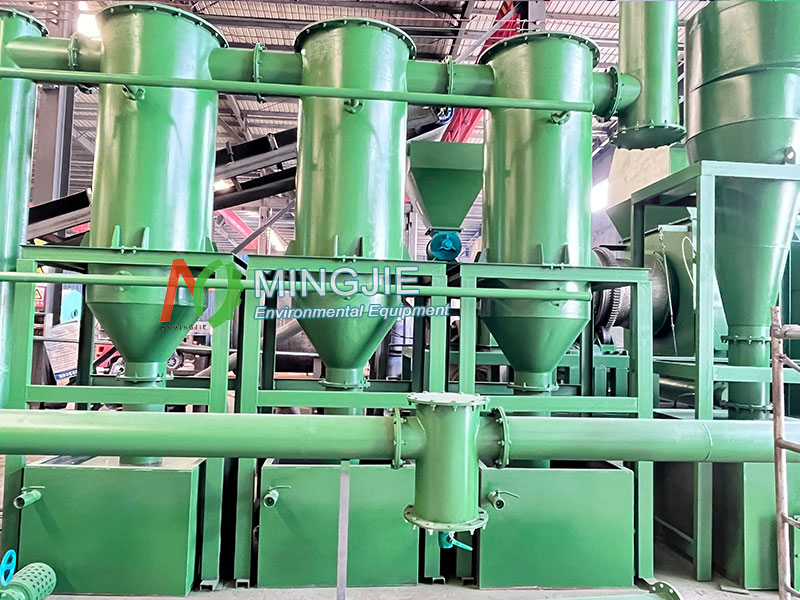

The temperature of the rice husk charcoal after pyrolysis is high, and it is easy to oxidize when directly exposed to the air. It needs to be quickly cooled by an air-cooled cooler or a water-cooled cooler to reduce the temperature to room temperature.
Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Manufacturer
Mingjie Group is a professional biomass pyrolysis plant manufacturer. We can design different Bio Charcoal Making solutions and carbonization equipment according to different biomass raw materials and customer needs.
The type of biomass raw material has a significant impact on the properties of biochar. Common biomass raw materials include agricultural waste (straw, rice husks, corn cobs), forestry waste (bamboo, sawdust), sludge, etc. Different raw materials have different chemical compositions and physical properties. And the biochar will also have differences in pore structure, surface chemical properties, carbon content, etc.