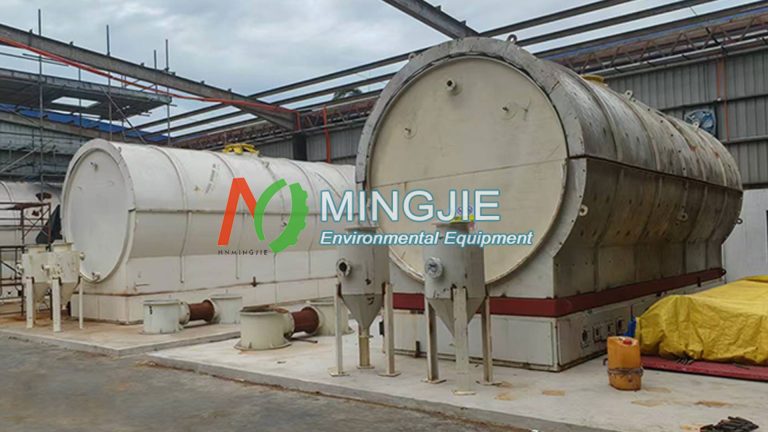
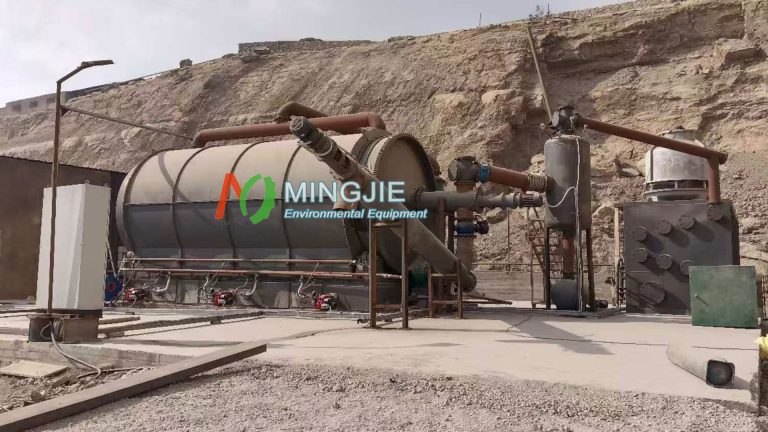
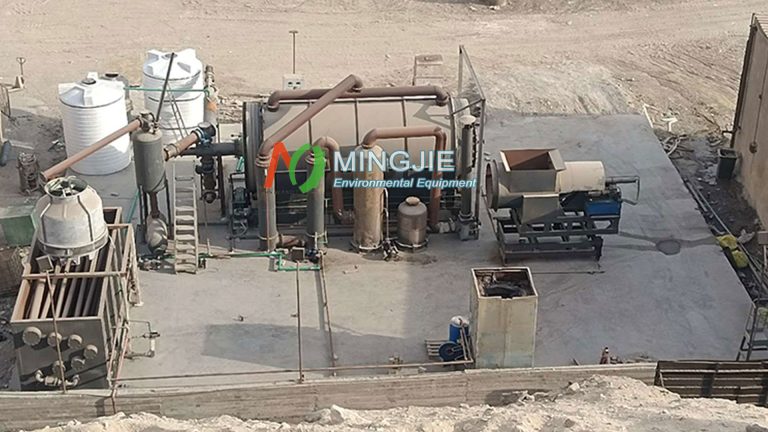
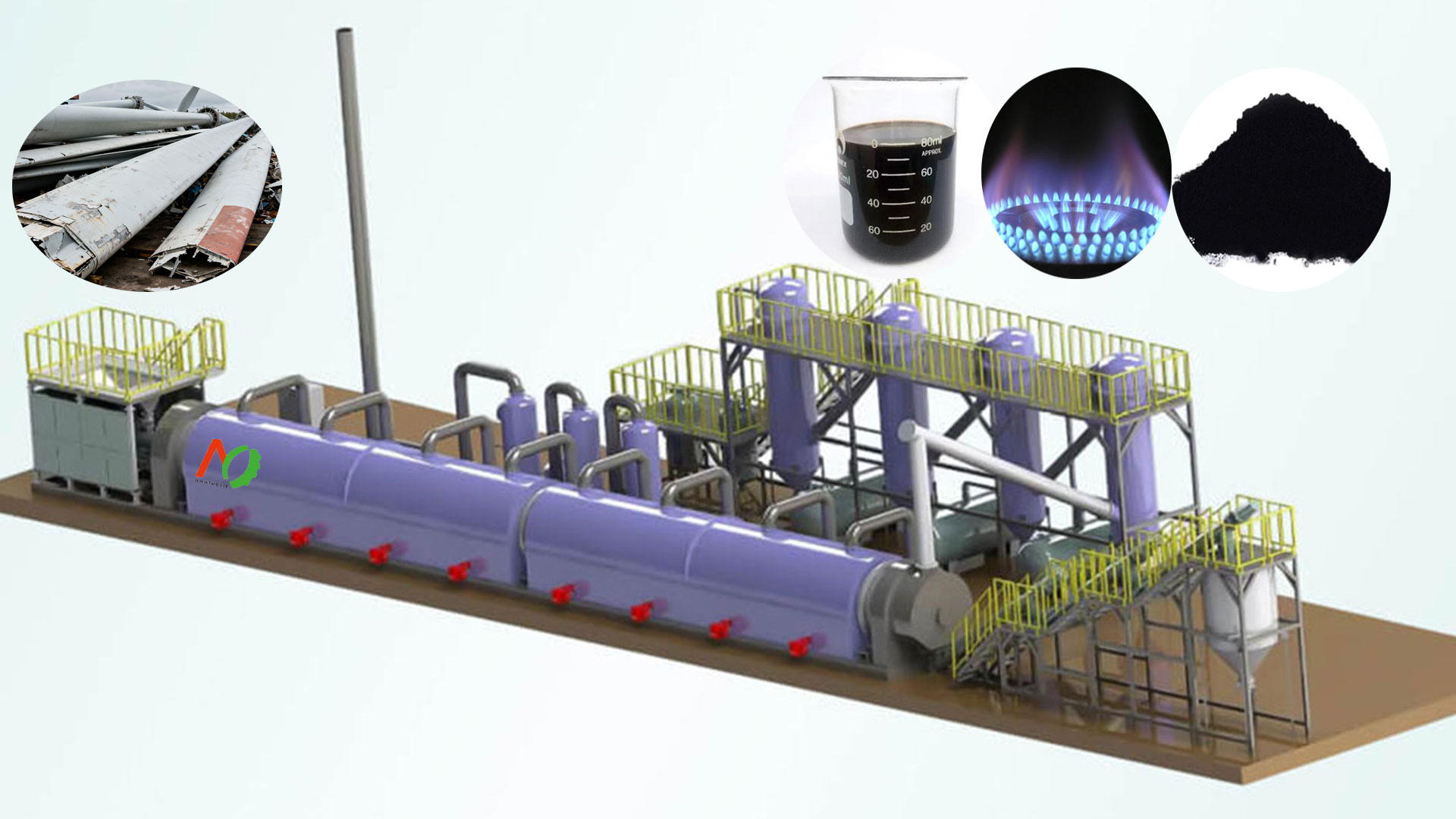
Pyrolysis offers a more advanced method for wind turbine blade recycling. Wind turbine blade pyrolysis involves heating and decomposing organic matter under anaerobic conditions. It can recover glass fibers while converting resins into oil, gas, or solid char, the latter of which can be used as energy.
Behind the booming wind power industry, the challenge of disposing of discarded wind turbine blades is gradually emerging. Wind turbine blades are typically made of composite materials such as glass fiber reinforced polymer (GFRP). These materials give the blades the ability to operate stably in harsh environments, allowing them to withstand decades of wind, rain, and strong wind impacts. However, these materials are extremely difficult to degrade in the natural environment, belonging to non-biodegradable materials, and require hundreds of years to decompose in landfills.
As early-installed wind turbines gradually reach their 20-25 year lifespan, a large number of blades face retirement. It is estimated that by 2050, the global cumulative total of discarded blades will reach a staggering 43 million tons. Currently, the main methods for large-scale disposal of discarded wind turbine blades are still incineration and landfill.
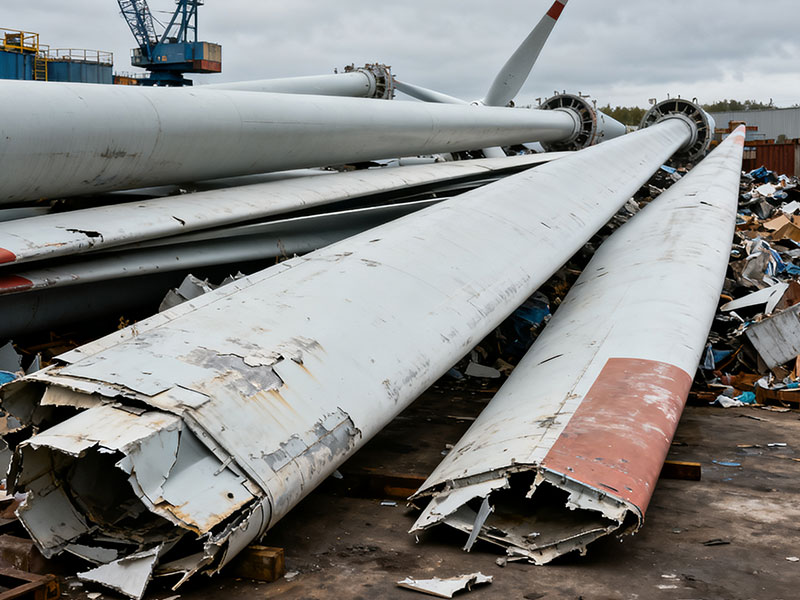

Incineration releases harmful gases, such as dioxins, causing severe air pollution. Landfilling, on the other hand, not only occupies vast amounts of valuable land resources but also leads to the rapid depletion of limited landfill capacity.
Among numerous explorations into solving the problem of disposing of waste wind turbine blades, pyrolysis technology has emerged as a leading solution. During wind turbine blade pyrolysis process, the composite materials in wind turbine blades undergo complex and orderly decomposition changes.
As the temperature rises, they decompose into combustible gases, liquid oil, and solid carbon black. Meanwhile, the glass fibers largely retain their fibrous form in pyrolysis machine. They remain as solid residue, becoming a valuable recyclable resource.
How to Achieve Wind Turbine Blade Recycling Through Pyrolysis Machine?
The pyrolysis process for wind turbine blade recycling generally includes three main stages: pretreatment, pyrolysis reaction, and product separation.
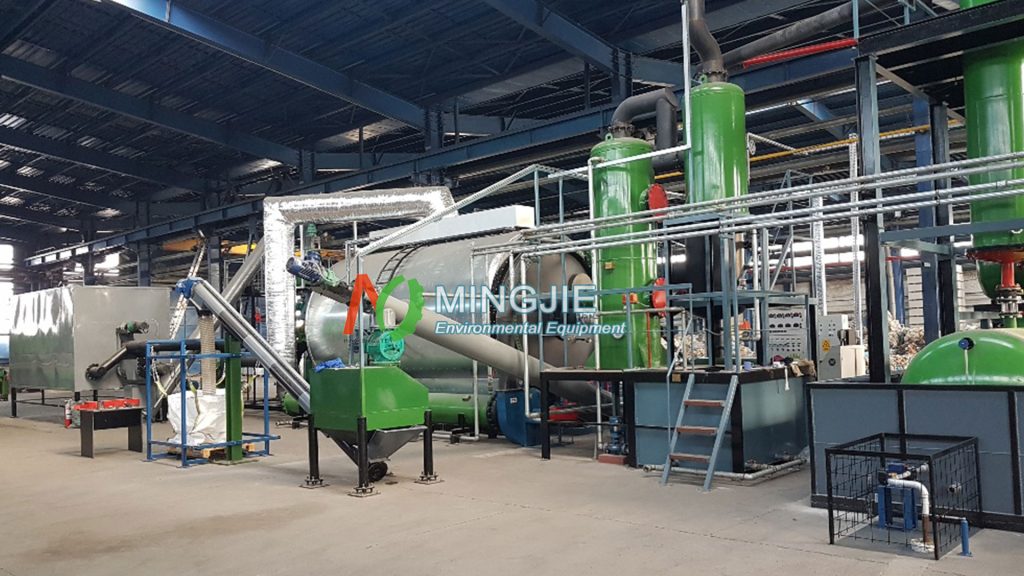

In the pretreatment stage, waste blades need to be cleaned and crushed to remove surface impurities and reduce blade size. This facilitates the subsequent pyrolysis reaction and also improves the processing efficiency of the pyrolysis equipment.
In the wind turbine blade pyrolysis reaction stage, parameters are precisely controlled according to the blade material characteristics and the requirements of target product. These parameters include pyrolysis temperature, heating rate, and reaction time, ensuring the blades decompose fully under the set conditions.
In the product separation stage, the gaseous, liquid, and solid products by wind turbine blade pyrolysis are effectively separated for further processing and utilization. This stage adopts various techniques, such as condensation, filtration, and adsorption.
Wind Turbine Blade Pyrolysis Products
Pyrolysis oil is a liquid product. Its composition is complex, containing various organic compounds such as aromatics, alkenes, phenols, alcohols, and ketones. These compounds give pyrolysis oil high chemical utilization value. From a fuel perspective, after appropriate upgrading, pyrolysis oil can be used as a liquid fuel. Pyrolysis oil also has broad application prospects in the chemical industry. Due to its rich content of various organic compounds, it can be used as a raw material for the production of resins, plastics, coatings, inks, and other chemical products.

Pyrolysis gas is one of the important byproducts produced during the pyrolysis process. Its main components include combustible gases such as hydrogen (H₂), methane (CH₄), and carbon monoxide (CO). These gases have high calorific value and are excellent energy carriers.
In the energy sector, pyrolysis gas can be directly used as fuel for power generation and heating. By feeding the pyrolysis gas into a gas turbine or internal combustion engine, the heat generated from combustion drives a generator, thus producing electricity.
Fibers are one of the solid products retained after pyrolysis, primarily glass fibers. These glass fibers largely retain their original fibrous morphology and properties during pyrolysis. They possess high strength, high modulus, high temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance, making them an excellent reinforcing material.