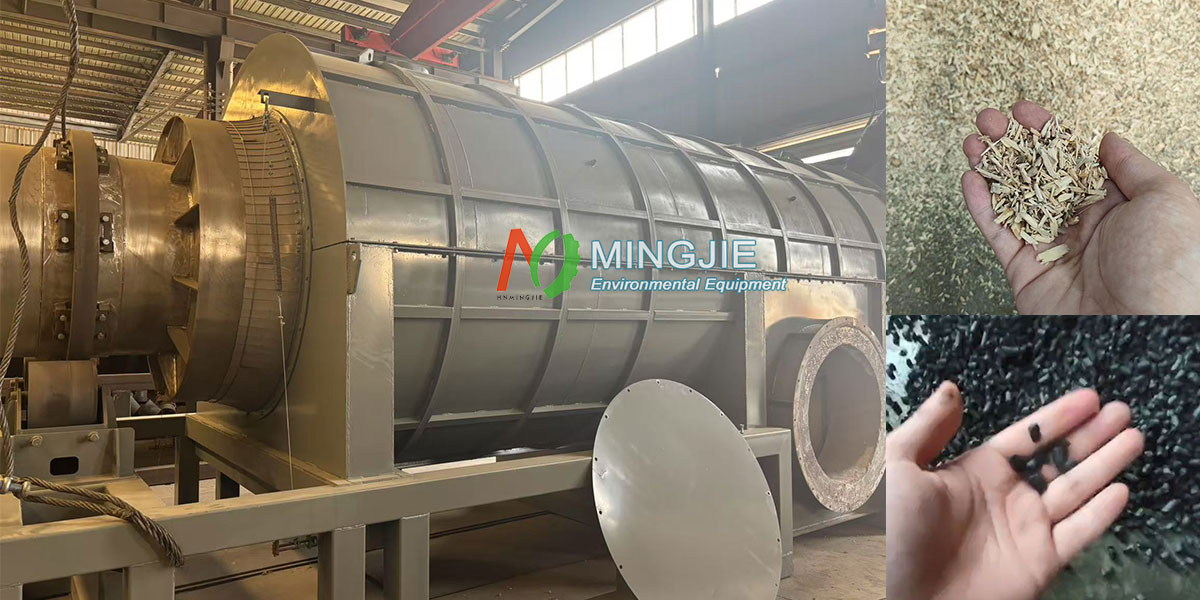
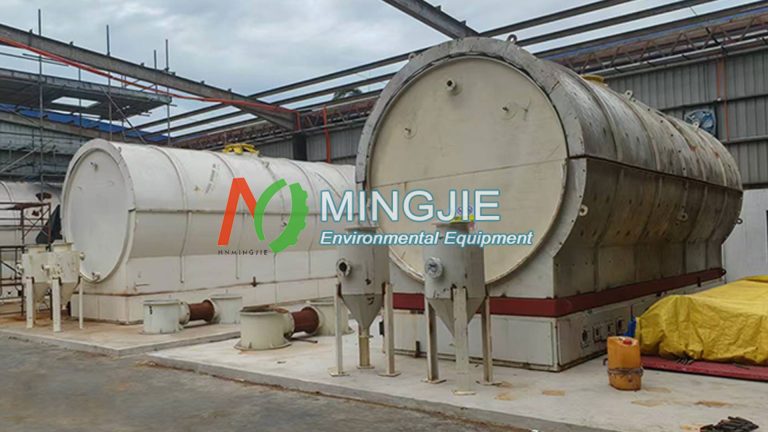
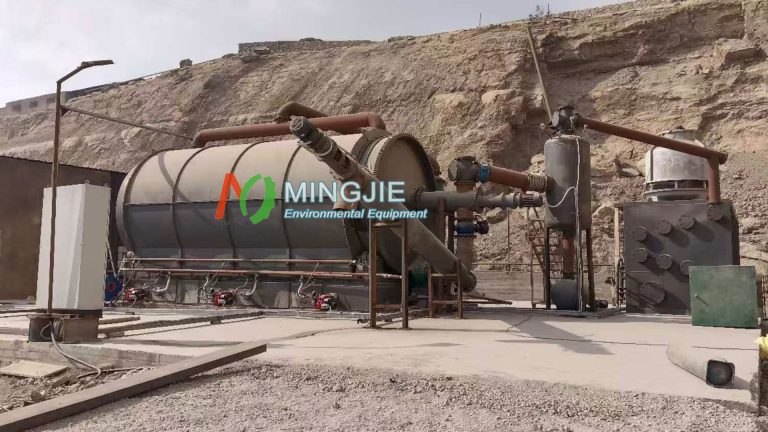
Driven by the dual goals of global carbon neutrality and the need for ecological and environmental governance, biomass pyrolysis machines, as a key device for converting waste biomass into biochar, are gradually gaining public attention. Biochar manufacturing machine provide innovative solutions for agricultural soil improvement and environmental pollution control. It becomes a key link between biomass resource recycling and carbon sequestration.
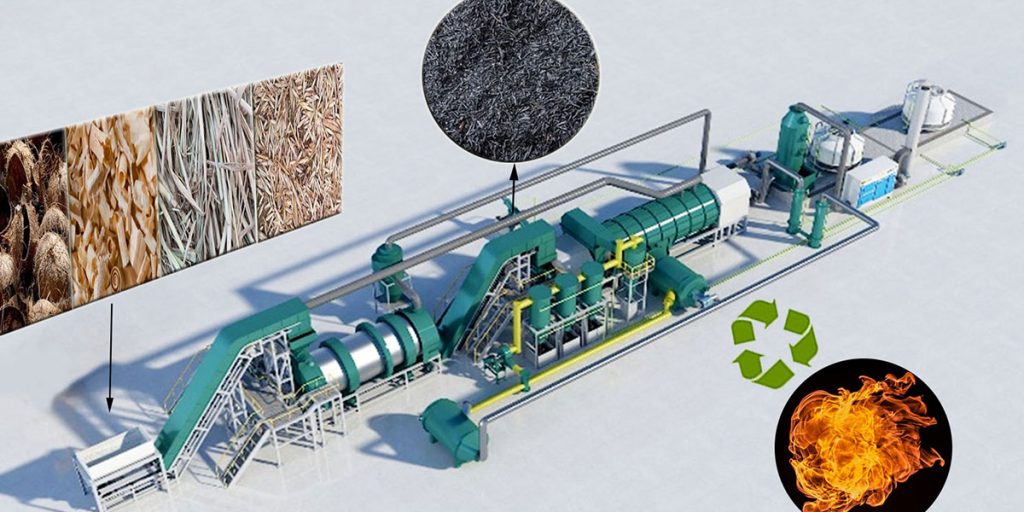
Biochar manufacturing machine primarily processes biomass feedstock through pyrolysis technology (a thermochemical conversion technology). Unlike traditional biomass combustion or composting, the core value of biomass pyrolysis lies in carbon sequestration, resource recycling, and high-value products.
Biochar making machine can sequester carbon from biomass in a stable form in biochar. Biochar can remain in the soil for hundreds or even thousands of years, reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
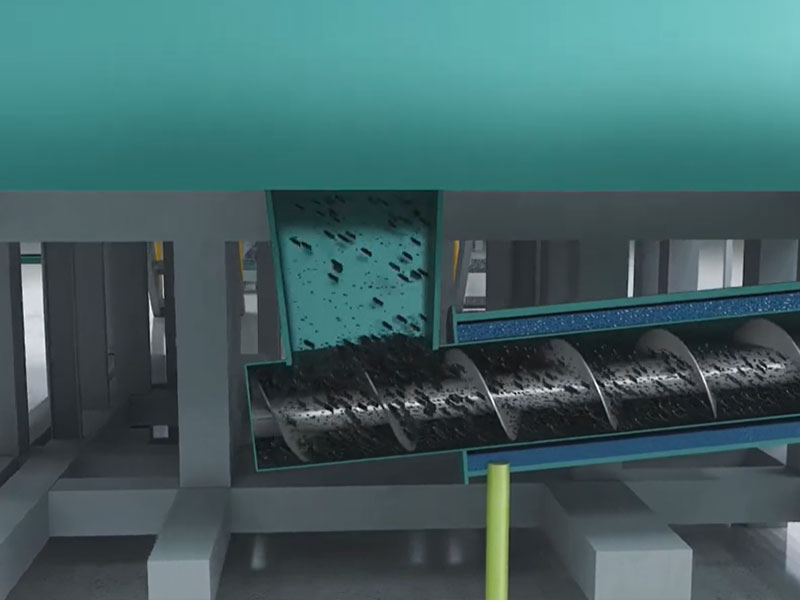

Biomass carbonization plant can transform waste into high-value products, reducing the burden on solid waste disposal. Biochar, with its porous structure, high specific surface area, and abundant surface functional groups, is suitable for a wide range of applications.
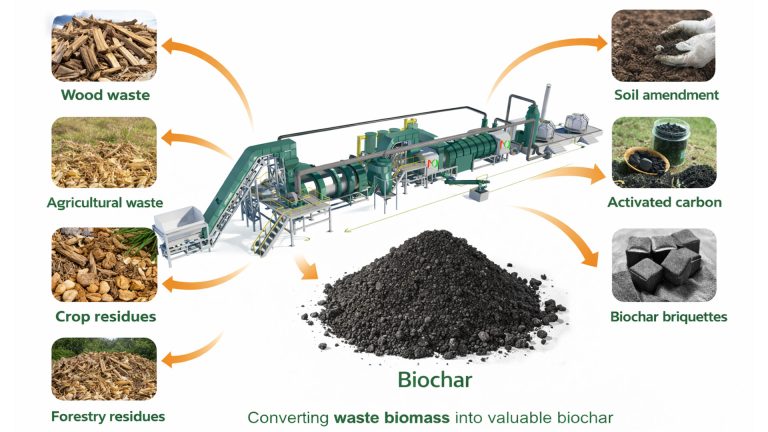
Raw Materials for Biochar Manufacturing Machine
Biochar manufacturing machine can use a wide range of raw materials, encompassing virtually all types of organic waste biomass.
- Agricultural waste: Crop straw, rice husks, fruit shells (coconut shells, walnut shells), sugarcane bagasse, livestock and poultry manure, etc.
- Forestry waste: Wood processing scraps, sawdust, branches, wood chips, etc.
- Municipal waste: Garden trimmings, sewage sludge, etc.
- Other specialized energy crops: Miscanthus and switchgrass, etc.
The choice of raw materials directly affects the biomass pyrolysis process and the physical and chemical properties of the final biochar (such as porosity, pH, and nutrient content).
How Biochar Equipment Achieves Carbon Sequestration
Biomass carbonization equipment can convert biomass carbon, which would otherwise quickly release CO₂, into stable, solid carbon for long-term storage. This disrupts the traditional carbon cycle of “biomass decay/combustion → CO₂ emissions.”

Under natural conditions, untreated biomass such as agricultural straw and forestry sawdust releases carbon through two pathways.
- Natural decay: Microorganisms decompose the organic carbon in the biomass, and within 1-3 years, approximately 80% of the carbon is released into the atmosphere as CO₂ or CH₄ (methane, which has a greenhouse effect 28 times greater than CO₂).
- Direct combustion: When burned as fuel, biomass carbon is instantly converted to CO₂, directly increasing atmospheric carbon concentrations. For example, open-air straw burning contributes to over 1 billion tons of CO₂ emissions globally annually.
Biochar manufacturing equipment uses an oxygen-free pyrolysis process to change the carbon’s form. During biomass pyrolysis process, unstable organic carbon in the biomass decomposes into bio-oil and syngas, while stable lignin carbon is carbonized to form aromatic carbon structures. This structure has extremely high bond energy, making it difficult for microorganisms to decompose in the natural environment, and can persist in carriers (soil and building materials) for hundreds to thousands of years.
Biochar Sequestration Applications
Soil Sequestration: When biochar is applied to soil, its porous structure bonds with soil particles to form a stable “carbon-soil complex.” This not only prevents the release of carbon from the biochar itself but also promotes indirect sequestration of atmospheric CO₂ by the soil.
Industrial Carbon Sequestration: Biochar is incorporated into materials such as concrete and plastics to create “functional carbon sequestration.” Biochar replaces some high-carbon raw materials (such as cement and plastic pellets) while also sequestering carbon over the life of the material (typically 20-50 years).
Calculations indicate that for every ton of biochar produced, 0.6-0.8 tons of carbon are fixed from the biomass (calculated based on a feedstock carbon content of 50%-60% and a biochar yield of 30%-50%). This is equivalent to reducing CO₂ emissions by 0.6-0.8 tons (the carbon to CO₂ mass conversion factor is 3.67, resulting in an actual equivalent emission reduction of approximately 2.2-2.9 tons of CO₂).




