Facing the challenge of billions of discarded tires worldwide each year, tire pyrolysis, with its unique resource conversion capabilities, is opening a green recycling path for “black pollution.” The core equipment for all of this is the tire pyrolysis machine.
Mingjie Group is a professional tire pyrolysis machine manufacturer in China. We design and manufacture pyrolysis equipment for processing solid waste, such as scrap tires, plastics, medical waste, and oil sludge. Pyrolysis plant provides a sustainable industrial solution for scrap tire recycling.
Mingjie Group is committed to providing safe, efficient, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective pyrolysis solutions for tire recycling projects. We customize pyrolysis systems based on the specific needs of solid waste projects, helping clients maximize resource utilization and achieve sustainable profit growth.
Tire Pyrolysis Machine Types
We provide batch pyrolysis plant and continuous pyrolysis plant to scrap tire recycling companies.
The primary difference between batch and continuous tire pyrolysis machines lies in the continuity of feeding and discharging. Batch pyrolysis machines have a low degree of automation and rely primarily on manual operation. Continuous pyrolysis machines, on the other hand, are highly automated and less dependent on human resources.
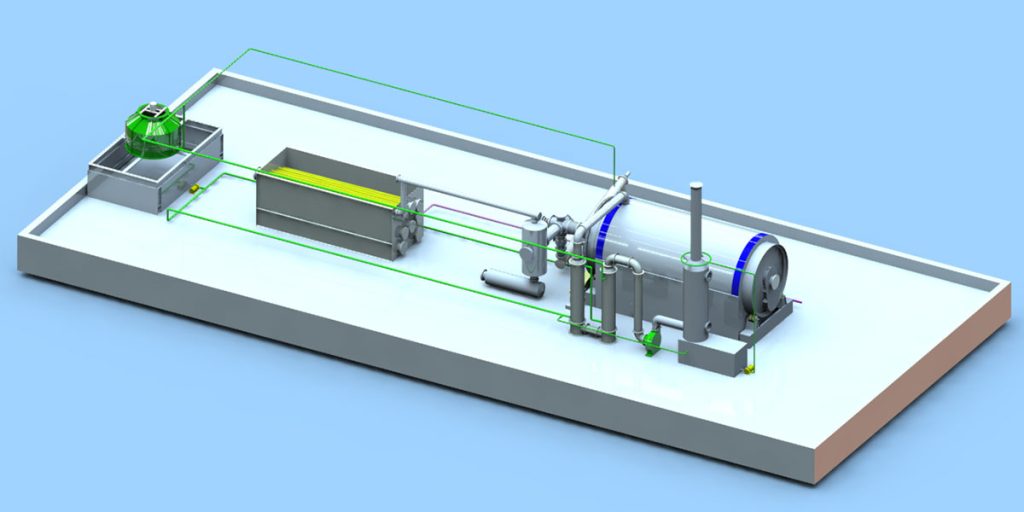
Batch Tyre Pyrolysis System
Batch pyrolysis plant is shut down after 16 to 20 hours to remove by-products such as carbon black and steel wire and to re-feed the waste tires. Mingjie batch pyrolysis plants include the MJ6, MJ-10, MJ-12, and MJ-15. A single batch tire pyrolysis machine can process 6-15 tons of waste tires per day.
Batch tire pyrolysis systems are ideal for small-scale operations and applications requiring high flexibility. They can directly process entire tires, have a lower initial investment cost, and are easier to operate.
Continuous Tyre Pyrolysis Plant
Continuous pyrolysis plant offers continuous feeding and discharging. Mingjie continuous pyrolysis plants include the MLL-20T and MLL-30T. A single continuous tire pyrolysis machine can process 25-40 tons of waste tires per day.
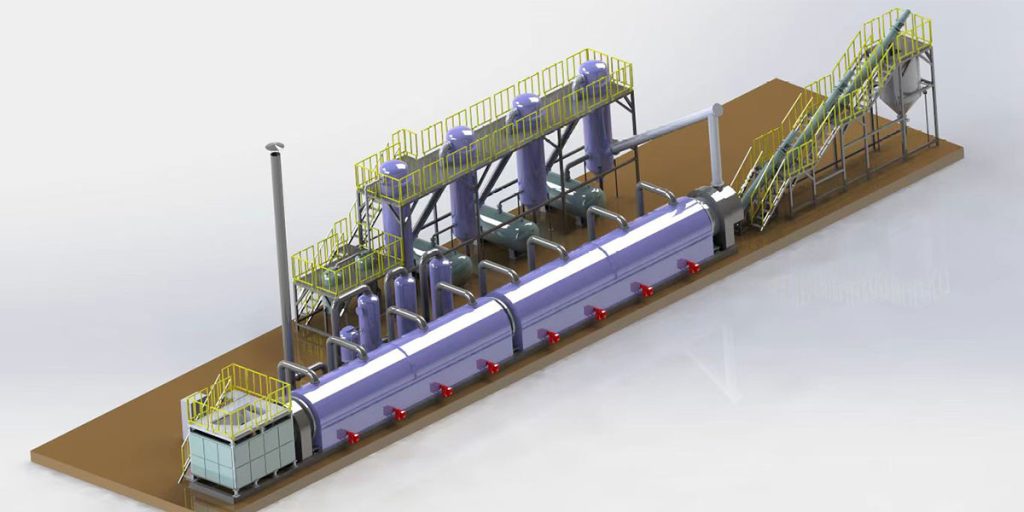

Continuous tire pyrolysis systems are designed for large-scale, continuous production. They achieve the highest conversion efficiency with pre-treated rubber powder. They offer higher output and a higher degree of automation, but require a larger initial investment.
Mingjie tyre pyrolysis plant features a modular design. It offers flexible expansion capabilities, adapting to projects of varying scale and complexity. We continuously optimize our pyrolysis process, leveraging years of industry experience and extensive data to help customers effectively reduce operational risks and downtime. Our pyrolysis equipment achieves exceptional waste tire conversion efficiency while significantly reducing pollution emissions and energy consumption.
Tire Pyrolysis Plant Structure
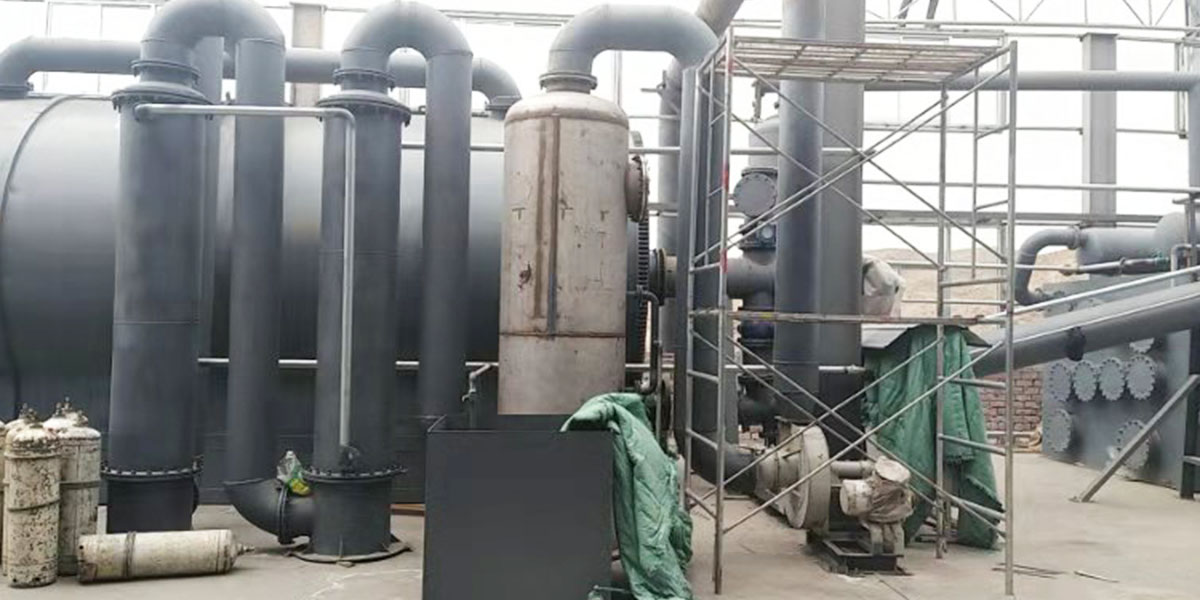
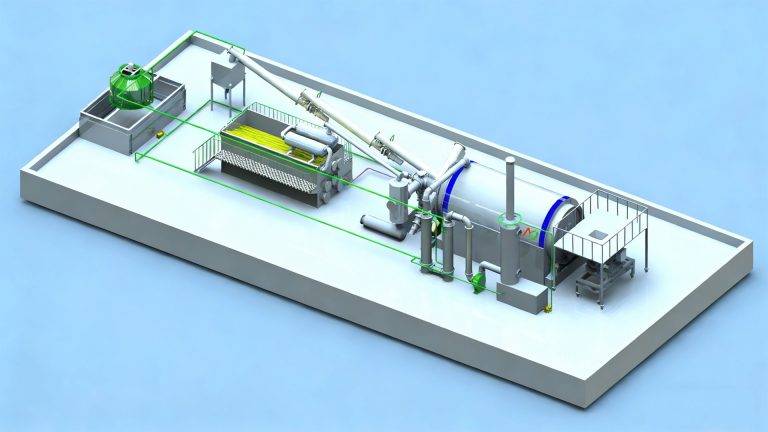
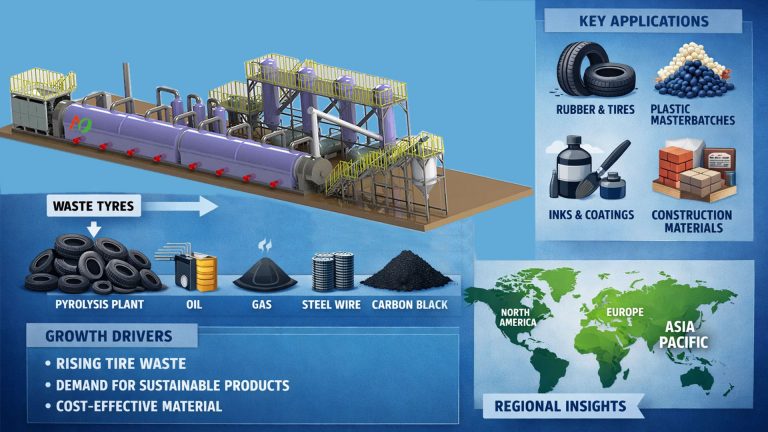
Tire to oil pyrolysis plants utilize high temperatures in a low-oxygen environment to break down rubber into valuable byproducts such as tire pyrolysis oil, pyrolysis gas, and carbon black. They provide a comprehensive, high-quality recycling solution for end-of-life tires. A tire pyrolysis system typically consists of a pyrolysis reactor, oil and gas condensation equipment, and flue gas purification equipment.
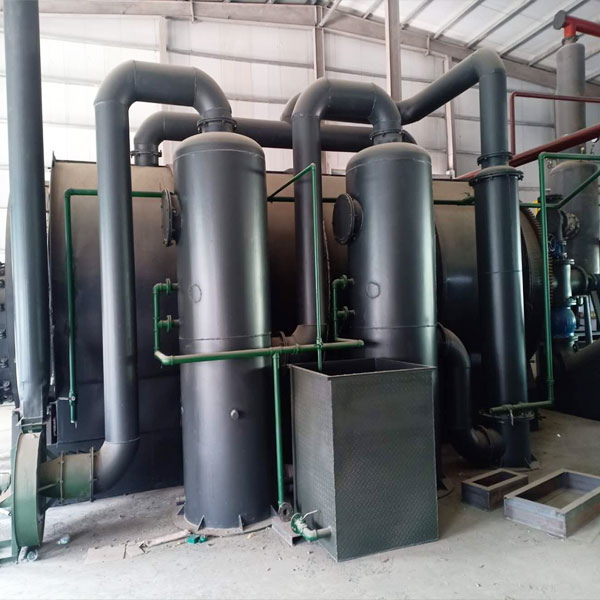


The tire pyrolysis machine is the core of the tire waste-to-energy system. Key supporting equipment includes the exhaust gas treatment system, discharge system, and non-condensable gas system.
At a certain temperature, waste tires begin anaerobic pyrolysis. The resulting oil-gas mixture then enters a condensation system, producing pyrolysis oil. The pyrolysis oil is then piped directly to a fuel oil tank. Non-condensable gases can be discharged into the air through a purification system or collected for heating in the pyrolysis reactor. The carbon black is discharged through a water-cooled spiral slag discharge system.
The pyrolysis exhaust will flow through the exhaust gas treatment pipeline into the environmental protection system for treatment. After undergoing desulfurization, denitrification, and activated carbon adsorption, it will meet environmental emission standards before being discharged.