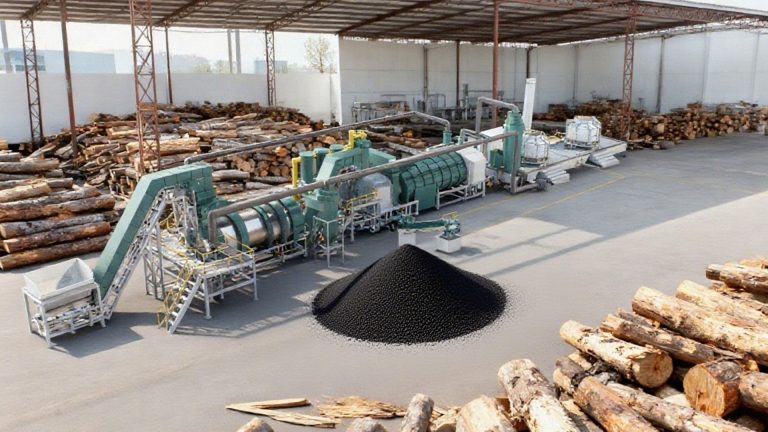
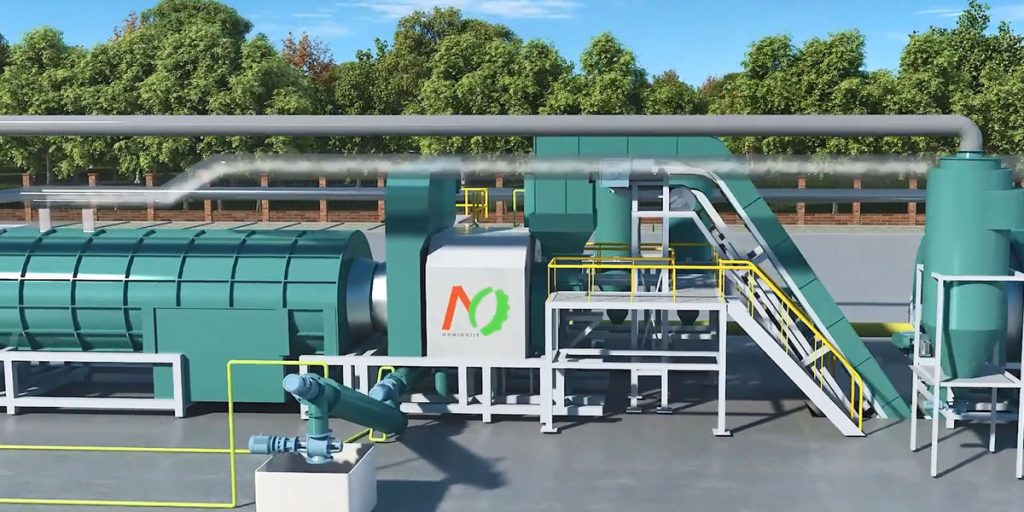
In addressing the global challenges of climate change, resource scarcity, and environmental pollution, biochar from biomass and waste stands out. Biochar is a carbon-rich material produced through a pyrolysis process. Biomass carbonization equipment can process agricultural residues, forestry waste, and even municipal sludge, transforming these burdens into “black gold.”
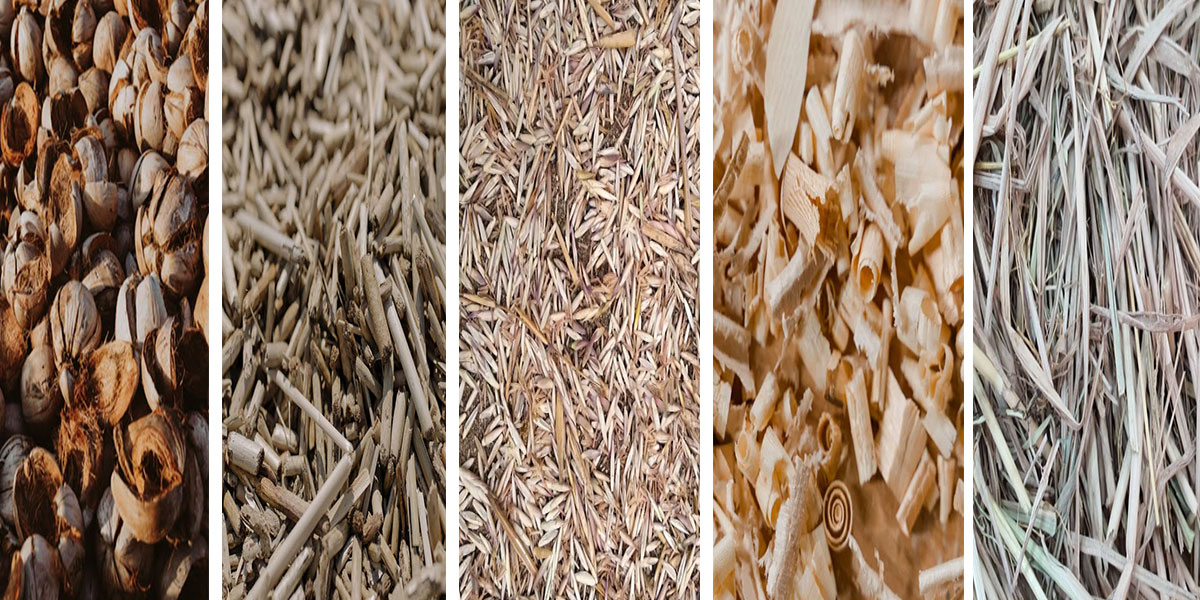
Biochar from Biomass and Waste can be used with a variety of raw materials.
- Agricultural waste: rice husks, straw, sugarcane leaves, fruit tree prunings, nut shells, etc.
- Forestry waste: sawdust, wood chips, wood processing scraps.
- Organic solid waste: urban landscaping waste, sewage sludge, livestock and poultry manure.
- Other: agricultural product processing by-products, etc.

How Biochar is Produced from Biomass and Waste
Biomass is heated in an oxygen-free or low-oxygen environment under controlled conditions (temperatures between 300-800°C) to induce reactions in its organic components. The biochar from biomass and waste production process consists of three key stages: thermal decomposition, carbonization, and polymerization.
Drying stage (100-200°C): Free and bound water in the biomass evaporates. The moisture content of the material drops from an initial 60%-70% to below 10%, paving the way for subsequent reactions.
Pyrolysis stage (200-500°C): Hemicellulose decomposes first, producing volatile organic compounds such as methanol and acetic acid. Subsequently, cellulose and lignin gradually break down, producing combustible gases such as hydrogen and methane.
Carbonization stage (500-800°C): The remaining solid residue undergoes aromatization to form a porous carbon material, known as biochar. This biomass pyrolysis process also releases small amounts of tar and non-condensable gases.

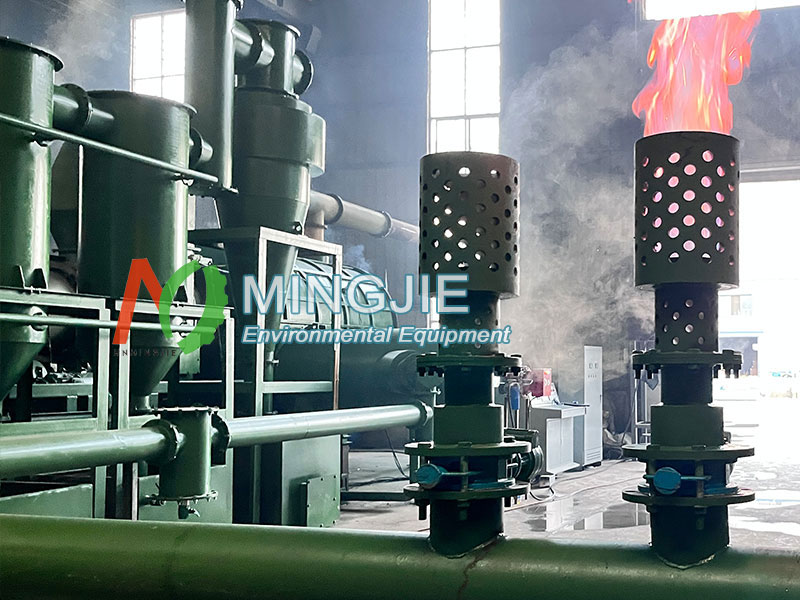
Advantages of Waste Biomass Pyrolysis
Compared to traditional biomass waste treatment methods, pyrolysis technology offers significant environmental and economic benefits.
Zero emissions: The entire process is carried out in a closed reactor, where volatile gases are collected and utilized, resulting in zero smoke and harmful emissions. Biochar, when returned to the field, absorbs heavy metals (such as cadmium and lead) and pesticide residues from the soil, reducing non-point source pollution.
High resource utilization: Achieves a “one-to-three” resource conversion. Biomass can simultaneously produce biochar, syngas, and biotar, leaving no residual waste.
Energy recycling: The syngas generated during the pyrolysis process (calorific value approximately 16-18 MJ/m³) can be directly used to heat the reactor, meeting over 70% of the process’s energy needs. Excess gas can be used for power generation or heating, achieving energy self-sufficiency.

Unique Value of Biochar from Biomass and Waste
The value of biochar stems from its unique physical and chemical properties. Biochar from biomass and waste has a stable carbon structure, large specific surface area, rich pore structure, and surface functional groups. These properties lend it to a wide range of applications.

Soil Improvement and Carbon Sequestration
Powerful Tool for Carbon Sequestration: Biochar from biomass and waste is chemically very stable and can remain in the soil for hundreds or even thousands of years. Converting biomass carbon into biochar and applying it to the soil effectively “locks” atmospheric CO₂ underground. This is a key component of negative emissions technology.
Soil Amendment: It improves soil aggregate structure, enhances water and fertilizer retention, and regulates pH. It also provides a habitat for beneficial microorganisms, thereby improving soil fertility and crop yields.
Environmental Remediation
Water Purifier: Biochar from biomass and waste can adsorb heavy metals, organic pollutants, and nutrients from water. This makes it suitable for remediation of industrial wastewater, agricultural runoff, and groundwater.
Soil Detoxifier: It can also immobilize heavy metals and organic pollutants in contaminated soil, reducing their bioavailability and mobility.
Resource Recycling and Energy Recovery
Closing the Waste Management Loop: Biochar production equipment provides a sustainable solution for treating the growing amount of organic waste. It avoids methane emissions from landfills and air pollution from incineration, and shifts waste management from “linear” to “circular” utilization.
Energy Byproducts: During the biomass pyrolysis process to produce biochar, syngas rich in hydrogen and carbon monoxide, as well as liquid bio-oil, are produced. These can be used as clean energy to power the process itself or exported, improving the economic efficiency of the entire system.
Other Applications
Building Material Additives: Biochar from biomass and waste can be used as an additive in cement or asphalt to improve performance and reduce carbon footprint.
Anaerobic Digestion Accelerator: Adding biochar to biogas projects can enhance microbial activity and system stability, thereby increasing biogas production.
Catalyst Support: Utilizing its porous properties, it can serve as a support for industrial catalysts.