Waste motor oil is not worthless waste, it possesses enormous resource recycling potential. Distilling waste motor oil can give it new value. Distillation equipment can effectively separate the various components in waste motor oil. It removes impurities and harmful substances, regenerating the waste oil into high-quality base oils.
These base oils can be widely used in the production of lubricants, fuel oils, and other products. They are then reintroduced into industrial production and daily life, achieving resource recycling.

Distilling waste motor oil is both an urgent need to address environmental pollution and an important way to achieve sustainable resource utilization. This resource recycling method reduces the extraction of new petroleum resources, alleviating energy shortages. It also reduces waste emissions, lessens the environmental burden, and has significant economic and environmental benefits.
With the continuous advancement of technology, advanced waste oil distillation equipment is emerging. Their unique technological advantages play a vital role in the field of waste oil distillation.
Waste Oil Distillation Machine for Resource Recycling
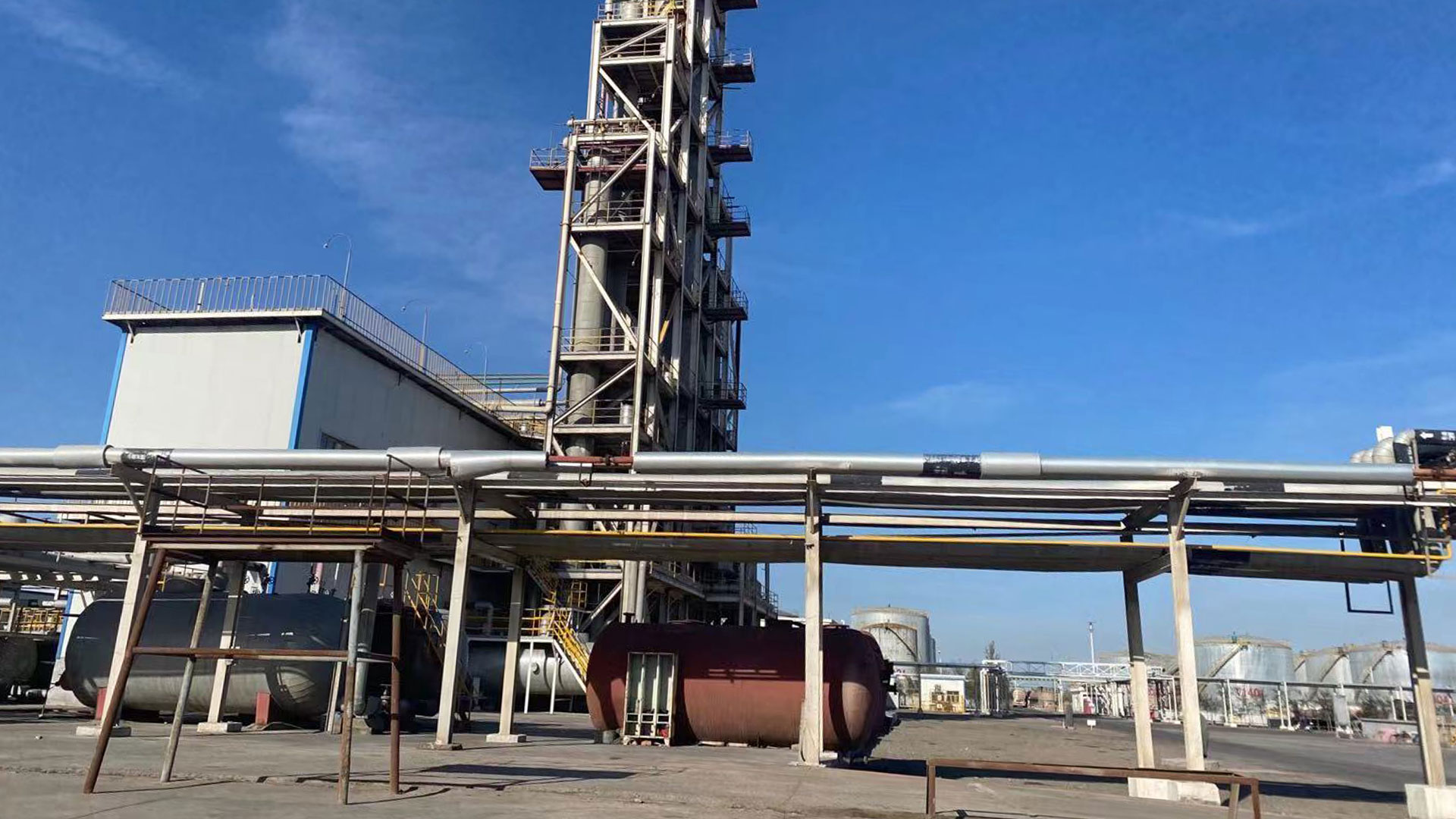
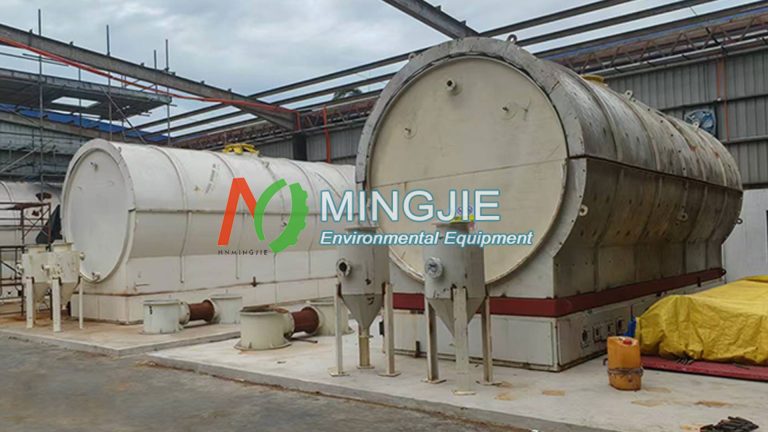
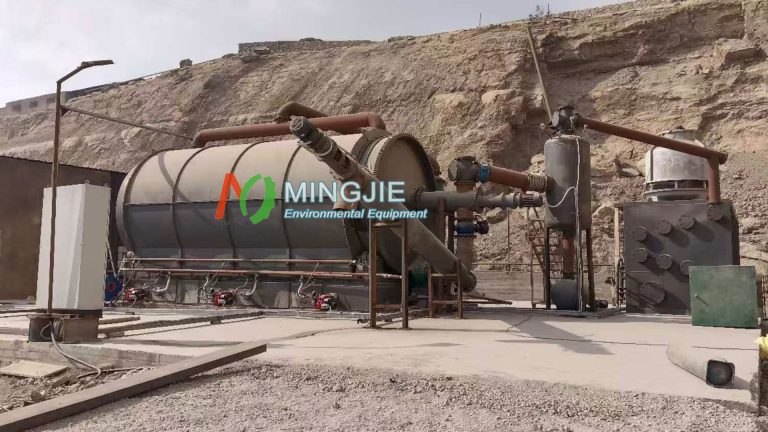
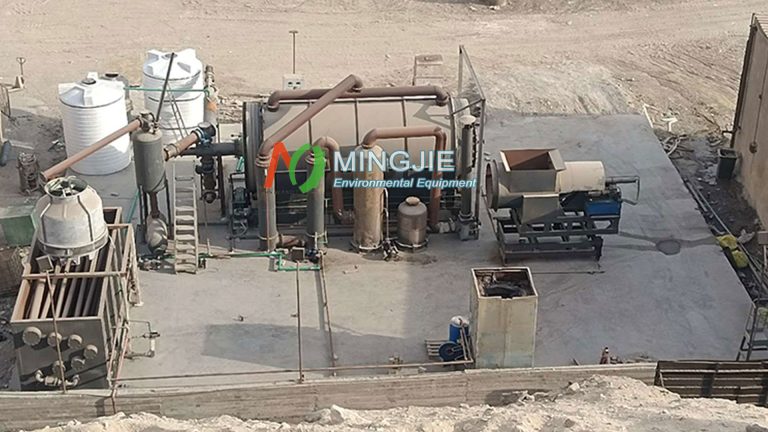
Waste oil distillation machine consists of multiple systems, including raw material tanks and preheating systems, vacuum distillation towers, condensers and oil-water separators, adsorption and decolorization towers, dust removal systems, oil storage tanks.

The core of distilling waste motor oil lies in separating components based on their boiling point differences. It’s based on the different boiling points of the components in a liquid mixture. The mixture is heated to vaporize, and then the vapor is condensed back into a liquid, thus separating the components.
During the distillation used motor oil process, when the waste motor oil is heated, the lighter fractions, such as gasoline and diesel, with lower boiling points, vaporize first. They rise to the top of the distillation column, are cooled by a condenser, and collected. The heavier fractions, such as lubricating base oils, with higher boiling points, remain at the bottom of the distillation column.
Distilling Waste Motor Oil Process
Pre-treatment by Sedimentation: The collected waste motor oil is poured into a large sedimentation tank. Gravity allows large particles of impurities and water to settle naturally to the bottom.
Generally, sedimentation takes at least 24 hours to ensure that impurities and water are separated as much as possible. After sedimentation pre-treatment, most of the large particles of impurities and water in the waste motor oil are removed. This provides a relatively pure feedstock for the subsequent distillation stage.
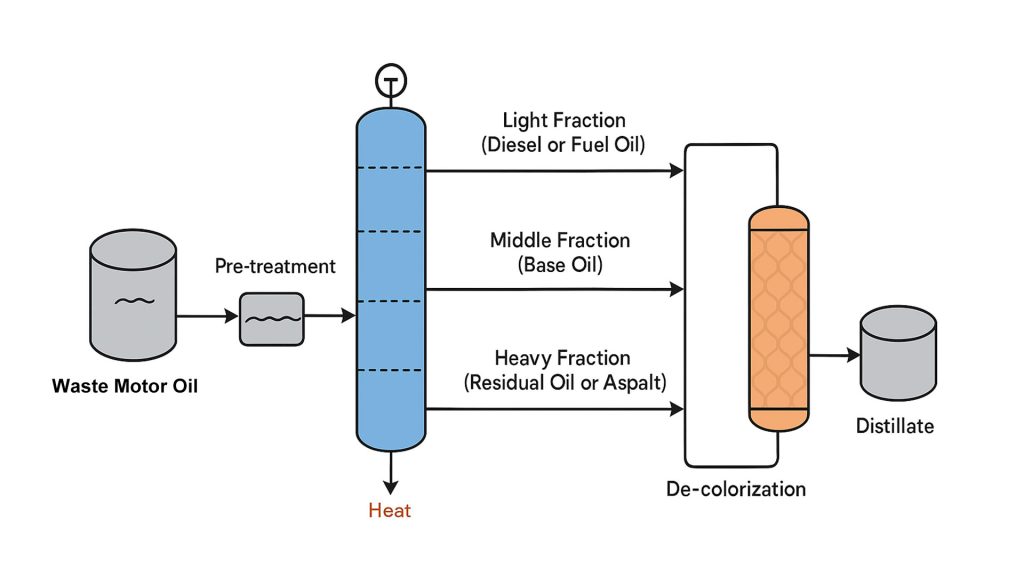
Distilling Waste Motor Oil Stage: The pre-treated waste motor oil is transported to a distillation column, where it is separated based on the differences in boiling points of different components. Distillation columns typically employ a multi-stage structure, with the temperature gradually decreasing from bottom to top.
During distilling waste motor oil process, the lighter fractions with lower boiling points, such as gasoline and diesel, are separated first. They vaporize at lower temperatures and are collected after being cooled by a condenser at the top of the column. As the temperature rises, heavier fractions, such as lubricating oil base oil, gradually vaporize and are collected at different points in the column.
Precise control of parameters (temperature and pressure) is crucial to ensure effective separation of each fraction and product quality. For example, precise control of the heating rate and cooling water flow in the overhead condenser is essential. Gasoline fractions are separated at approximately 180°C, while diesel fractions are collected within the 180-360°C temperature range. Lubricating oil base oil is obtained at even higher temperatures.
Pickling Process: The distilled lubricating oil base oil is heated to approximately 35°C. Concentrated sulfuric acid is slowly added, at a concentration of about 6-8% of the oil’s weight. The concentrated sulfuric acid reacts with impurities such as gums and asphaltenes in the oil through a sulfonation reaction. This converts the impurities into insoluble substances, causing them to precipitate. Continuous stirring is required during the reaction to ensure complete precipitate formation.
After the reaction, the oil is allowed to stand for a period of time to allow the impurities to separate from the oil. The lower layer of acid sludge is then discharged. The pickling process effectively removes impurities such as gums and asphaltenes from the oil, improving its quality and stability.
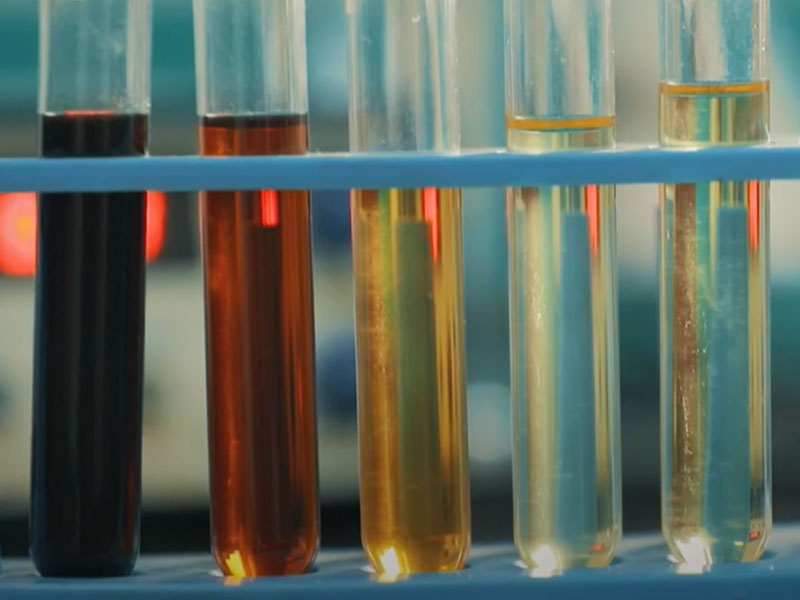

Alkaline Washing Stage: The acid-washed oil is heated to 90℃, and approximately 5% sodium carbonate powder is added. The sodium carbonate neutralizes the residual acidic substances in the oil, bringing the oil’s pH to equilibrium and making it clear and transparent.
Stirring is required during the alkaline washing process to promote the reaction. After the reaction is complete, the oil is allowed to settle and separate, and the lower layer of wastewater is discharged. The alkaline washing stage neutralizes the residual acidic substances in the acid-washed oil, further improving the oil quality and reducing corrosion to equipment.
Filtration Stage: Even after acid and alkali washing, the oil may still contain some fine solid particles, requiring further purification through filtration. During filtration, these impurities are trapped by the filter element, resulting in pure, regenerated base oil. For applications with high oil quality requirements, multi-stage filtration can also be used.




