According to statistics, hundreds of millions of tons of waste plastic are generated globally every year, but the proportion that is effectively recycled remains low. How to achieve efficient waste plastic recycling has become an important issue in the circular economy and sustainable development.
Common waste plastics include PET, HDPE, LDPE, PP, PS, and mixed plastics. Different types of plastics have significant differences in recycling methods and utilization value.

Types of Waste Plastic
PET/PETE (Polyethylene terephthalate): Transparent, strong, and has good barrier properties, but not heat-resistant (usually <65°C). Used for beverage bottles, cooking oil bottles, and salad dressing bottles. PET/PETE has a high recycling rate.
HDPE (High-density polyethylene): Opaque, high hardness, corrosion-resistant, and relatively safe. Used for milk bottles, shower gel bottles, medicine bottles, and plastic buckets. Easily recyclable and has high market value.
PVC/V (Polyvinyl chloride): Soft and elastic or hard, may contain plasticizers. Used for cling film, flexible water pipes, building materials, and toys. Difficult to recycle. Produces toxic gases when burned; not recommended for food packaging.
LDPE (Low-density polyethylene): Soft, transparent, and resistant to low temperatures. Used for plastic bags, cling film, and food packaging. Low recycling value, often landfilled or incinerated.
PP (Polypropylene): High temperature resistance (~120°C), relatively safe, and high hardness. Used for microwaveable food containers, yogurt cups, medicine bottles, and bottle caps. Recyclable. A relatively safe food contact material and reusable.
PS (Polystyrene): Hard and brittle or foamed (styrofoam), not heat-resistant. Used for foam food containers, instant noodle bowls, disposable tableware, and packaging fillers. Difficult to recycle. May release styrene (a potential carcinogen) at high temperatures.
Other types (PC, PLA): Complex composition and varying properties. Used for water bottles, baby bottles, some food containers, and bioplastics (PLA).

Trends in Waste Plastic Recycling
With increasingly stringent environmental regulations and the continuous advancement of carbon reduction targets, the waste plastic recycling is showing the following trends:
- From low-value recycling to high-value utilization.
- From single-process recycling to multi-technology collaboration (mechanical + pyrolysis + chemical recycling).
- Deep integration with carbon reduction and carbon trading mechanisms.
- Accelerated application of intelligent sorting and automated recycling equipment.
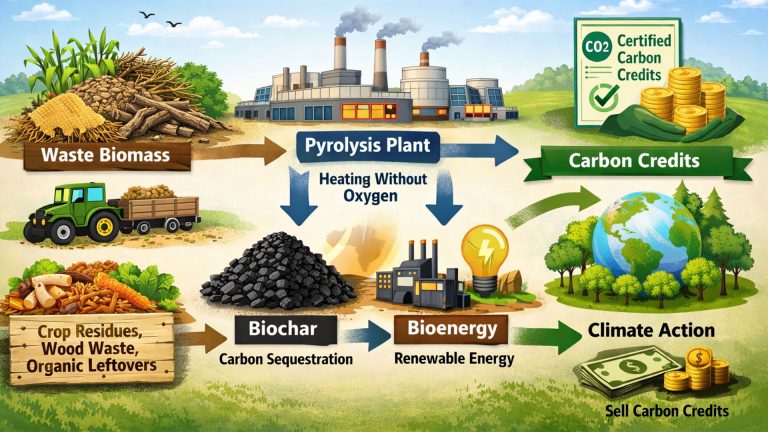
In particular, pyrolysis technology for waste plastic recycling is becoming an important solution for mixed plastics and difficult-to-recycle plastics. Plastic pyrolysis equipment is particularly suitable for polyolefin plastics (PE, PP). It heats them under oxygen-free conditions, converting them into pyrolysis oil, which can be used as a chemical raw material.
Advantages of Plastic Pyrolysis
- High resource utilization potential: Converts waste plastics into marketable fuels and chemicals.
- Wide processing range: Can process contaminated, composite, and mixed low-value waste plastics (except PVC), effectively complementing mechanical waste plastic recycling.
- Significant volume reduction: Greatly reduces the volume of waste plastics (usually by more than 80%), significantly saving landfill space.
- Carbon emission reduction pathway: Plastic pyrolysis oil can replace fossil fuels, theoretically forming a partial carbon cycle.

Pyrolysis equipment provides an efficient chemical pathway for waste plastic recycling, especially mixed waste plastics and plastic films (difficult to recycle by mechanical method). It works in conjunction with mechanical recycling to jointly build a circular economy system for plastics. The plastic pyrolysis products have the potential for resource utilization.
- Pyrolysis oil: Its main components are similar to those of diesel fuel. After distillation and refining, it can be used as marine fuel oil or boiler fuel. This is currently the most valuable product from plastic pyrolysis recycling.
- Pyrolysis gas: Its main components are hydrogen and methane, with a high calorific value. It is usually recycled within the system to provide heat for the pyrolysis reaction itself, reducing external energy consumption.
- Solid residue: Mainly composed of carbon black and inorganic substances, it can be used as low-grade carbon black. It can also be processed into solid fuel, activated carbon, or used in building materials.