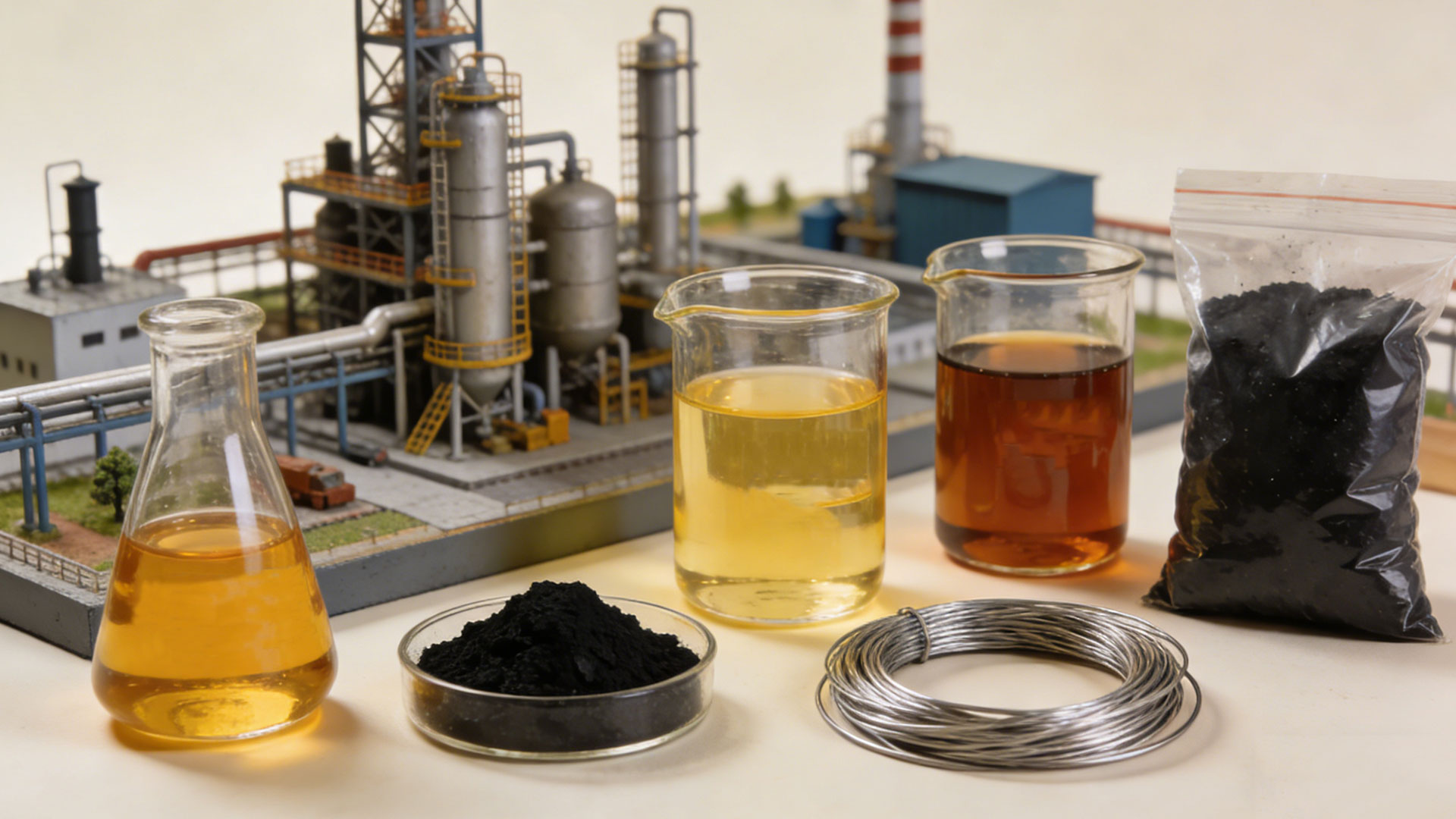
Tire pyrolysis plant can convert waste tires into pyrolysis oil (fuel), syngas (energy), steel wire (scrap metal), and carbon black. The main application areas of waste tire to oil plant include fuel oil production, carbon black manufacturing, and steel wire recycling.
In 2024, global production of fuel oil extracted from waste tires exceeded 58 million barrels. More than 2.3 million tons of carbon black were produced from tire pyrolysis equipment. Over 850,000 tons of high-quality steel wire were recovered from waste tires.
Pyrolysis oil can be used as an industrial heat source or blended with marine fuel. The recovered carbon black can be used in rubber compounds, plastic colorants, inks, and specialty composites. Syngas provides fuel for the pyrolysis system. Steel wire can be recycled in the steelmaking process.

Applications of Waste Tire to Oil Plant
Fuel Oil Production: This is the most important application of waste tire to oil plants, with global pyrolysis oil production exceeding 1.9 million tons in 2024. Approximately 68% of pyrolysis plants primarily produce fuel oil for furnaces, boilers, and industrial burners.
The conversion of pyrolysis oil into diesel fuel is also receiving significant attention. $230 million has been invested in building pyrolysis oil distillation plants to refine pyrolysis oil into diesel.
Carbon Black Production: In 2024, tyre to oil pyrolysis plants produced over 2.3 million tons of carbon black. More than 400 companies use recycled carbon black in the production of tires, plastics, and inks. Demand from the rubber industry continues to grow, particularly in India, China, and Germany.
The recycling of carbon black has attracted $780 million in global investment, with tire manufacturers forming alliances with pyrolysis operators. In 2024, eleven tire companies signed long-term procurement contracts for recycled carbon black.
Steel Wire Recycling: Nearly 900,000 tons of steel wire were recycled globally in 2024. This steel wire is either reprocessed for construction or sold to foundries. Europe accounts for 36% of the recycled steel wire trade volume, followed by Southeast Asia.
Waste Tire to Oil Machine Types
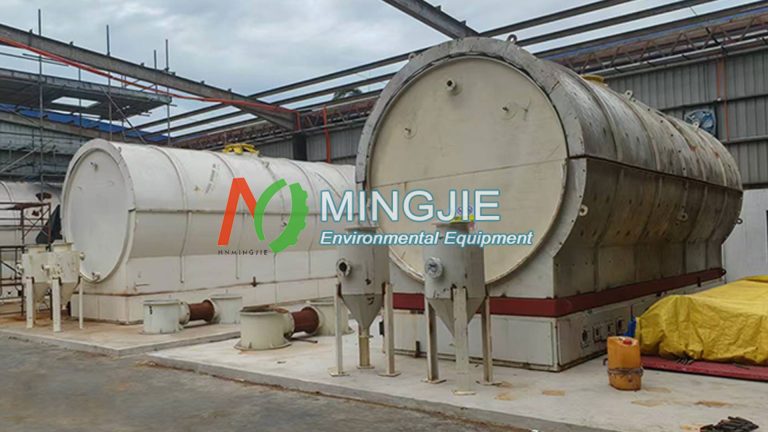
There are two main types of waste tire to oil machines: batch pyrolysis equipment and continuous tyre pyrolysis plant.
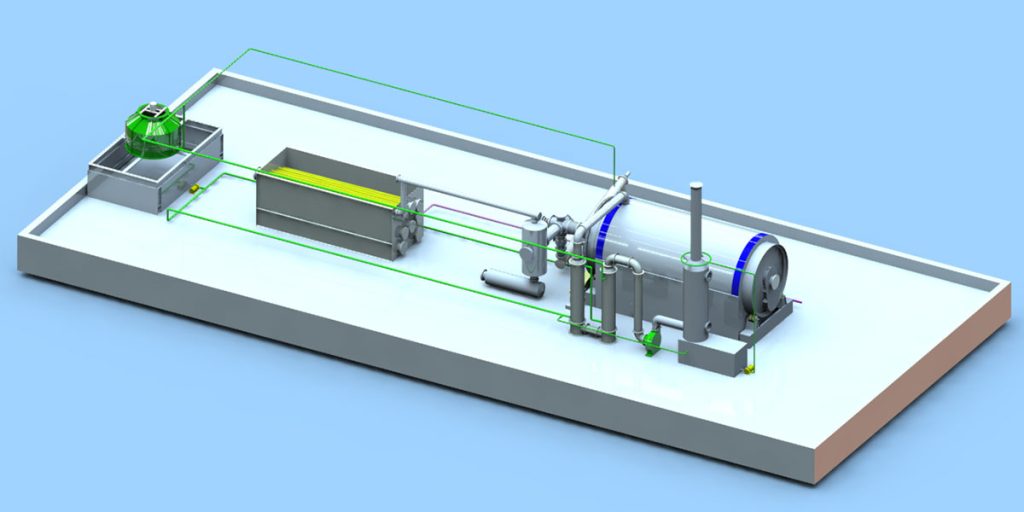
Batch Pyrolysis Machine
Batch pyrolysis units are ideal for small to medium-scale operations due to their low operational complexity. In 2024, over 3,200 batch pyrolysis waste tire to oil plants were in operation globally, processing approximately 310 million tires. They are primarily located in regions lacking advanced automation technology. The average daily processing capacity of a batch pyrolysis unit is 6 to 15 tons.
Batch pyrolysis equipment accounts for approximately 52% of the total installed pyrolysis equipment. They are favored for their relatively low initial investment and operational flexibility. Batch pyrolysis waste tyre to oil plant benefits primarily from their cost-effectiveness and suitability for small to medium-scale operations. They allow for batch processing of waste tires. Operators can effectively control the pyrolysis environment, which is crucial for obtaining high-quality products under varying waste tire conditions.
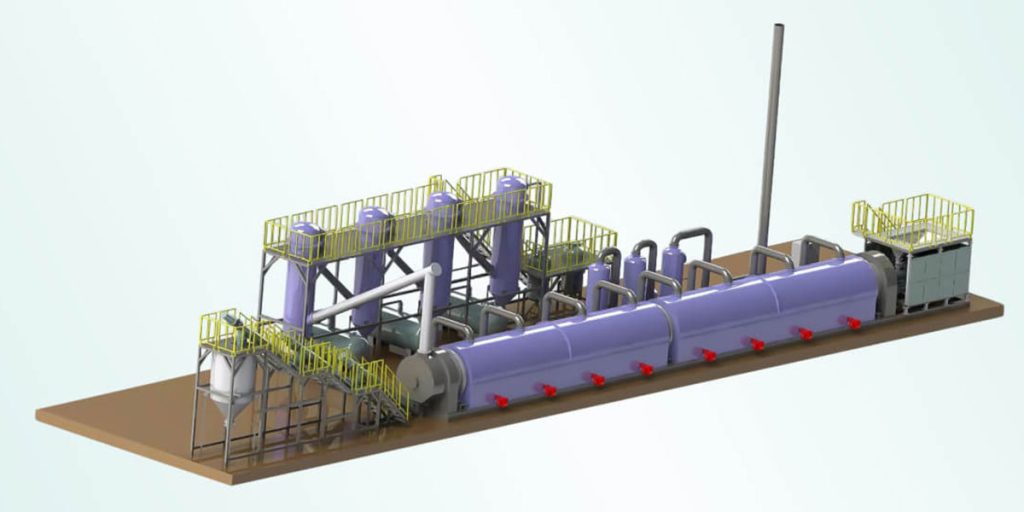
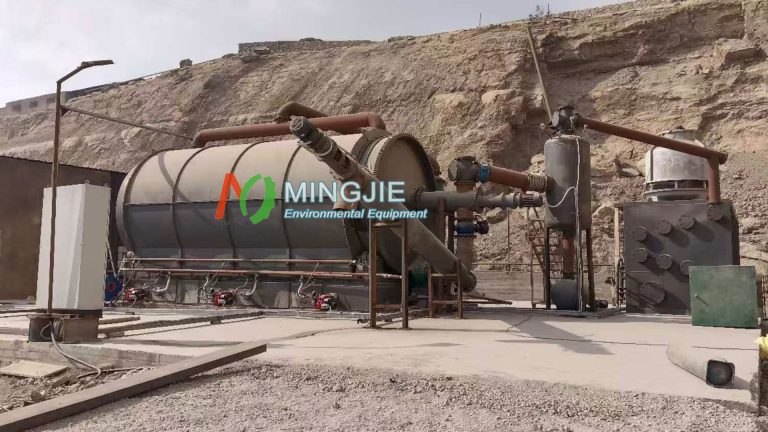
Continuous Pyrolysis Machine
Continuous pyrolysis system is designed for industrial-scale processing and operate 24/7. In 2024, over 2,100 continuous pyrolysis waste tire to oil plants were in operation worldwide. Each unit processes an average of 20 to 24 tons of tires per day. North America and Europe are the main regions where these continuous pyrolysis units are located. Last year alone, continuous systems recovered over 1.2 million tons of fuel oil and 600,000 tons of carbon black.
Fully continuous pyrolysis equipment accounts for approximately 48%. It is gaining increasing attention due to its high throughput and automation capabilities. Fully continuous pyrolysis machines are preferred by larger companies, because they can process tires more efficiently with less human intervention. These units enable continuous feeding and discharge, simplifying the tire recycling process. They significantly improve the operational efficiency of large tire recycling companies in maximizing output and minimizing labor costs.




