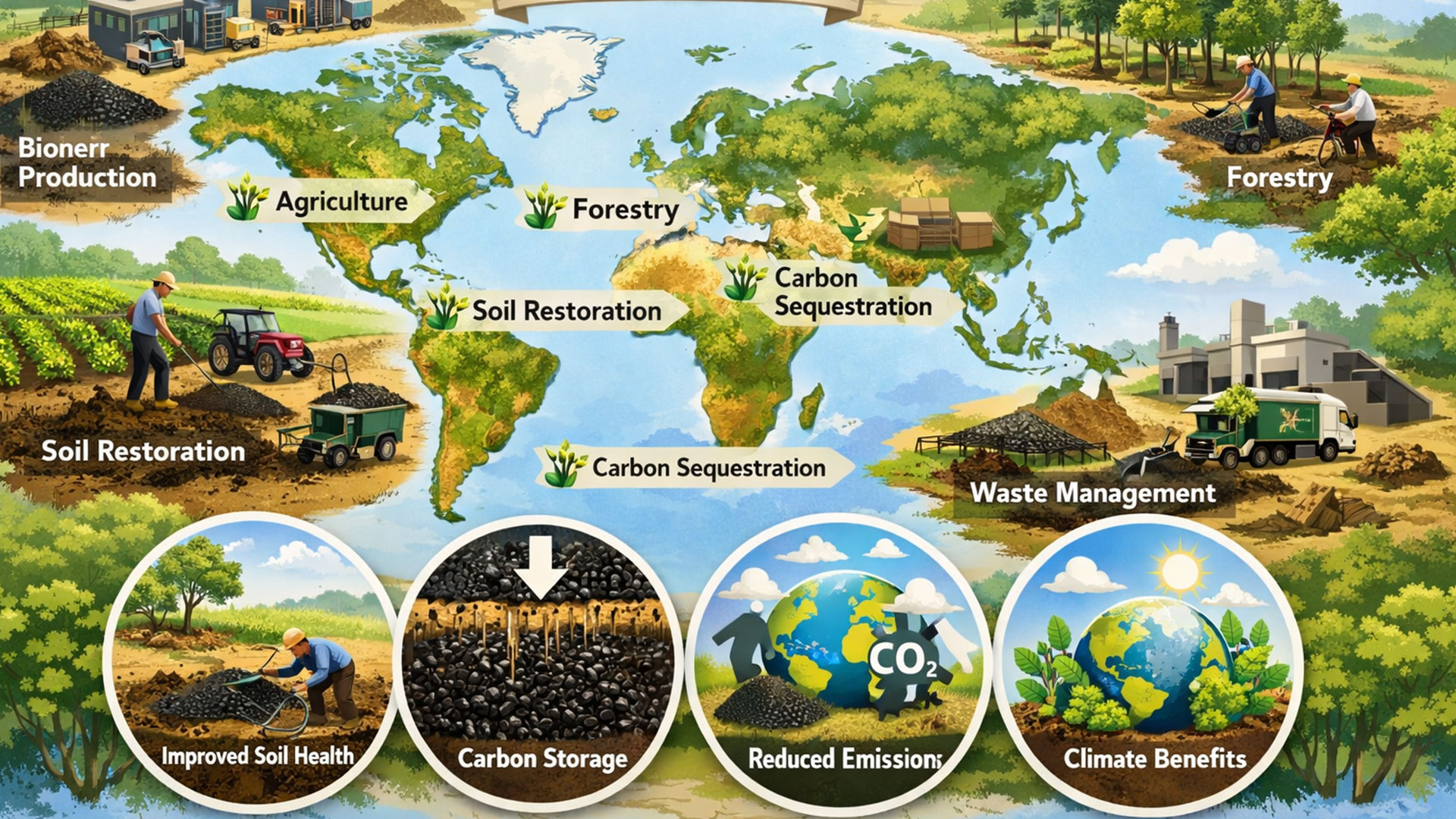
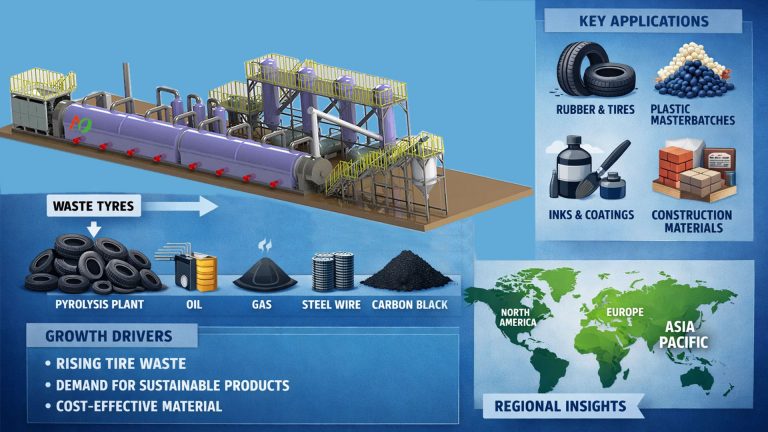
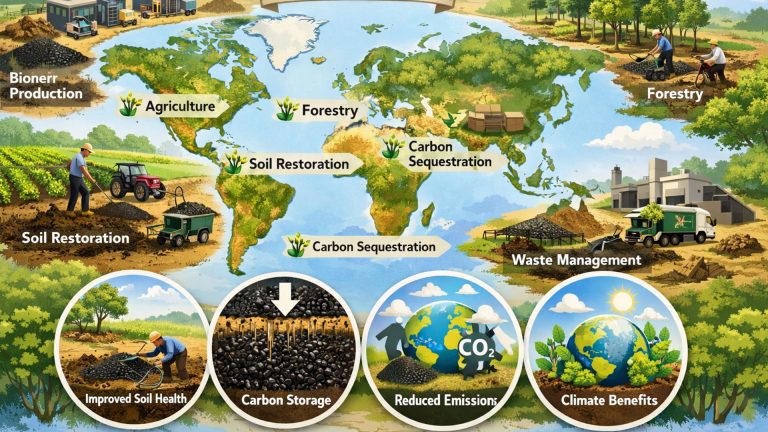
The global biochar market is experiencing continuous expansion, driven by a focus on sustainable agricultural and environmental practices. The global biochar market size was US$859 million in 2025 and is projected to reach US$969 million in 2026, representing an annual growth rate of approximately 12.8%. The increasing applications of biochar in soil conditioning, carbon sequestration, and the utilization of waste biomass are supporting this market momentum.
Biochar is increasingly being used in carbon credit programs as a tool for permanent carbon sequestration. Biomass pyrolysis is the preferred biochar production technology compared to gasification.
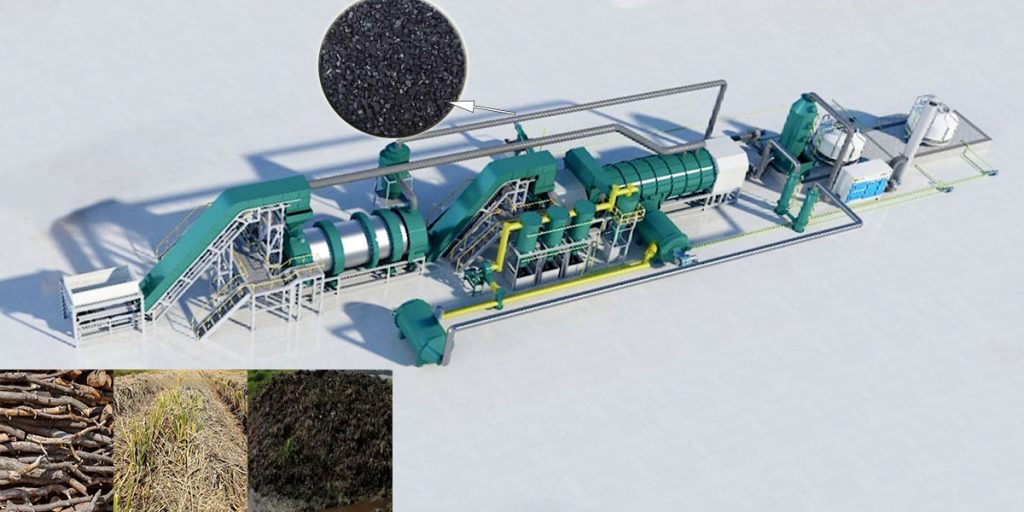

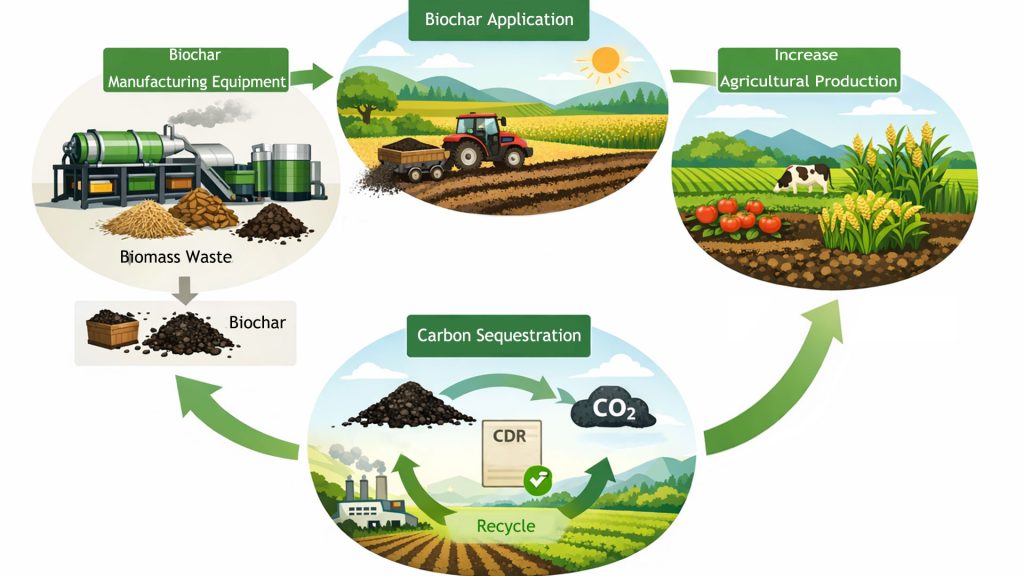
The pyrolysis process takes place under low-oxygen conditions, allowing it to lock in carbon and convert biomass waste into a stable, carbon-rich material. Mingjie biomass pyrolysis plant can produce high-quality, stable biochar with consistent carbon retention capabilities.
Global Biochar Market Influencing Factors
A key driver of the biochar market is the increasing emphasis on carbon sequestration and emission reduction strategies. When applied to soil, biochar retains nearly 70%-80% of its carbon content, significantly reducing carbon emissions into the atmosphere. Due to biochar’s long-term carbon stability, approximately 55% of sustainability-focused agricultural programs promote its use.
Studies show that using biochar can reduce soil greenhouse gas emissions by approximately 20%-30%. Furthermore, nearly 50% of environmentally friendly agricultural programs consider biochar a practical tool for achieving negative carbon agriculture outcomes, thus accelerating its adoption in multiple regions.
Solutions Needed for Biomass Waste
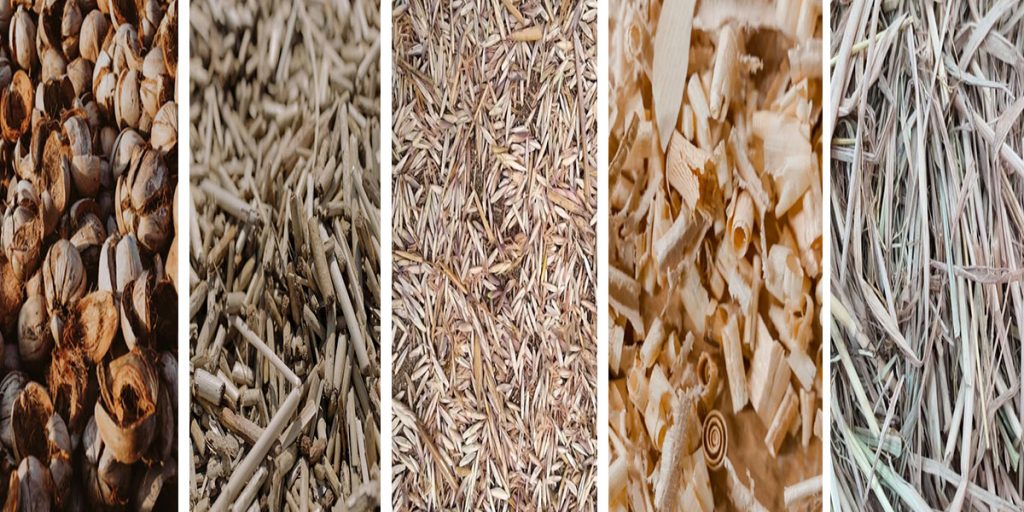

One of the main drivers of the global biochar market is the increasing demand for biomass solutions. Rising prices of primary fuels necessary for energy production are a major factor driving this growth. As traditional fuel prices increase, more people are seeking sustainable alternative energy sources.
Biochar, produced from biomass, offers a sustainable method of energy production and is crucial in meeting this demand. Furthermore, biochar improves soil fertility and sequesters carbon, both of which are beneficial to the environment.
Investment in Agricultural Sector
The development of the biochar market is primarily driven by government investments in the agricultural sector, which promote agricultural growth and sustainable development. Countries worldwide are providing funding to support sustainable farming practices and improve soil health.
The increasing popularity of organic farming and growing awareness of its benefits further propel the application of biochar. Biochar application in agriculture supports the development of globally ecologically sustainable and climate-resilient agriculture, while also contributing to improved soil fertility.
Over 70% of biochar use is concentrated in crop cultivation and pasture management. Due to restrictions on synthetic soil conditioners, the adoption of biochar in organic farming systems has increased by approximately 40%. Livestock farming accounts for nearly 12% of biochar demand, where it is used as a feed additive and bedding material.
Biochar, as a soil amendment, can improve soil fertility. It can enhance water retention and soil structure, thereby promoting soil improvement and organic food production.
Biochar Applications in Livestock Farming: Adding biochar to livestock feed can significantly improve animal health. Biochar provides essential nutrients, enhancing the overall health of animals, thereby promoting growth and improving their disease resistance.
Studies have shown that adding biochar to livestock feed also reduces ammonia emissions, improving air quality for both workers and animals. This aligns with the principles of sustainable agricultural practices by reducing the negative environmental impact of livestock farming.
Carbon Credits Drive the Global Biochar Market
Biochar carbon credits are credits that represent durable carbon sequestration. This permanent sequestration, also known as carbon removal or capture, physically locks away carbon in a stable form over extended periods. Through carbon sequestration, biochar generates guaranteed, certified carbon credits.
Furthermore, biochar production can generate Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR) carbon credits. These credits can be traded or sold, providing a second revenue stream for biochar plant and incentivizing further carbon sequestration efforts.
Globally, 93% of industrial-grade biochar production capacity is already locked in long-term contracts by the end of 2025. For 2026, 40% of carbon credits are already locked in, meaning buyers are already competing for next year’s credits. To meet the demand in the biochar market, biochar manufacturers need to add or expand biochar production lines.