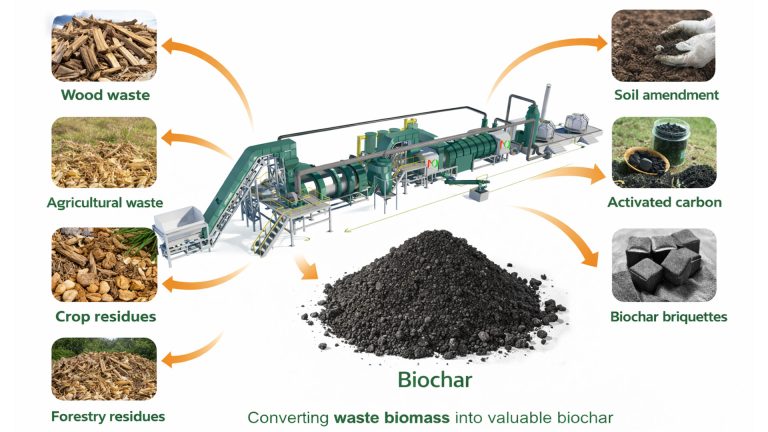
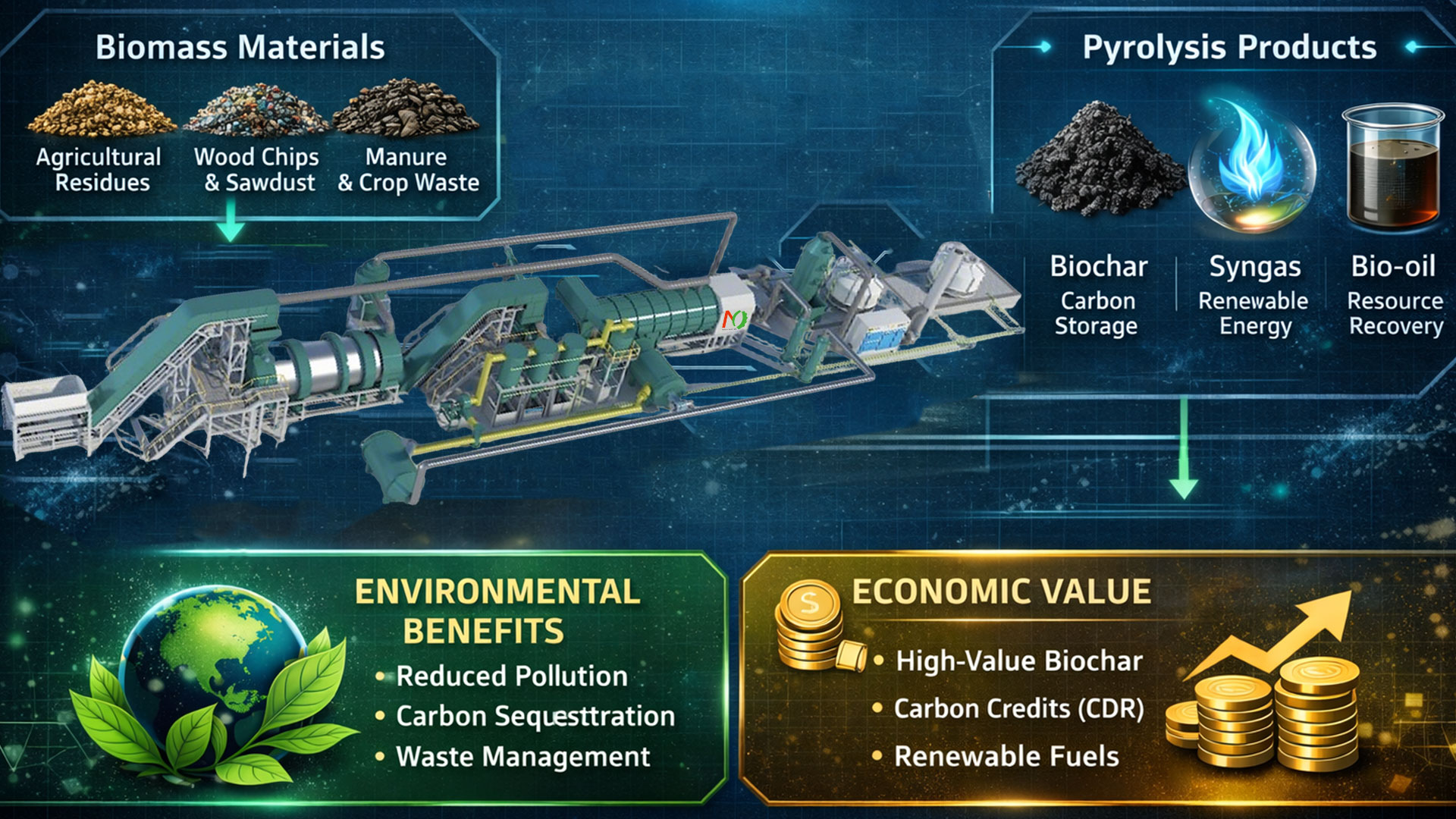
Continuous biomass pyrolysis is a key technology with significant environmental value, energy value, and carbon reduction potential. Through large-scale, continuous operation, biomass pyrolysis equipment provides a sustainable solution for biomass waste treatment. It continuously converts biomass into biochar, syngas, and bio-oil. Biochar is an important vehicle in the current carbon removal (CDR) and carbon credit markets.
At the same time, continuous biomass pyrolysis plants create new economic growth points for the agricultural, energy, and environmental protection industries. In the context of global low-carbon transition and circular economy, continuous biomass pyrolysis equipment is expected to become an important pillar for the high-value utilization of biomass resources.
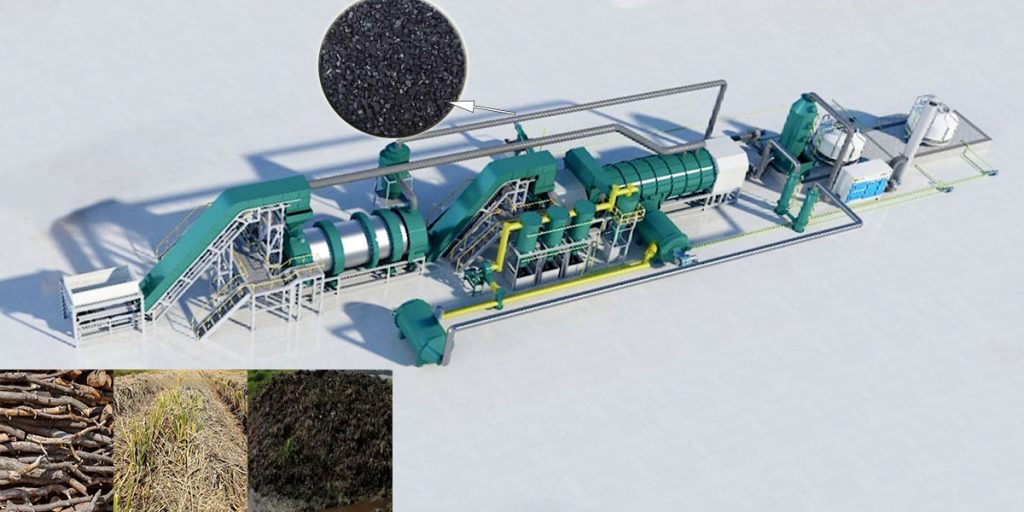

Biomass continuous pyrolysis technology has opened up an innovative path in the field of waste treatment. It provides an effective solution for the treatment of solid waste such as agricultural and forestry waste, livestock manure, and industrial sludge. Continuous pyrolysis technology can achieve the reduction, harmless treatment, and resource utilization of biomass waste.
Continuous Biomass Pyrolysis Process
Continuous biomass pyrolysis is carried out in a closed system. Continuous pyrolysis system can achieve stable operation and energy self-sufficiency, representing a highly continuous and automated pyrolysis process.
After crushing, drying, and screening, the biomass is continuously fed into the pyrolysis reactor through a feeding system. In an oxygen-free environment, the cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin in the biomass decompose during the pyrolysis reaction. The pyrolysis vapors are condensed to form bio-oil, and the non-condensable gases are recovered as combustible gas. The biochar is continuously discharged and cooled for subsequent use.
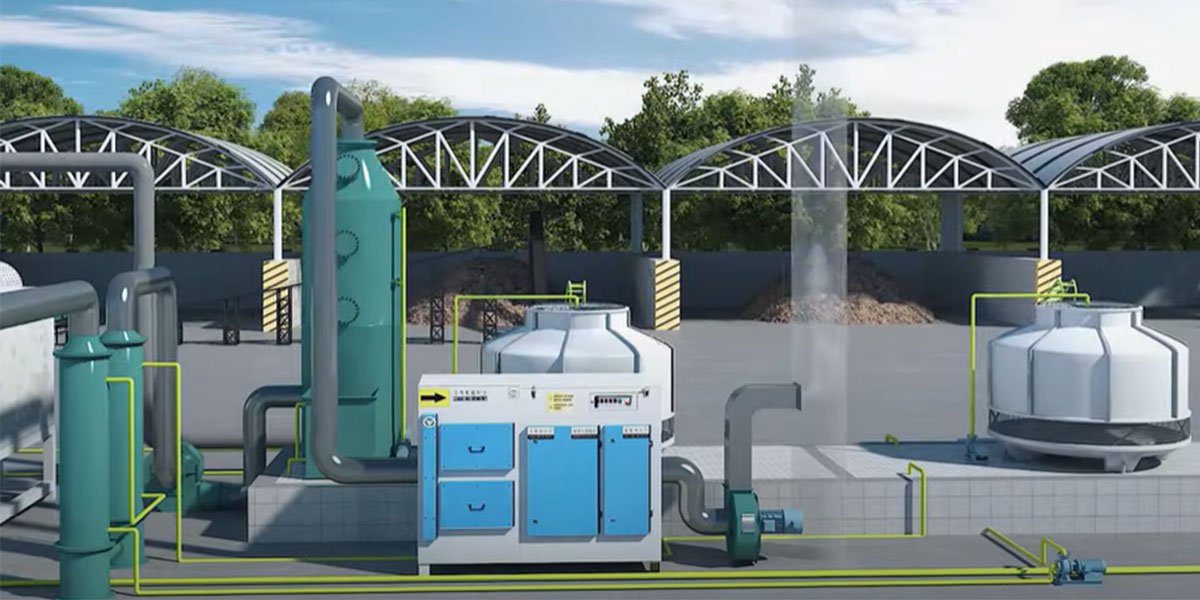
Energy recovery and exhaust gas treatment are also indispensable steps in the continuous biomass pyrolysis process. The collected syngas is fed back to the pyrolysis furnace burner as heating fuel, achieving self-heating of the system.
Before being discharged, the combustion flue gas needs to be treated by a flue gas purification system, such as a bag filter and an alkaline scrubbing tower. This removes pollutants such as dust, SO₂, and NOx, ensuring that emissions meet environmental standards.
Benefits of Continuous Biomass Pyrolysis
- Reduced open burning of biomass: Effectively avoids pollution emissions caused by straw burning.
- Achieves negative or low carbon emissions: Biochar sequesters carbon elements long-term, and combined with life cycle assessment (LCA), can achieve net carbon removal.
- Promotes agriculture and ecological restoration: Applying biochar to farmland can improve degraded soil and increase crop yields and drought resistance.
- Reduces waste disposal pressure: Converts dispersed agricultural and forestry waste into storable, transportable, high-value-added products.
- Industrial-scale operation offers significant advantages: continuous feeding and discharge, high equipment utilization. High level of automation and low labor costs. Suitable for medium to large-scale biomass processing projects.
- Carbon credits are becoming an important supplementary income source for continuous biomass pyrolysis projects. Biochar can participate in carbon dioxide removal (CDR) or carbon credit trading.

Summary
Continuous biomass pyrolysis plant is expected to make a more significant contribution to global sustainable development. With the continuous optimization of pyrolysis equipment, continuous biomass pyrolysis plants will achieve higher biochar conversion efficiency.
High-performance pyrolysis reactors can withstand higher temperatures and pressures, improving the stability of biomass pyrolysis. Advanced automated control systems enable precise monitoring and intelligent control of the entire pyrolysis process. This further improves the efficiency of biochar production and the stability of product quality.
The applications of biochar in agriculture, environmental protection, and materials science will continue to deepen.
- In agriculture, biochar serves as a soil conditioner and fertilizer enhancer. It helps improve soil fertility, promote crop growth, and reduce the use of chemical fertilizers.
- In the environmental field, biochar can be used for wastewater treatment, exhaust gas treatment, and soil remediation. It can effectively adsorb and immobilize pollutants.
- In the materials field, biochar can be used as a raw material to prepare high-performance activated carbon, electrode materials.