Pyrolysis oil is a liquid product obtained from the thermal decomposition of waste tires and waste plastics under oxygen-free or oxygen-deficient conditions. Crude pyrolysis oil contains sulfur, chlorine, oxygen-containing compounds, gums, asphaltenes, acidic substances, and highly unstable components. This not only corrodes equipment but also makes it difficult to use directly as fuel. Therefore, pyrolysis oil refining has become a key technology in the waste resource utilization chain for increasing product value.
Mingjie pyrolysis oil distillation equipment is widely used to recover and refine tire oil, plastic oil, and other pyrolysis oils into diesel fuel. The pyrolysis oil refining unit adopts a high-vacuum distillation process to convert waste oil into diesel fuel.
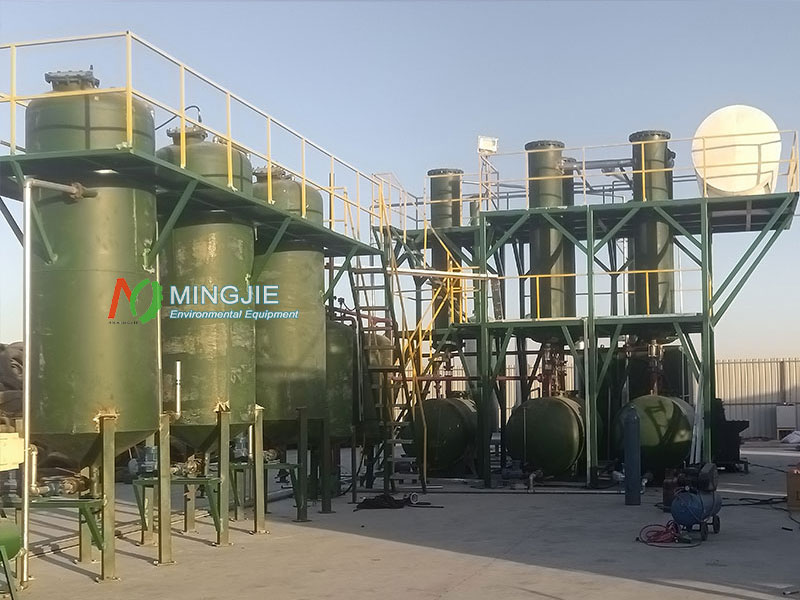

After refining, pyrolysis oil can be widely used in various fields such as transportation, power generation, and chemical industries. It has become an ideal alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
The fuel oils from pyrolysis oil refining can be directly used in vehicles such as cars and ships. This reduces reliance on petroleum-based fuels, lowers exhaust emissions, and contributes to the green transformation.
Sources of Pyrolysis Oil
Pyrolysis oil has a wide range of raw material sources, mainly including three categories: waste plastics, waste tires, and industrial oil sludge. Pyrolysis equipment uses chemical recycling methods to convert solid waste into pyrolysis oil, synthesis gas, and carbon black under oxygen-free, high-temperature conditions.

Among waste plastics, pure polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene have the highest oil yield, reaching 90%-95%. However, the oil yield of food packaging bags with complex compositions drops to about 40%.
Waste tires mainly consist of rubber and metal, with an oil yield of approximately 30%-45%.
Oil sludge mainly originates from various stages of petroleum exploration, production, storage, transportation, and refining. Its oil content is ranging from 5% to 50%.
Pyrolysis Oil Refining Technology
Crude pyrolysis oil is complex in composition, dark in color, and contains impurities. It requires further refining to improve its quality and value. Advanced waste oil distillation equipment utilizes a high-vacuum distillation process to convert pyrolysis oil into diesel fuel.
Pyrolysis Oil Distillation
Distillation and fractionation are key technologies for achieving component separation in the pyrolysis oil refining process. Their principles are based on the differences in boiling points of the various fractions in the pyrolysis oil.
Distillation is a relatively basic separation method. It involves heating the pyrolysis oil to its boiling point, where the lower-boiling point fractions evaporate first into a gaseous state. The gaseous fractions are then cooled and liquefied through a condenser, thus separating them from the higher-boiling point fractions.
Fractionation is a more refined separation technology developed from distillation. It utilizes a fractionation column to achieve more effective separation of fractions with similar boiling points in the pyrolysis oil through multiple evaporation and condensation cycles.
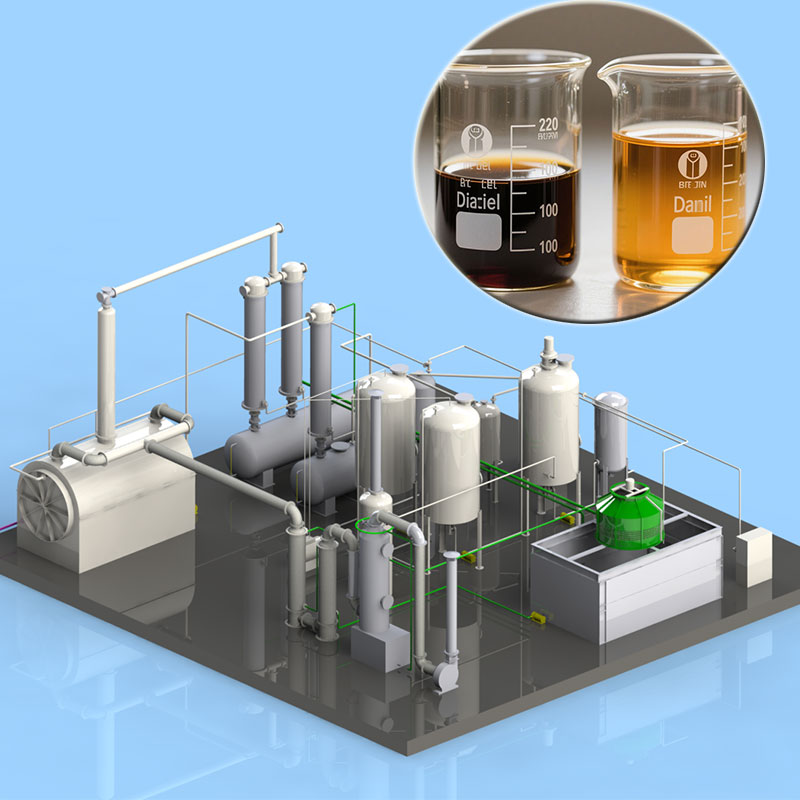

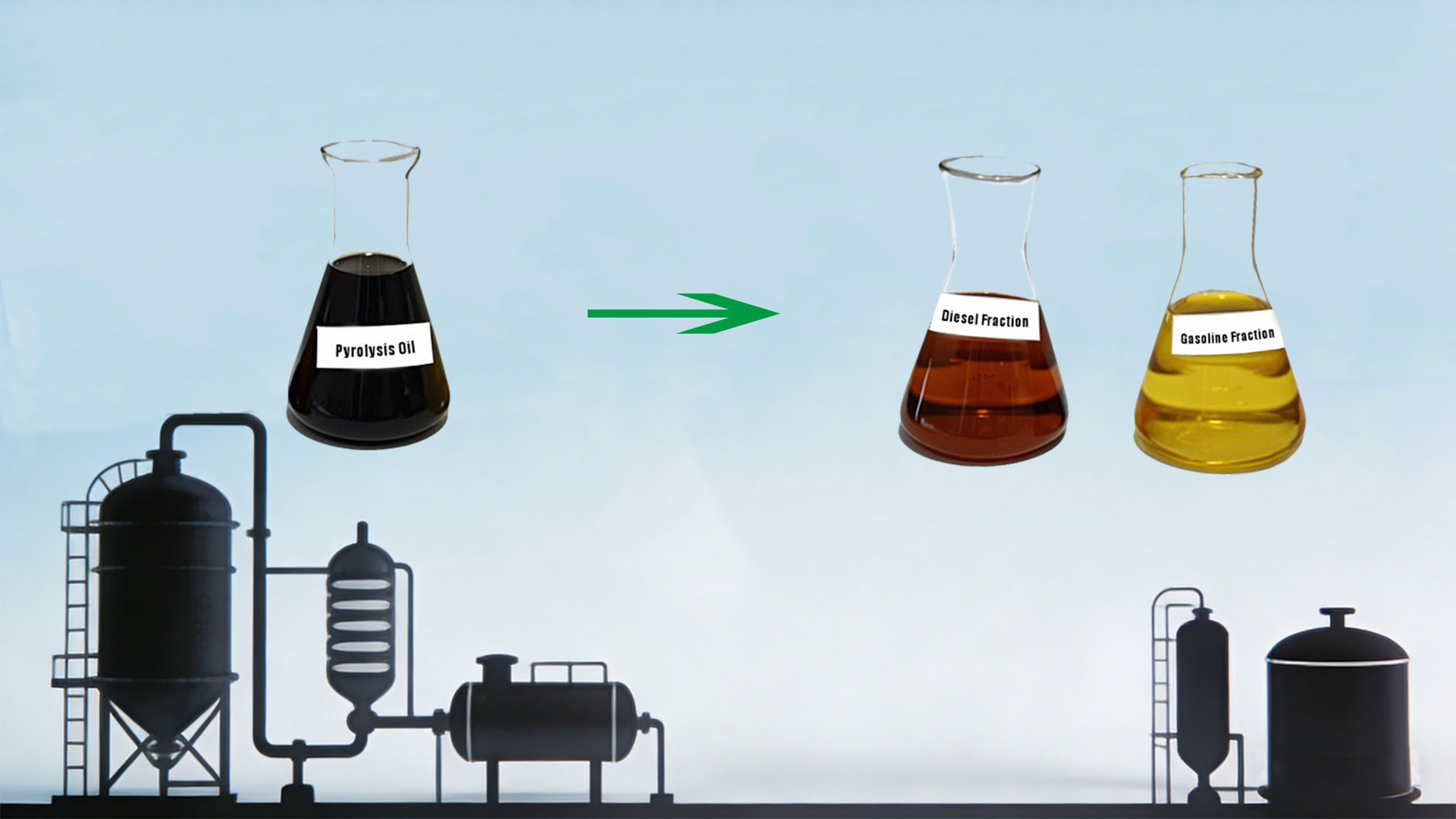
Pyrolysis Oil Distillation Products
Through distillation and fractionation, pyrolysis oil can be separated into light, medium, and heavy fractions.
- The light fraction mainly contains low-boiling point hydrocarbon compounds, such as gasoline and kerosene. These fractions have high volatility and low viscosity, making them suitable as fuel for vehicles such as cars and airplanes.
- The medium fraction has moderate boiling points and viscosity and can be used as fuel such as diesel, for industrial engines, ships, and other equipment.
- The heavy fraction contains high-boiling point macromolecular compounds, which can be further processed to produce products such as lubricating oil and asphalt.
Pyrolysis Oil Decolorization
In addition to distillation, decolorization is another crucial step in pyrolysis oil refining process. Common decolorization methods include:
- Activated clay decolorization: Utilizing the strong adsorption properties of activated clay to remove pigments and impurities.
- Acid-base refining: Decolorization through a combination of acid washing and alkali refining.
- Oxidative decolorization: Using oxidizing agents such as hydrogen peroxide to decompose pigments.