At present, there are three main pyrolysis processes in the world: slow pyrolysis, fast pyrolysis and flash pyrolysis. In slow pyrolysis or carbonization processes, low temperatures and long residence times favor the formation of charcoal.
Pyrolysis technology is the decomposition of heated organic matter in an oxygen-free environment, where the heating is controlled by a temperature range and provides the energy required to decompose the macromolecular structures in the biomass.
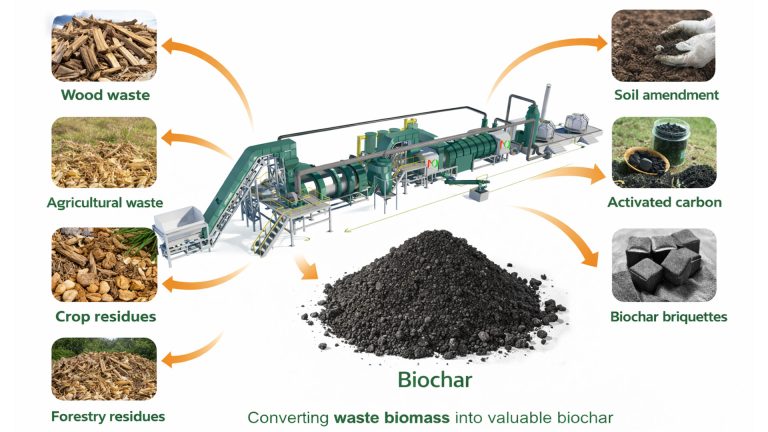
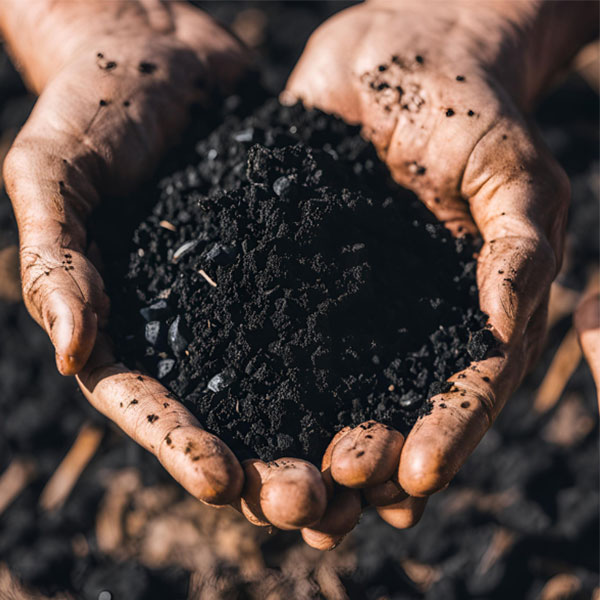
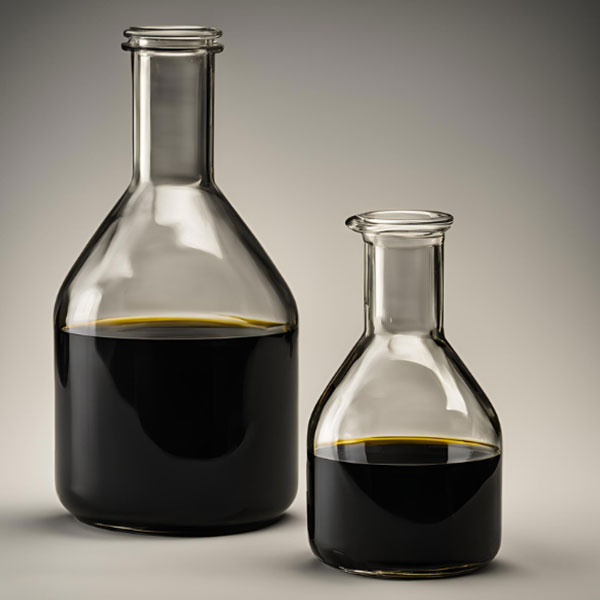
During the biomass pyrolysis process, the biomass is converted into biochar, bio-oil and synthesis gas. And depending on the conditions in the pyrolysis reactor, one of the products can be maximized.

Turn Waste Biomass to Energy
Energy demand is on the rise as population grows and economies and technologies continue to develop around the world. The depletion of fossil fuels and extreme climate change have prompted the search for alternative and renewable energy sources to meet the world’s energy needs. At the same time, there is a need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and control pollution.
Among alternative energy sources, biomass can be a promising sustainable energy source due to its high diversity and availability. Biomass can be defined as all biodegradable organic materials derived from animals, plants or microorganisms.
Biomass is the third most important energy source for power generation and thermal energy applications. The most common biomass feedstocks are banana peels, rice and coffee husks, bagasse, palm oil processing residues and animal manure.
Thermal conversion of biomass can produce different types of energy, such as combustion, pyrolysis, gasification, fermentation and anaerobic decomposition. Among all biomass conversion technologies, the pyrolysis technology has many advantages, including fewer emissions and all by-products can be reused. Biomass pyrolysis products include solid biochar, liquid tar, and synthesis gas.



Biomass Pyrolysis Process
There are several types of pyrolysis processes, namely slow pyrolysis, fast pyrolysis, and flash pyrolysis. They can be used to convert biomass, depending on the biomass pyrolysis process and pyrolysis temperature employed. The products of biomass pyrolysis are bio-oil, biochar, and syngas. The physical and chemical properties of these pyrolysis products depend on the quality of the biomass.
The main feature of the biomass pyrolysis process is the thermal degradation of solid fuels, which involves the breaking of carbon-carbon bonds and the formation of carbon-oxygen bonds. Temperatures up to 400-550 °C are required for biomass pyrolysis.
Slow Pyrolysis
Slow pyrolysis involves a process called continuous carbonization, where the biomass is slowly heated to temperatures above 400 °C in the absence of oxygen. In this process, the biomass is pyrolyzed at a low heating rate with minimal liquid and gaseous products and maximum biochar production.
The highest biochar yield is achieved when feedstocks with a high lignin content are pyrolyzed at moderate temperatures (around 500 °C). Generally, biomass with a high amount of volatile matter provides a large amount of syngas and bio-oil, while fixed carbon increases the biochar yield.
Fast Pyrolysis
Fast pyrolysis is a method of converting biomass into liquid products. The resulting pyrolysis oil (bio-oil) is an energy fuel of medium density. It can be converted into hydrocarbons in diesel and gasoline by distillation equipment.
During fast pyrolysis, biomass decomposes very quickly, mainly producing steam and aerosols, as well as small amounts of coal and gas. After cooling and condensation, the pyrolysis products become a dark brown liquid. Its calorific value is equivalent to half that of conventional fuel oil.
Flash Pyrolysis
The main characteristics of flash pyrolysis are very fast heating speed and very short residence time of biomass in the reactor. These characteristics favor the generation of steam, making the process very similar to gasification.

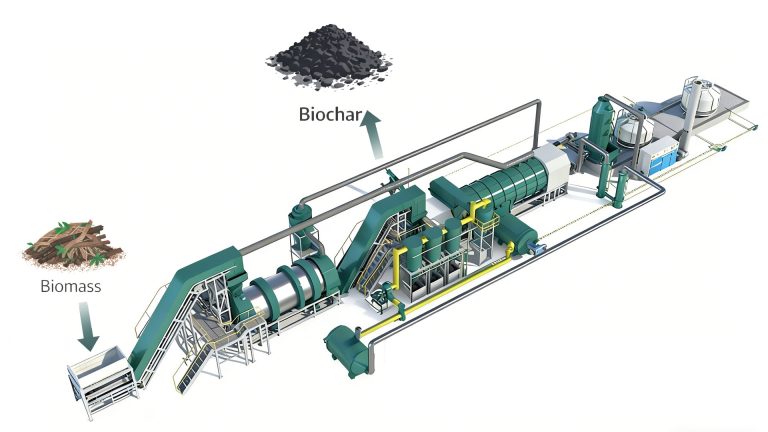
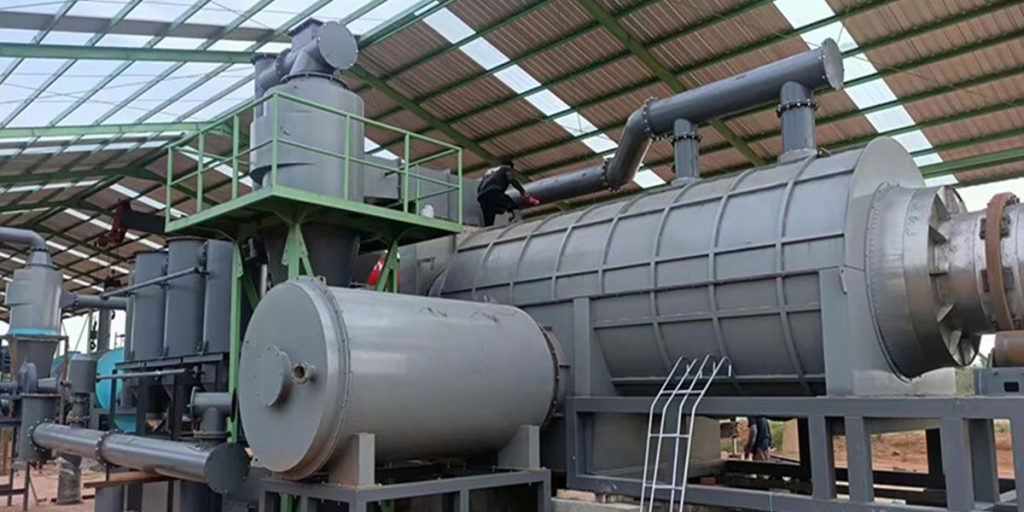
Biomass Carbonization Plant
The heart of biomass pyrolysis is the pyrolysis plant, where all reactions take place. Traditional biochar production methods can no longer meet the current market requirements for biochar quality. For example, quality standards such as H/C molar ratio, PAHs (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons), and heavy metal content have become important indicators.
At present, the mainstream trend has shifted to large-scale and continuous production. Mingjie biomass carbonization plant not only improves efficiency, but also ensures higher quality biochar products.
Biochar production equipments play a vital role in sustainable waste biomass management. Biomass pyrolysis plants convert biomass into valuable biochar. This not only helps protect the ecological environment, but also plays a key role in combating climate change.

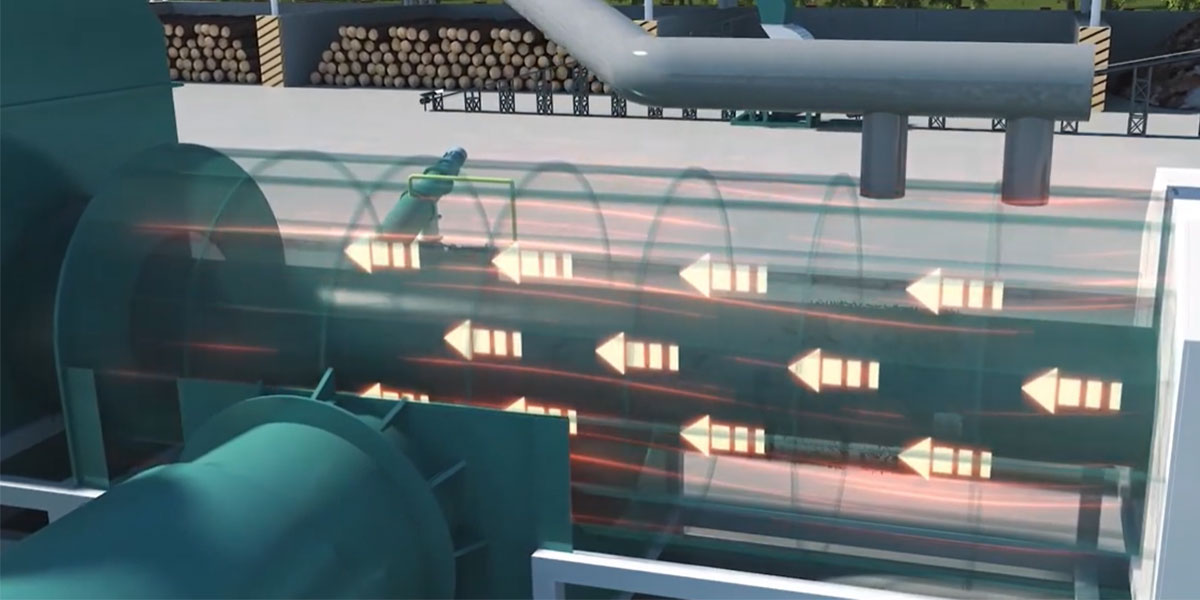
The combustible gas generated by the biochar production equipment re-enters the heating system through the pipeline, replacing the external fuel and providing energy for the biomass carbonization plant. Excess combustible gas can be discharged in the external exhaust combustion chamber to reduce the pressure of the reactor.
The high-temperature flue gas generated is cooled by the flue condenser and enters the dust removal system for further purification. The waste heat of the high-temperature flue gas generated in the combustion chamber can be used as a heat source for the dryer.