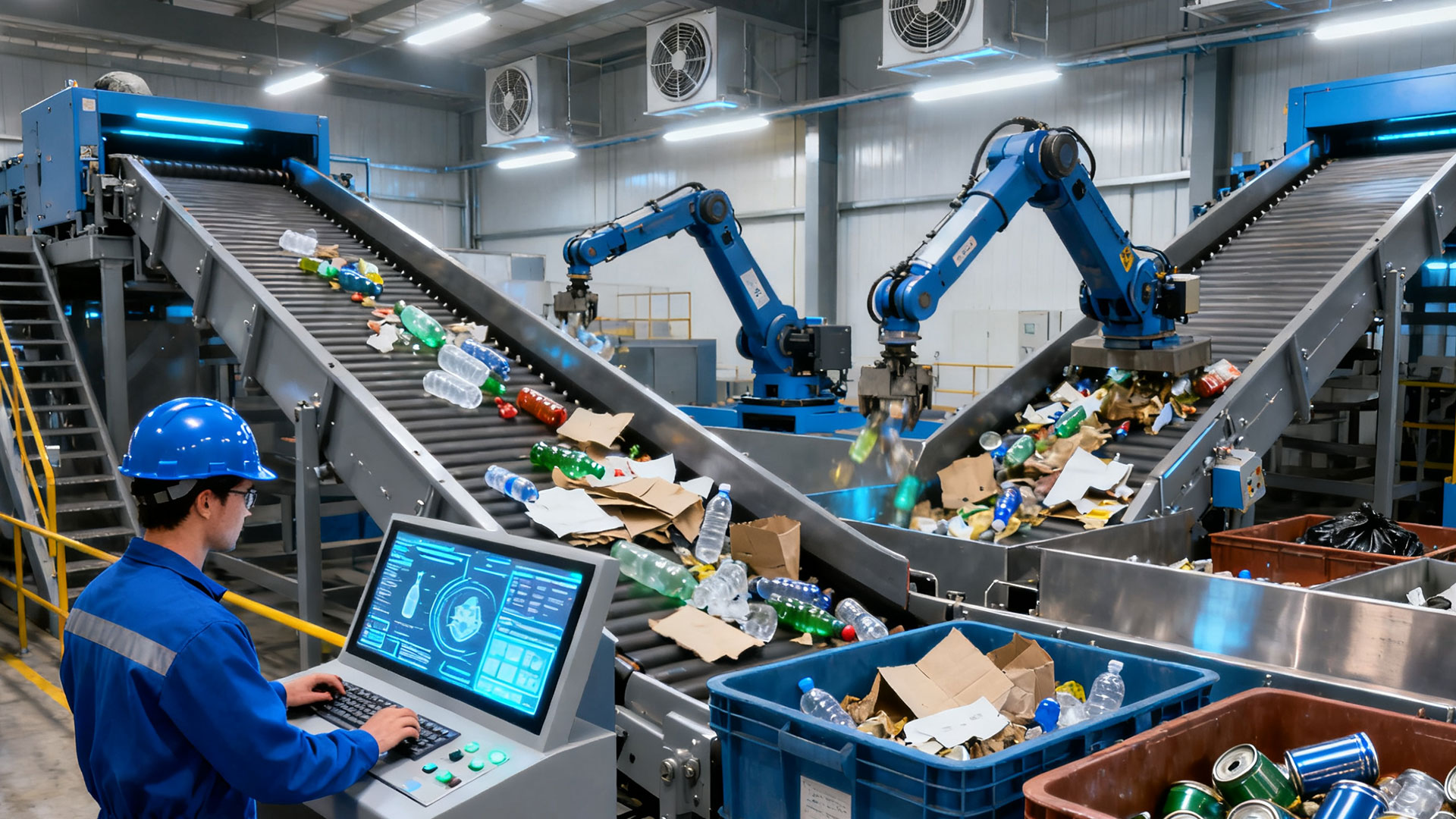
Solid waste treatment technologies primarily include pyrolysis, incineration, high-temperature composting, and sanitary landfills. Landfill and incineration are the most widely used end-of-life treatment methods worldwide. Their core focus is on reducing pollution emissions and improving resource utilization.
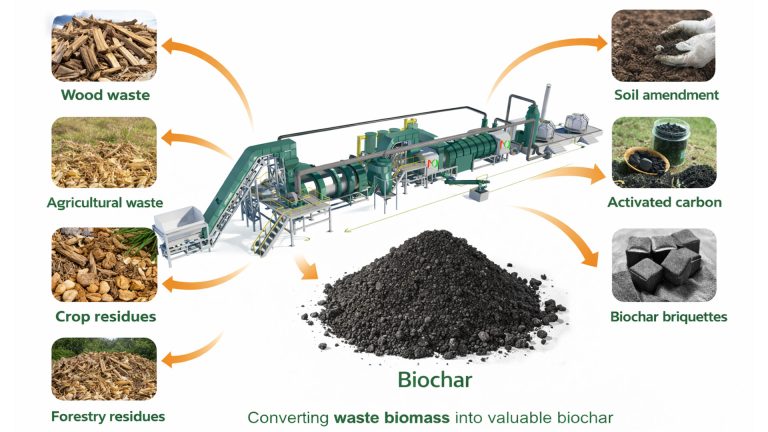
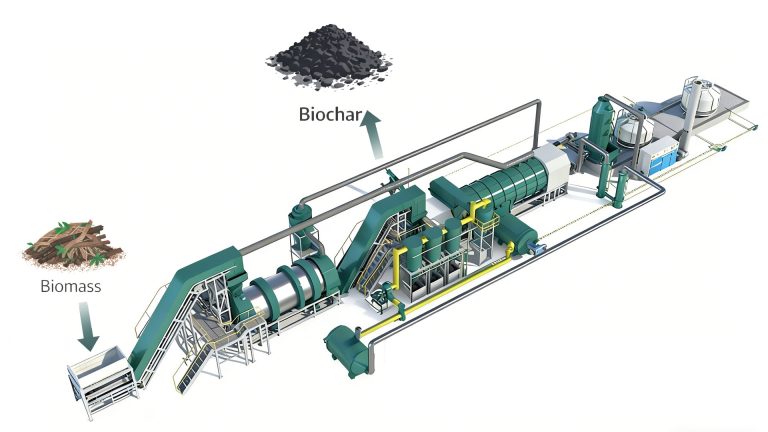
Pyrolysis technology has proven to be a promising solid waste treatment method. Pyrolysis equipment has been used in industrial production, such as converting tire plastics into fuel oil and producing biomass into biochar.
Solid Waste Treatment by Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis of solid waste is a chemical decomposition process. It decomposes combustible solid waste at high temperatures in the absence or anoxic conditions, ultimately producing combustible gases, oils, and solid carbon. Pyrolysis plant heats solid waste in a completely oxygen-free environment, breaking the chemical bonds in the organic matter, producing small molecules (gaseous and liquid) and solid residue.
Solid Waste Treatment by Pyrolysis is suitable for municipal solid waste, medical waste, sewage sludge, and industrial waste plastics and rubber. The pyrolysis process varies depending on the heat supply method, product state, and pyrolysis reactor structure.
- Based on the heating method, solid waste pyrolysis can be categorized as internal or external.
- Based on the state of the pyrolysis products, pyrolysis can be categorized as gasification, liquefaction, and carbonization.
- Based on the structure of the pyrolysis reactor, pyrolysis plant can be categorized as fixed, moving bed, or rotary.
Solid Waste Incineration
Solid waste incineration is a traditional method of solid waste treatment. It reduces waste volume by burning organic matter within the waste. However, this carries the environmental risk of pollutants generated by combustion. Incineration converts waste into ash, exhaust gases, and heat.
Ash is mostly composed of inorganic matter from the waste, typically in the form of solids and particulates in the exhaust gases. Before exhaust gases are released into the atmosphere, pollutants and particulates must be removed. The remaining residue is landfilled. In some cases, the heat generated by incineration is used to generate electricity.
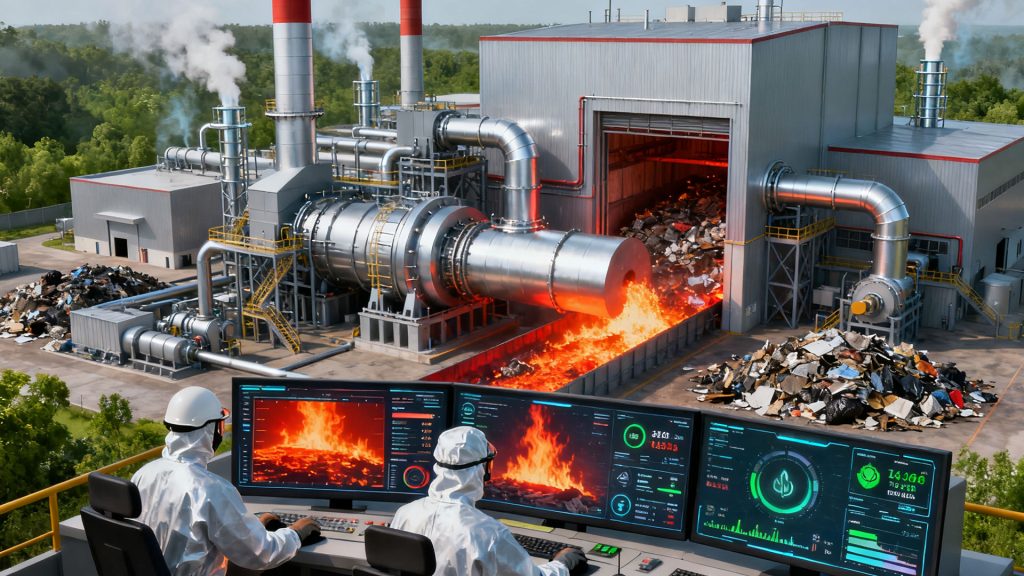

Differences between Incineration and Pyrolysis
- Plastic pyrolysis is a fundamentally different process from incineration. Incineration is exothermic, while pyrolysis is endothermic.
- The products of incineration are primarily carbon dioxide and water. The products of solid waste pyrolysis are primarily combustible low-molecular compounds, pyrolysis oil, pyrolysis gas, and carbon black.
- Large amounts of heat generated by incineration can be used for power generation, while smaller amounts can be used to heat water or generate steam for local use. The products of pyrolysis are fuel oil, combustible gas, and carbon black, which are easy to store and transport over long distances.
The advantage of solid waste pyrolysis is that it produces less waste. It can process difficult-to-treat materials that are not suitable for incineration. Pyrolysis waste to energy can reduce secondary pollution caused by incineration and the amount of waste that needs to be disposed of in landfills.
High-Temperature Composting
High-temperature composting is an important method for producing farm fertilizer. It utilizes the oxidative and decomposing capabilities of widely occurring microorganisms to promote the controlled biochemical degradation of biodegradable organic matter in solid waste.
The high temperatures generated during the composting process also kill various pathogens and insect eggs. High-temperature composting is suitable for waste with a biodegradable organic matter content greater than 40%.
Currently, the main targets for composting are municipal solid waste, sewage treatment plant sludge, human and animal feces, agricultural waste, and food processing waste. High-temperature composting can achieve resource utilization, but it is inefficient and requires a long composting cycle.
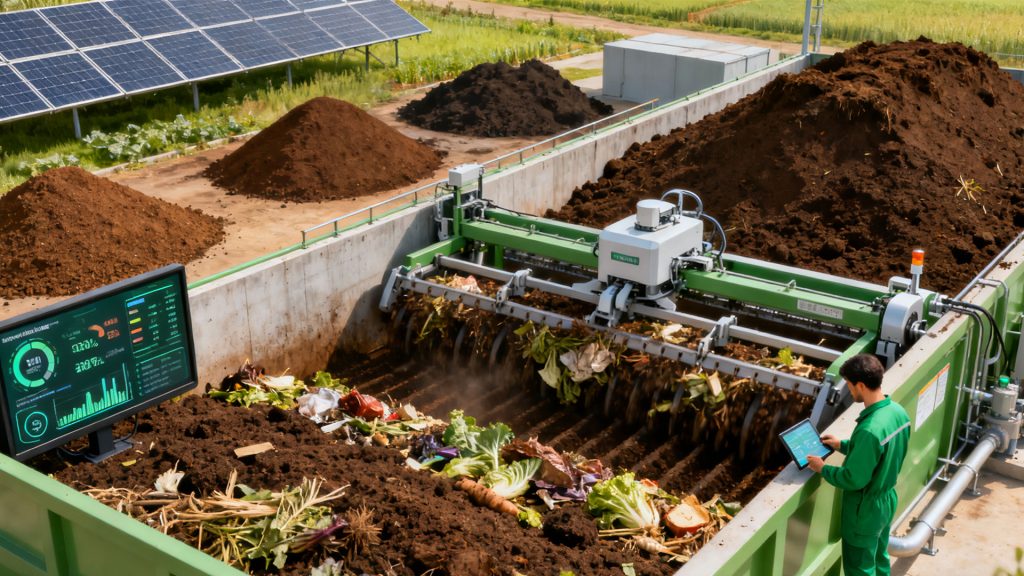

Biomass Pyrolysis vs. Composting
The main advantages of biomass pyrolysis over high-temperature composting are high energy recovery efficiency, shorter processing cycles, and more significant volume and quantity reduction. Furthermore, biomass pyrolysis machine can better stabilize carbon and treat hazardous substances.
Pyrolysis equipment converts waste biomass into valuable energy, producing stable biochar. It’s a powerful tool for achieving “negative carbon emissions.”
Continuous biomass carbonization plant offers fast processing speeds and excellent volume reduction, making it suitable for modern, large-scale waste treatment centers.

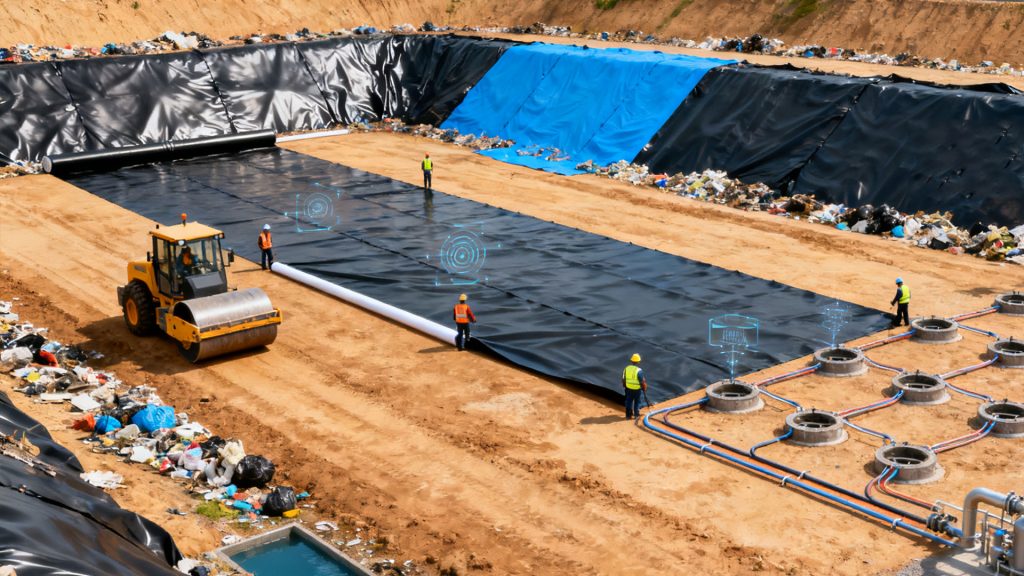
Sanitary Landfill
Sanitary landfill involves treating municipal solid waste through measures such as anti-seepage, leveling, compaction, and covering. This solid waste treatment method employs measures such as bottom-level anti-seepage, layered landfilling, and a top layer of soil cover after compaction. It allows the waste to ferment under anaerobic conditions, achieving harmless treatment.
Sanitary landfills offer high processing capacity and low costs, but they require land and are difficult to locate. The landfill gas generated directly is primarily methane, which is prone to explosion hazards. Currently, most landfills vent the gas, increasing greenhouse gas emissions and wasting energy.

Biomass Pyrolysis vs. Landfill
| Comparative Dimensions | Biomass Pyrolysis | Sanitary Landfill |
| Resource Recovery Methods | Actively generate energy and products • Biochar: for soil improvement and carbon sequestration. • Bio-oil/syngas: for fuel or power generation. | Passive recovery • Collecting landfill gas to generate electricity, but the efficiency is low (about 50%) and there is a lot of leakage. |
| Carbon Footprint and Climate Change | Carbon Negative Potential • Carbon is fixed as stable biochar, storing it for centuries. • Process energy consumption is far lower than emissions. | Greenhouse Gas Emissions • Anaerobic decomposition of organic matter produces large amounts of methane, which has a greenhouse effect 21-28 times greater than that of CO₂. • It is the primary anthropogenic source of methane emissions. |
| Environmental Pollution Control | Controlled and centralized • Pollutants (exhaust gas, tar) are centrally treated in a closed system. • Biochar can immobilize heavy metals. | Long-term risks and spread • High risk of leachate leakage, potentially leading to permanent groundwater contamination. • Significant odor, dust, and pest and disease problems. |
| Land Resource Utilization | Intensive and Efficient • Small footprint and modular deployment. • Significant capacity reduction (>70%). | Extensive waste • Permanently occupies a large amount of land resources, creating a “garbage siege” situation. • High ongoing site maintenance costs. |
| Processing Cycle and Efficiency | Fast and Efficient • Processing takes hours. • Continuous production, regardless of weather conditions. | Slow and lengthy • Degradation takes decades or even centuries. • Requires long-term monitoring and maintenance. |
| Economic and Social Benefits | Creating Economic Value • Diversified products generate sustainable returns. • High-tech industry. | Long-term Cost Burden • Extremely high costs for land acquisition, construction, maintenance, and site closure. • Negative impacts on surrounding properties and the environment. |
Solid waste pyrolysis is a positive resource-creating process, transforming waste into high-value products. Landfilling solid waste treatment is only a limited use of natural degradation processes.
Biomass Pyrolysis is a carbon sink, helping to combat climate change. Landfilling is a significant carbon source, exacerbating climate change.
Pyrolysis confines pollutants within the system, resolving the fundamental dilemma of land resources being consumed by waste. The contamination risks of landfilling are pervasive, long-term, and difficult to reverse.
Solid Waste Treatment by Pyrolysis offers an immediate solution, and solid wste pyrolysis projects have the potential to be profitable. Landfilling, on the other hand, leaves problems for future generations, and landfills remain a permanent financial burden on municipalities.