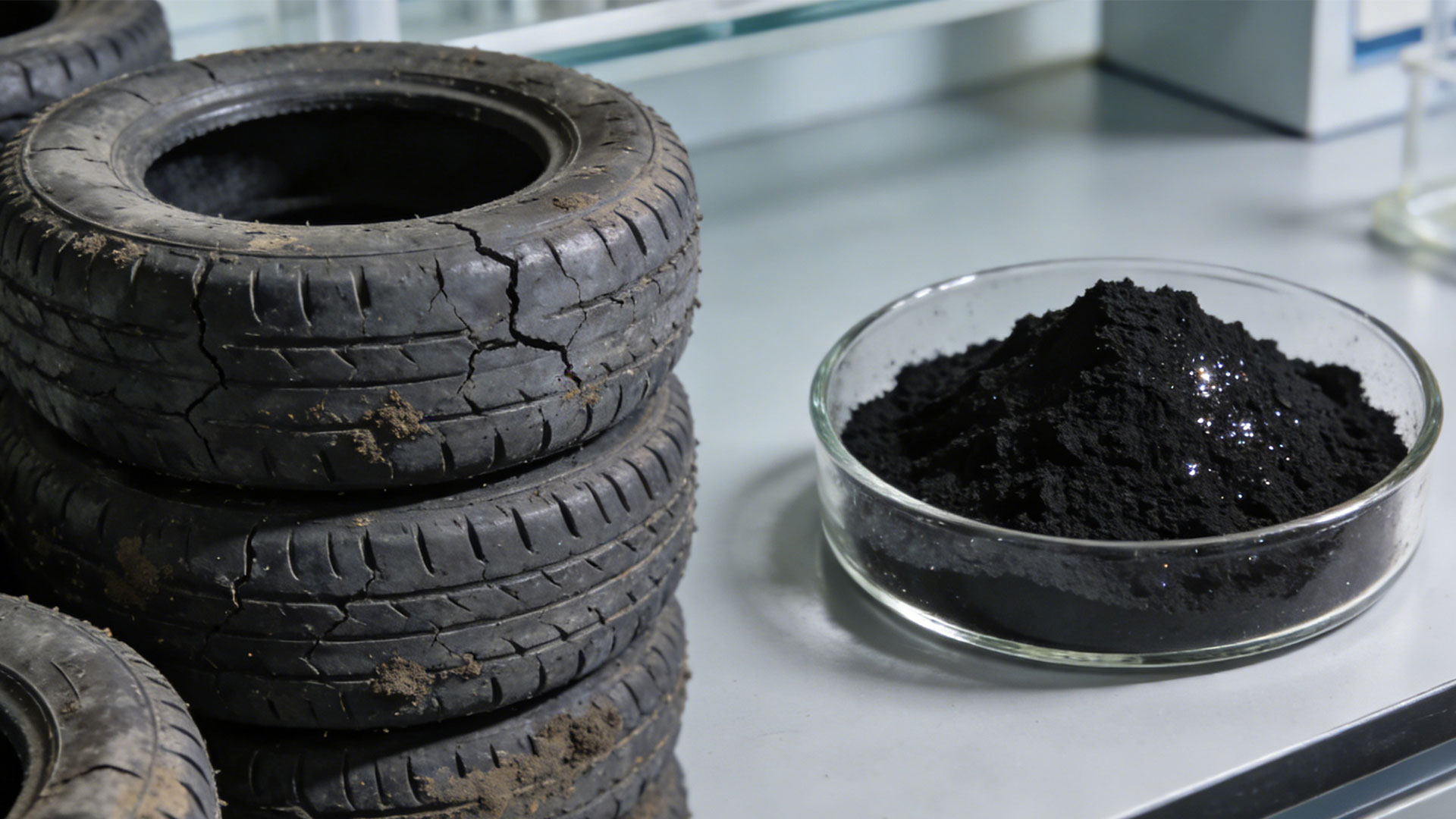
Regarding the pyrolysis products of waste tyres, the collection and processing technologies for pyrolysis gas and pyrolysis oil are relatively mature. However, tyre pyrolysis carbon black is increasingly favored by researchers due to its complex composition and diverse applications.
The global pyrolytic carbon black market is experiencing a period of rapid growth. According to several industry research reports, its market size is projected to maintain a compound annual growth rate of over 10% until 2030.

Pyrolysis carbon black accounts for 33% to 40% of the waste tyre pyrolysis products. The carbon content in the carbon black is 70%, the ash content is 14%, and the remaining 16% consists of other components. Compared with commercial carbon black, waste tyre pyrolysis carbon black has a higher content of inorganic minerals. And its surface contains a variety of carbon black mixtures, resulting in poorer surface activity.
Differences Between Tyre Pyrolysis Carbon Black and Commercial Carbon Black
Tyre pyrolysis carbon black exhibits significant differences in physicochemical properties compared to conventional carbon black. These differences stem from their different raw materials and production processes.
Differences in Specific Surface Area
In terms of specific surface area, conventional carbon black typically has a relatively stable range. This allows it to exhibit good adsorption performance and reactivity in certain applications.
However, the specific surface area of tyre pyrolysis carbon black is affected by the type of rubber in the waste tyres, additives, and pyrolysis process conditions, resulting in a wider range of variation. This difference in specific surface area leads to different characteristics when interacting with other substances.

Differences in Impurity Content
Regarding impurity content, conventional carbon black is produced with strict control over raw materials and processes. High-quality conventional carbon black can have an impurity content of less than 1%, ensuring its stability and reliability in high-end product applications.
In contrast, pyrolysis carbon black originates from waste tyres, which contain various additives such as vulcanizing agents, antioxidants, and plasticizers during their production. These additives partially remain during the pyrolysis process, resulting in a higher impurity content in the pyrolysis carbon black. This not only affects the purity of the tyre pyrolysis carbon black, but may also negatively impact its subsequent application performance.
Differences in Microstructure
In terms of microstructure, conventional carbon black particles have a relatively regular shape and a fairly uniform particle size distribution. This allows it to disperse evenly in materials such as rubber, effectively performing its reinforcing and filling functions.
However, the particle morphology of pyrolysis carbon black is more complex. Due to the non-uniformity of the pyrolysis process and the influence of different components in the waste tyres, its particle size varies, the shape is irregular, and the particle size distribution range is wider. This difference in microstructure leads to relatively poor dispersibility and compatibility with other components in materials. This affects the application performance of tyre pyrolysis carbon black in certain high-performance materials.
Factors Affect the Properties of Pyrolytic Carbon Black
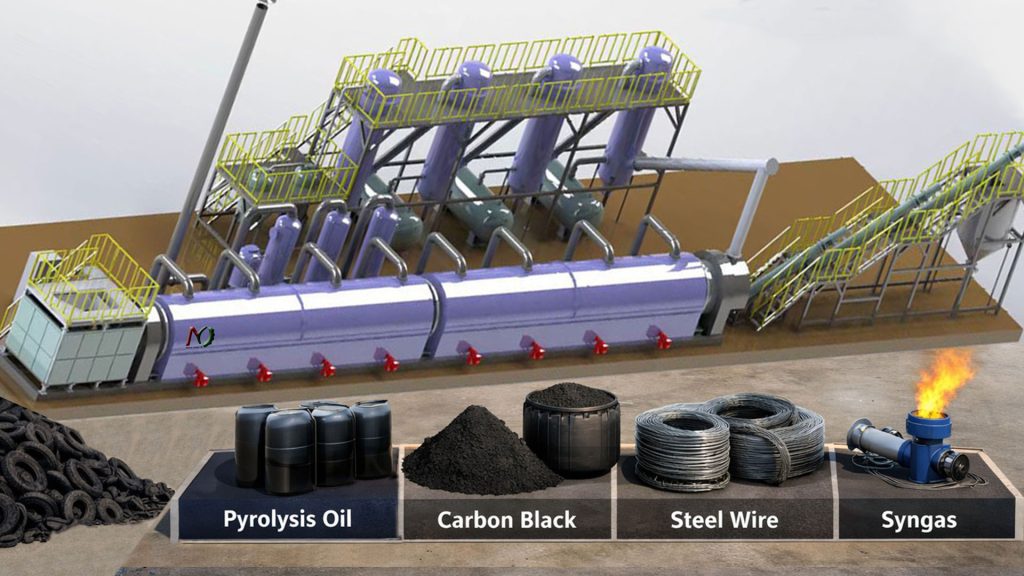

Tyre pyrolysis machine is a key piece of equipment for converting waste tires into carbon black. However, the pyrolysis process has a more complex impact on the quality of the resulting carbon black. Its yield and quality are often affected by factors, such as temperature, pressure, particle size, and reactor type.
To optimize the physicochemical properties of pyrolysis carbon black, modification is used to improve its quality. Modification has become an important way to expand the reuse of waste tire pyrolysis carbon black.
Two methods are commonly used: impurity removal and surface modification. The modified pyrolytic carbon black can replace commercial carbon and be used as a filler material, adsorbent material, catalyst support material, etc.