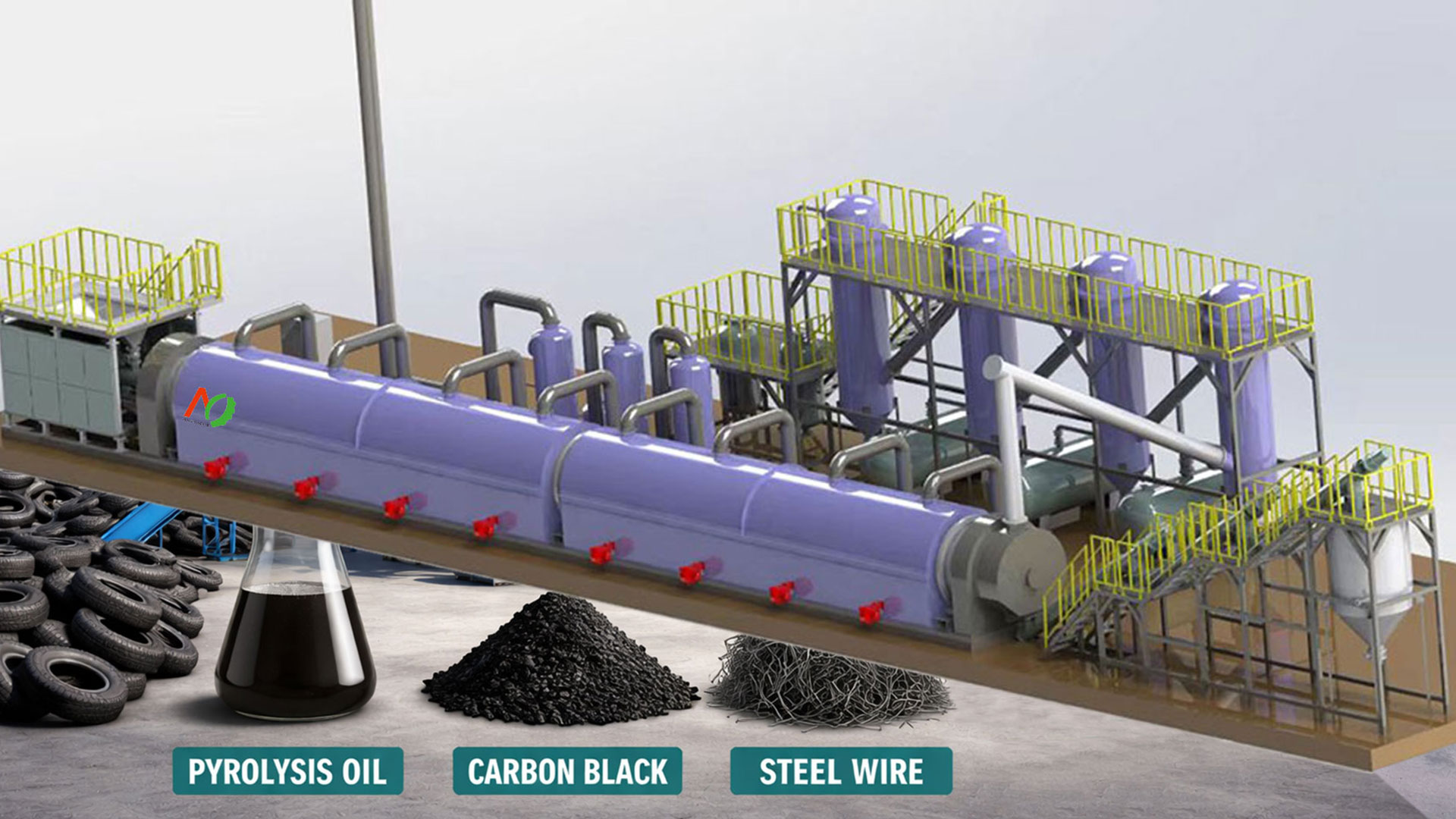
Waste tire to oil pyrolysis technology is an important method for processing rubber. The pyrolysis system primarily works by utilizing the principle that rubber undergoes cracking at high temperatures. In a high-temperature, oxygen-free or oxygen-deficient environment, the components of waste tires undergo complex chemical reactions.
During the waste tire to oil pyrolysis process, the rubber decomposes to produce oil and gas. Through subsequent processes such as condensation and separation, fuel oil can be obtained. The fiber materials in the tires decompose at high temperatures, generating hydrocarbons and a small amount of gas. The steel wires, which do not easily melt at high temperatures, can be easily recovered through magnetic separation.
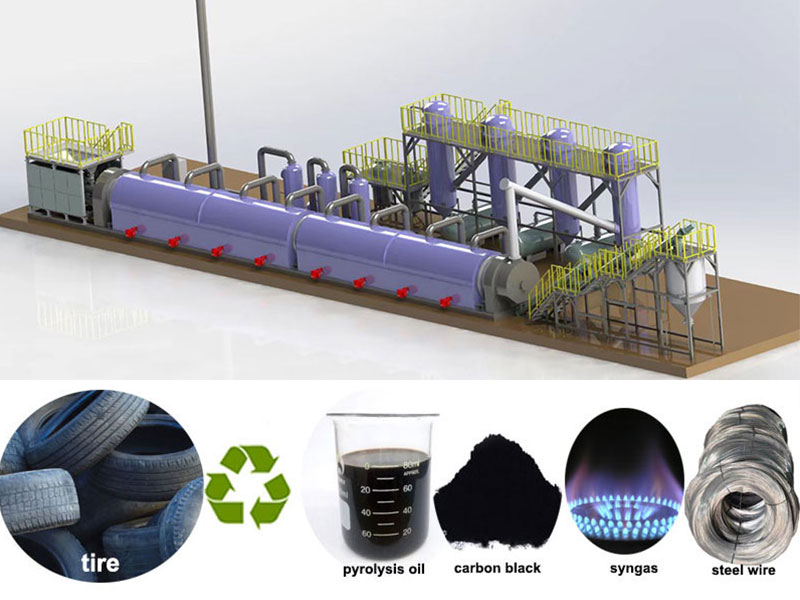

The main components of the syngas are short-chain organic compounds, including hydrogen and C1-C4 hydrocarbons. Syngas has a high calorific value, reaching 33 MJ. It can be used as fuel to provide part of the energy for the waste tire to oil pyrolysis process.
Pyrolysis oil is the liquid product obtained by condensing the volatile fraction from the pyrolysis of waste tires. It is a black, opaque liquid with a pungent odor. Tire pyrolysis oil is a very complex mixture containing more than 100 compounds. After purification, it can be converted into gasoline (C₅ – C₁₀), diesel (C₁₄ – C₁₈), and heavy oil (>C₁₈).
Tire Pyrolysis Oil as Fuel
Pyrolysis oil is highly acidic, has a high sulfur content, and poor thermal stability. Furthermore, its viscosity, flash point, and other physical properties prevent it from being directly burned or used as engine fuel. The sulfur content of pyrolysis oil is typically 1.0–2 wt%, while that of ordinary commercial diesel is less than 0.05 wt%.
Pyrolysis oil has a complex composition, and the presence of low-boiling-point compounds results in a flash point typically below 30°C. A lower flash point indicates lower safety. Therefore, pyrolysis oil must be further refined to improve its performance.
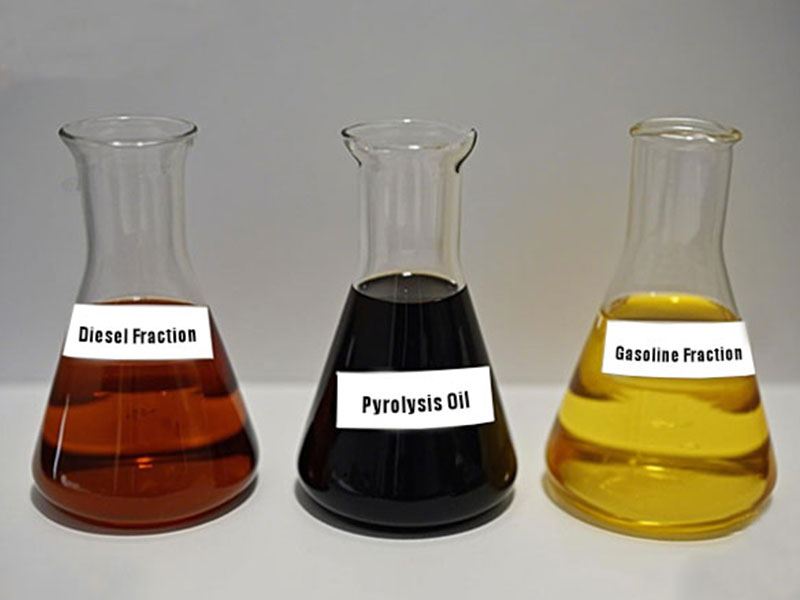

Conversion of Tire Pyrolysis Oil to Diesel
Tire pyrolysis oil must be processed before it can be used as fuel oil. Distillation can improve the usability of pyrolysis oil. Mingjie pyrolysis oil distillation plant can achieve the conversion of tire oil to diesel and gasoline. After distillation, the pyrolysis oil can be divided into three parts: light naphtha fraction, middle distillate fraction, and heavy distillate fraction.
The distillation plant extracts a light fuel fraction from tire pyrolysis oil using distillation. The light fuel fraction (LFF) is a light yellow, translucent liquid with a specific gravity of 0.76 g/cm³. This light component mainly consists of benzene compounds, ethylbenzene, and toluene derivatives. The composition of the light fuel is very similar to gasoline extracted from petroleum, making it feasible to replace traditional gasoline with this light fuel.
The processed pyrolysis oil can be mixed with diesel or other fuels in different proportions to meet standards. The processed pyrolysis oil can also provide high-calorific-value fuel for boilers.
What Equipment is Needed for Waste Tire to Oil Pyrolysis?
The waste tire to oil pyrolysis plant relies on the coordinated operation of its various systems to transform waste tires into a variety of useful resources. Each system plays an indispensable and crucial role in the waste tire to oil pyrolysis process.
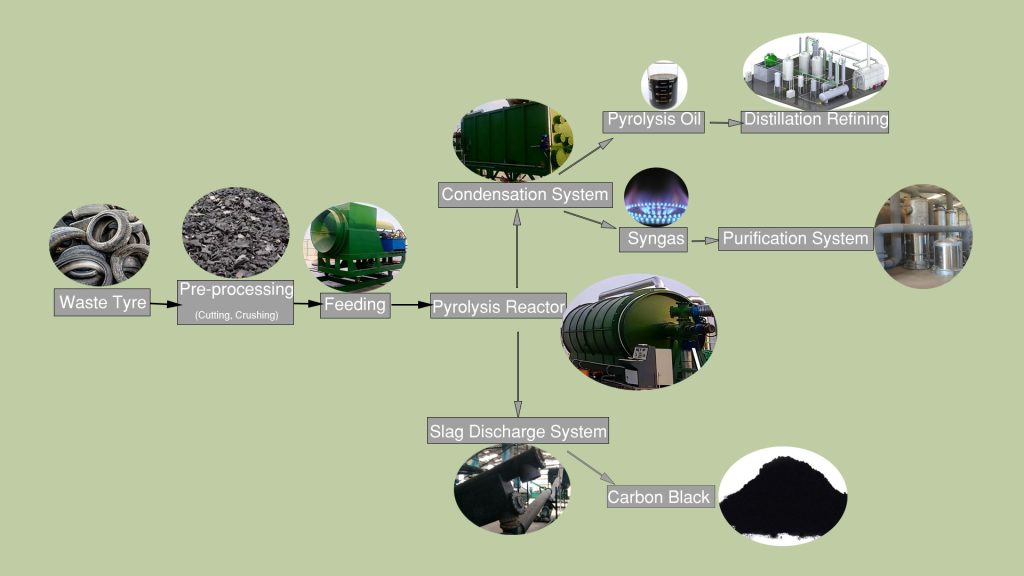
Pyrolysis Reactor
The pyrolysis reactor, as the core component of the waste tire to oil pyrolysis system, is where the pyrolysis reaction of waste tires takes place. The pyrolysis reactor rotates continuously, ensuring that the waste tires are heated more evenly during the process. Even heating helps to fully pyrolyze the waste tires, improving the efficiency of tire-to-oil conversion.
Heating System
The heating system provides the necessary high-temperature conditions for the pyrolysis reactor to facilitate the pyrolysis reaction of waste tires. Common heating methods include electric heating, gas heating, and fuel oil heating.
Condensation and Separation System
The condensation system is a crucial link in converting the oil-gas mixture into liquid oil. Condensers and cooling towers play important roles in this process.
The condenser utilizes the principle of heat exchange. It gradually cools the high-temperature pyrolysis gases, causing the oil and gas components to liquefy.
The cooling tower further cools the cooled gases and circulating water. It ensures that the condenser can operate continuously and effectively, allowing the pyrolysis gases to be successfully converted into liquid oil.
Slag Discharge System
The water-cooled screw system discharges and collects the pyrolysis carbon residue. The processed carbon black can become an important raw material for industrial production, widely used in rubber, plastics, inks, and other industries.
Gas Purification System
The exhaust gas purification system includes equipment such as dust collectors, desulfurization towers, and scrubbers. Its main function is to comprehensively treat the waste gas generated during the pyrolysis process.
The gas purification system removes particulate matter from the exhaust gas through a dust collector, making the exhaust gas cleaner. A desulfurization tower is used to remove sulfur dioxide and other acidic gases from the exhaust gas. Further purification of the exhaust gas is carried out through a scrubber to ensure that the final discharged exhaust gas meets environmental standards.
Automatic Control System
The PLC control system is responsible for monitoring and precisely controlling every aspect of the tire pyrolysis to oil process. Through various sensors and automated devices, it can monitor the parameters of the waste tire to oil pyrolysis equipment in real time and adjust them as needed.




