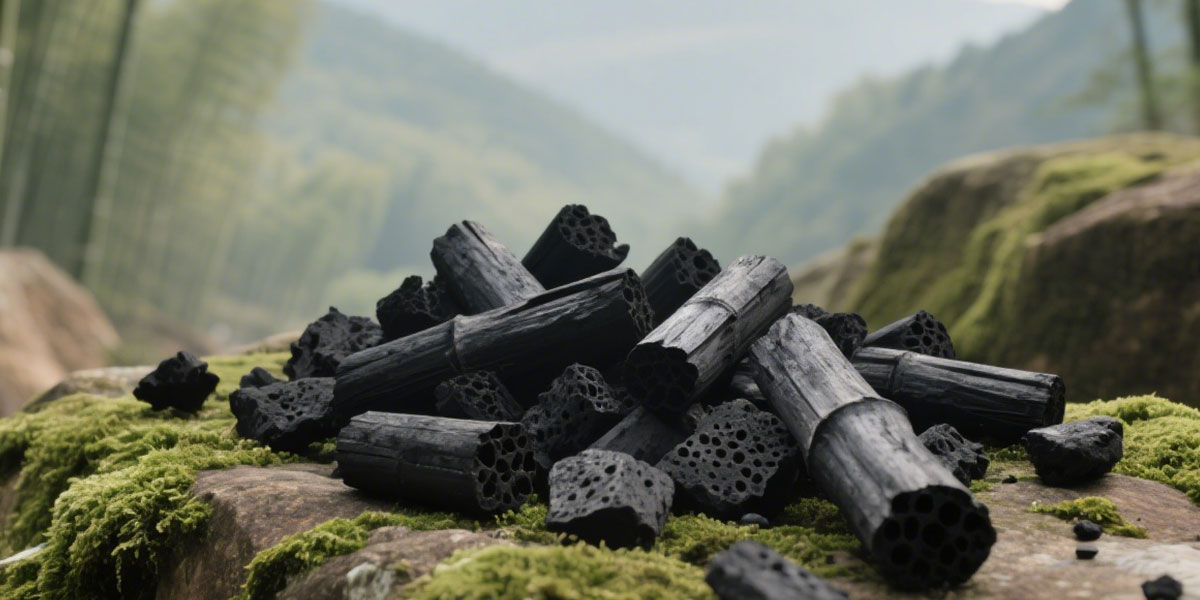
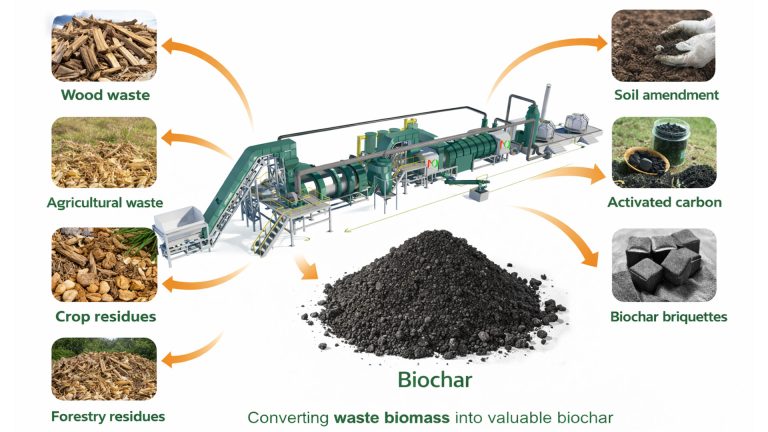
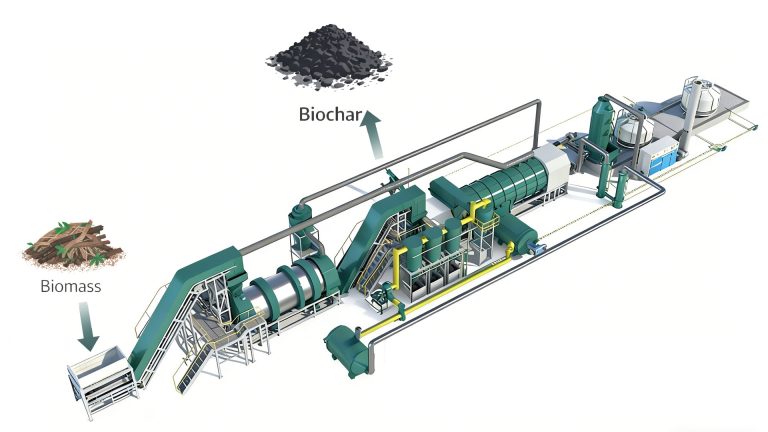
With the widespread use of bamboo, the amount of waste bamboo is also increasing. Discarded bamboo products due to damage and aging have become a pressing issue. Biomass pyrolysis technology offers a new approach to addressing this challenge. Biomass carbonization plant uses continuous pyrolysis technology for bamboo biochar making.
The conversion of waste biomass to biochar not only effectively reduces the environmental impact of waste bamboo, but also gives it new value. Biochar is a solid substance rich in carbon.
Bamboo biochar has a wide range of applications in agriculture, environmental protection, energy and other fields. It provides strong support for the sustainable development of various industries, and demonstrates enormous development potential and broad market prospects.
Bamboo Biochar Making Methods
Common bamboo biochar making methods include dry distillation and pyrolysis.
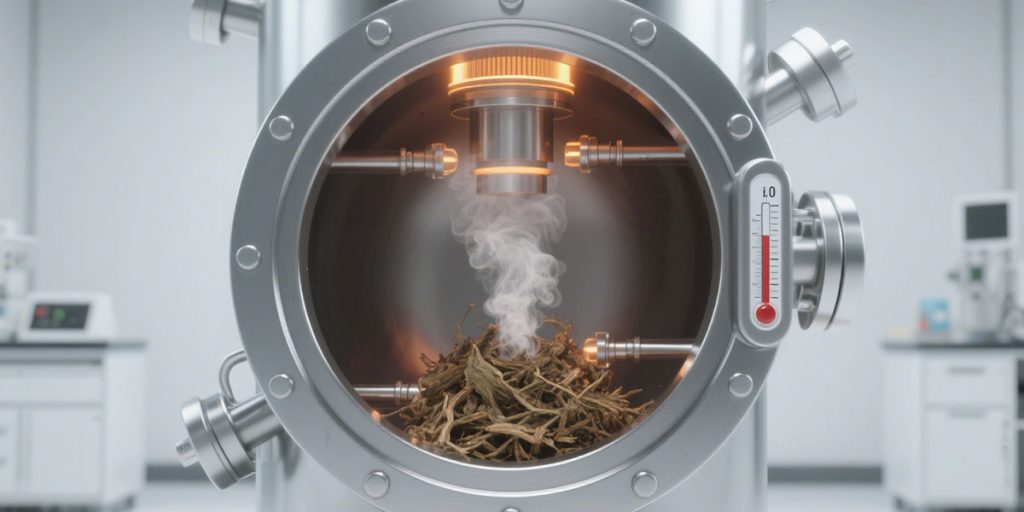

Dry Distillation
Dry distillation is a more traditional bamboo biochar making method. It involves placing bamboo in a sealed container and heating it in an airtight environment. As the temperature rises, the moisture in the bamboo evaporates first. Then, organic matter begins to decompose, producing volatile substances such as wood tar and wood gas. The remaining solids are biochar.
The advantages of dry distillation are relatively simple equipment and easy operation, making it suitable for small-scale production. However, its disadvantages are low pyrolysis efficiency, a long production cycle, and potential environmental pollution if improperly handled, including components such as wood tar. Dry distillation temperatures typically range from 500 to 700°C, and reaction times range from several hours to over ten hours.
Pyrolysis Carboniztion
Pyrolysis for bamboo biochar making involves the rapid heating of bamboo in an oxygen-deficient or low-oxygen environment.
Bamboo needs to be crushed into smaller particles or powder. This step is crucial. On the one hand, small particle size increases the specific surface area, allowing for more efficient pyrolysis and carbonization. On the other hand, a uniform particle size distribution helps ensure consistent quality of the biochar product.
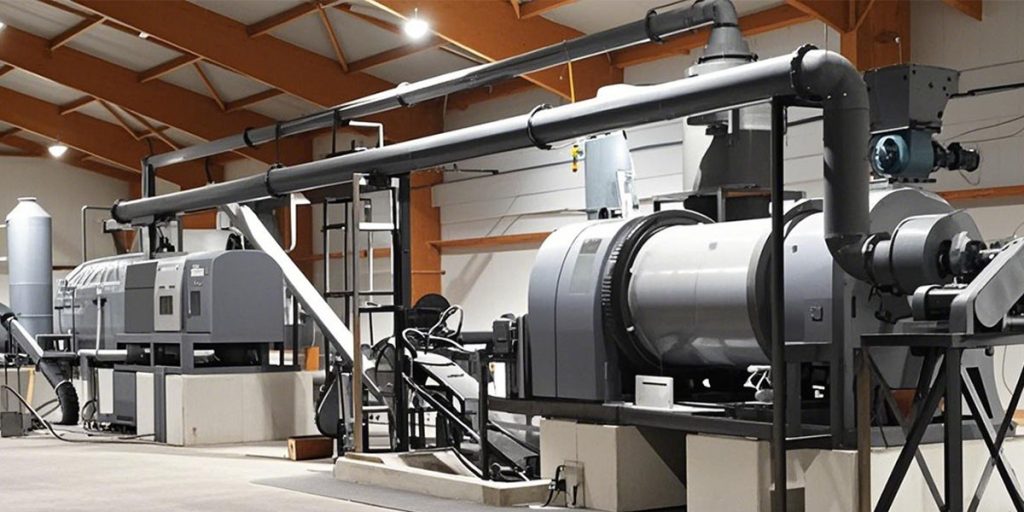

The pyrolysis carbonization process is typically divided into three stages:
- The drying stage, at temperatures between 100 and 200°C, primarily removes moisture from the bamboo.
- The pyrolysis stage, at temperatures between 200 and 600°C, begins a substantial decomposition of organic matter, producing biochar, wood vinegar, tar, and combustible gases.
- The carbonization stabilization stage, at temperatures above 600°C, further stabilizes the biochar structure and completely releases volatile components.
The advantages of biomass pyrolysis lie in its rapid pyrolysis rate, high production efficiency, and ability to better control the composition and properties of the product. The combustible gases produced by bamboo pyrolysis can be recycled and used as energy to feed the pyrolysis process, achieving energy recycling.
For large-scale industrial biochar production, continuous pyrolysis offers advantages due to its high efficiency, environmental friendliness, and energy recycling.

Pyrolysis Bamboo to Biochar Making Process
Pyrolysis carbonization is the core step in converting waste bamboo into biochar. It involves heating bamboo in an oxygen-deficient or low-oxygen environment to induce thermal decomposition of the organic matter in the bamboo.
During the bamboo pyrolysis carbonization process, large organic molecules in the bamboo, such as cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, gradually break down and decompose. These molecules are then converted into small molecules, including gas, liquid, and solid products. The solid product is bamboo biochar.
After biomass pyrolysis carbonization, biochar is hot and thermally unstable. It requires cooling to ensure stable performance and facilitate subsequent collection and storage. This cooling process generally uses indirect cooling to prevent direct contact between the biochar and air, preventing re-oxidation at high temperatures.
Mingjie bamboo charcoal making machine uses a water-cooled spiral device to transfer heat from the biochar to a cooling medium, gradually lowering its temperature. The bamboo biochar is conveyed to a cooler via a spiral conveyor. Cooling water pipes within the cooler absorb heat from the biochar, lowering its temperature from several hundred degrees Celsius to room temperature.
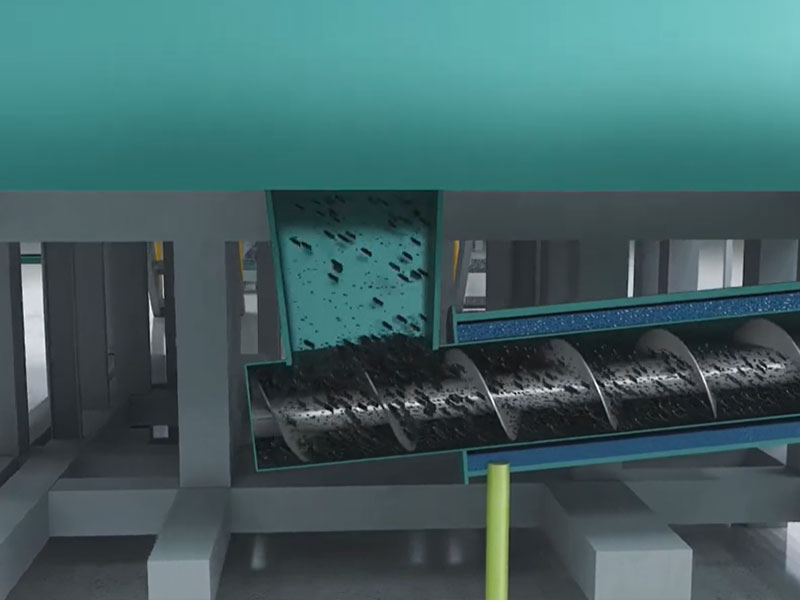
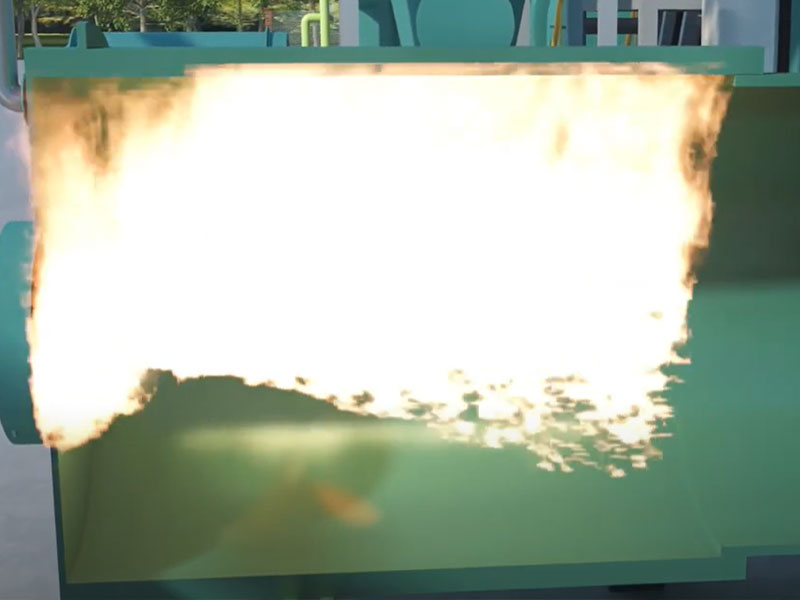


The bamboo pyrolysis carbonization process produces a large amount of gases, such as carbon monoxide, methane, and tar. Gas purification and recovery technologies can be used to address non-condensable combustible gases.
High-efficiency gas purification equipment, such as cyclones, bag filters, and spray towers, removes contaminants such as tar and particulate matter from the gases. The purified combustible gas is then recycled and fed to the combustion chamber to heat the carbonization reactor.