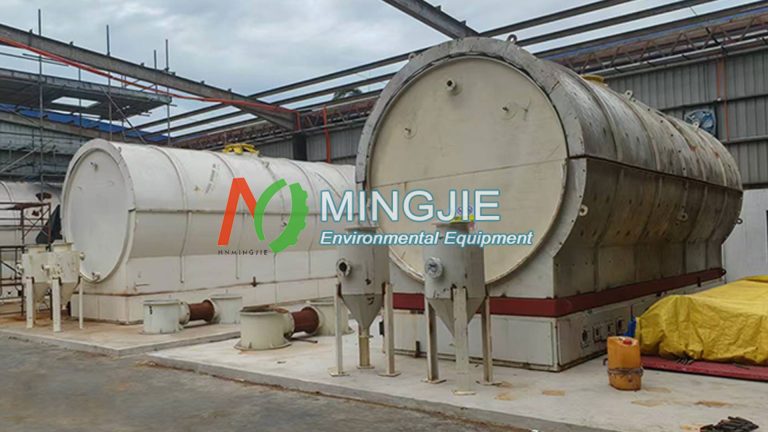
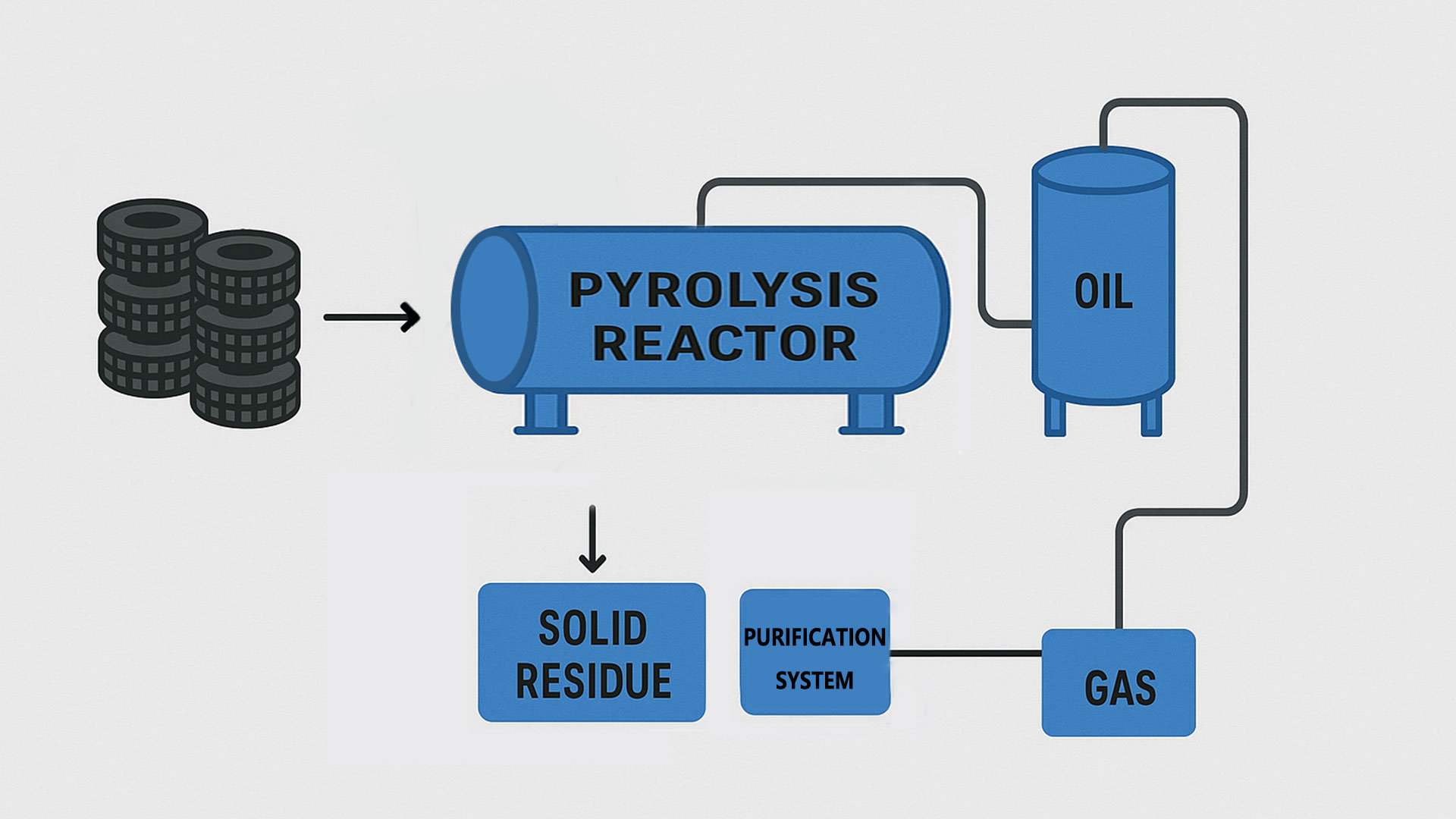
The core function of waste tyre to oil plant is to convert waste tires into usable oil products through a series of processes. Pyrolysis is the key technology. The entire waste tyre to oil process can be broadly divided into four main stages: pyrolysis, condensation, separation, and distillation.
Waste Tyre to Oil Process
Pyrolysis Stage
First, the pretreated waste tires are fed into the pyrolysis reactor of the waste tyre to oil plant. Then, in an anaerobic or low-oxygen environment, the reactor is heated to a specific temperature range (between 300°C and 550°C).
Under these high-temperature anaerobic conditions, the large molecular organic compounds in the waste tires undergo a series of complex chemical reactions, including cracking, decomposition, and rearrangement. These reactions break down long-chain molecules into smaller molecular fragments, primarily in the form of pyrolysis gas and pyrolysis oil.
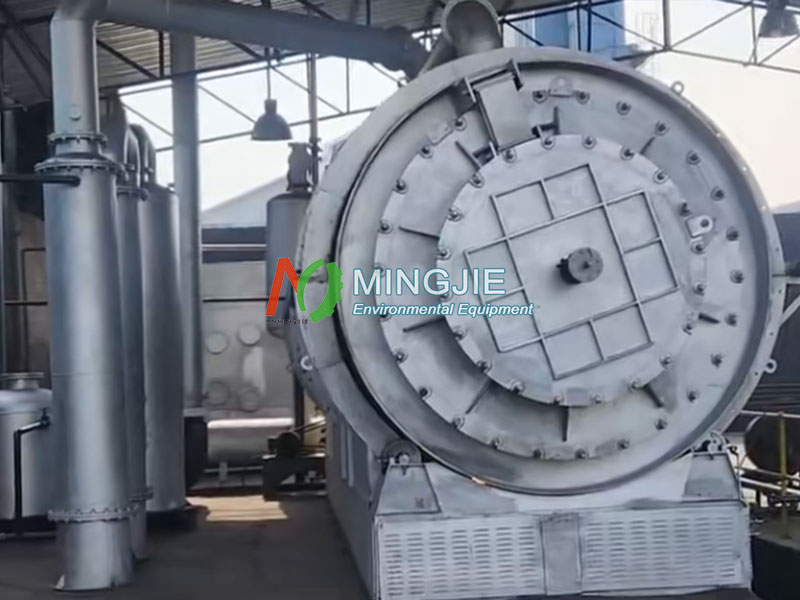


Condensation Stage
The oil-gas mixture is then transported to a condensation system via dedicated pipelines. The condensation system consists of multiple condensers that rapidly lower the temperature of the gas and vapor mixture using a cooling medium. As the temperature decreases, the oil vapor condenses into a liquid – crude tire oil.
Simultaneously, some non-condensable gases that cannot be condensed into a liquid at atmospheric pressure are collected separately. These pyrolysis gases typically have a certain calorific value and can be recycled as fuel. After purification, they are used to heat the pyrolysis equipment, achieving energy recycling.
Separation Stage
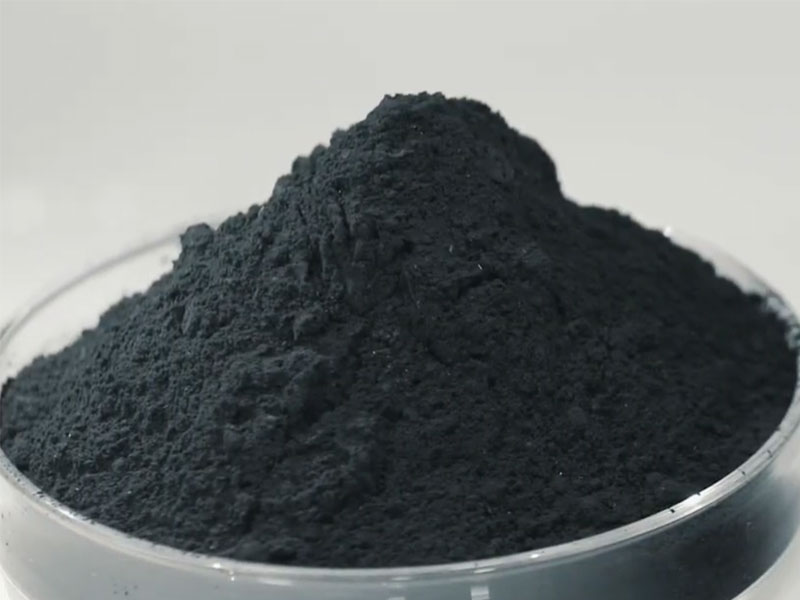
After the tire pyrolysis process, some solid residue remains in the pyrolysis reactor, mainly including carbon black and a small amount of unremoved steel wire. The waste tyre to oil plant is equipped with a residue discharge system that safely discharges these residues after the reactor cools. The steel wire in the residue can be recycled and sold to steel mills for reprocessing. The carbon black can be further processed into commercial carbon black or used as a fuel additive.


Distillation Stage
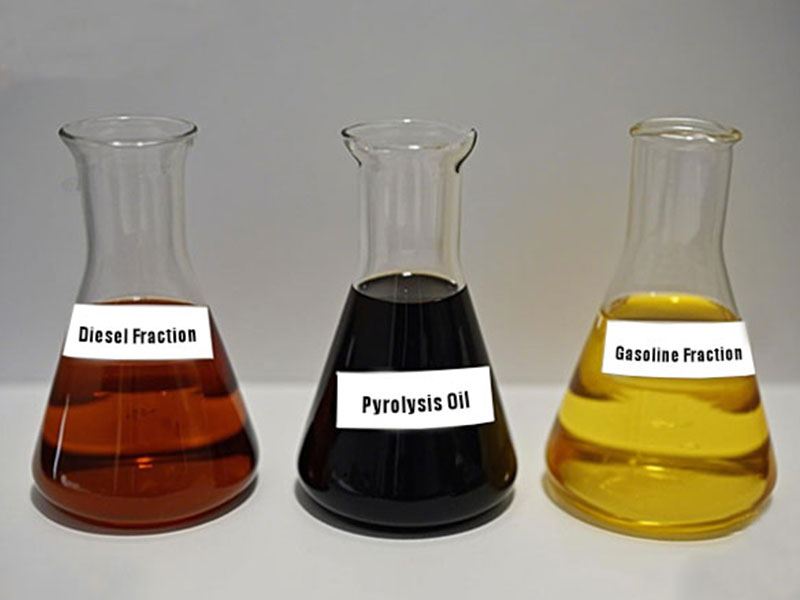
The crude tire oil obtained in the condensation stage still contains some impurities. To improve oil quality and expand its applications, the crude oil needs to undergo a purification stage. In some advanced tire oil recycling system, pyrolysis oil distillation unit is also added. Through distillation at different temperatures, crude oil is further separated into different grades of oil products, light fuel oil and heavy fuel oil.
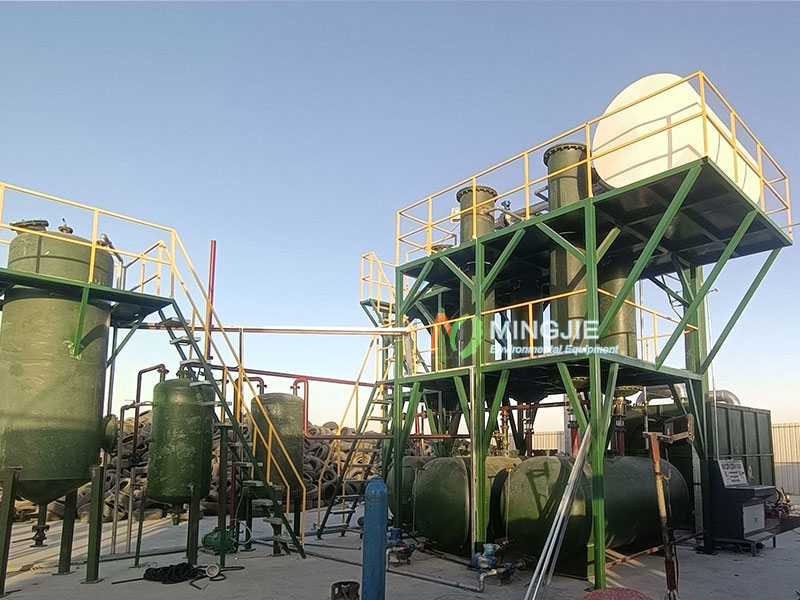

Core Components of Waste Tyre to Oil Plant
High-performance waste tyre to oil plant consists of several core components that work together to ensure the stability, efficiency, and environmental friendliness of the entire production line.
Pyrolysis Reactor
The pyrolysis reactor is the heart of the waste tire to oil plant. It is typically constructed from high-temperature and corrosion-resistant materials to withstand the high temperatures and pressures of the pyrolysis process. The design of the pyrolysis reactor is also crucial.
Advanced reactors employ a horizontal structure with an internal rotary stirring device. This ensures that the waste tires are heated evenly within the reactor, thereby increasing the oil yield. Furthermore, the pyrolysis reactor is equipped with a temperature and pressure monitoring system, which monitors the internal temperature and pressure in real time.
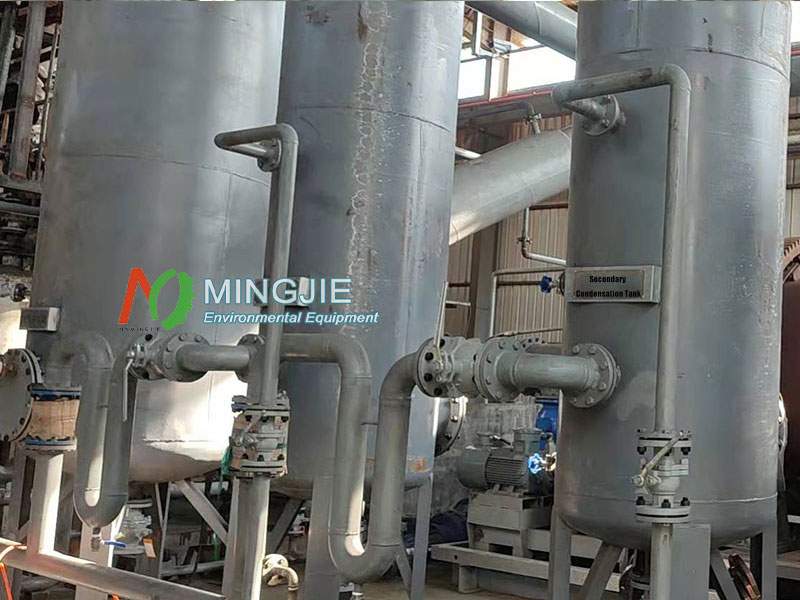

Condensation System
The condensation system is responsible for converting pyrolysis oil vapor into liquid crude oil, and its efficiency directly affects the oil production rate of the equipment. Modern waste tyre to oil plant typically adopts a multi-stage condensation design, including a primary condenser, a secondary condenser, and a tail gas condenser.
- The primary condenser first cools the high-temperature oil vapor to a certain temperature, liquefying most of the vapor.
- The secondary condenser further cools the remaining gas and vapor, ensuring that more oil vapor is condensed.
- The tail gas condenser is used to cool the non-condensable pyrolysis gas. It removes moisture and light oil from the gas, improving the purity of the pyrolysis gas for recycling.
The condenser typically uses stainless steel tubes with a large heat exchange area. This improves heat exchange efficiency and ensures effective condensation.
Dust and Gas Treatment System
Environmental protection is a critical issue in the operation of a waste tyre to oil plant. To prevent environmental pollution caused by the emission of harmful gases and dust, the waste tyre to oil plant is equipped with a comprehensive dust and gas treatment system. The dust treatment section mainly uses cyclone dust collectors and bag filters.
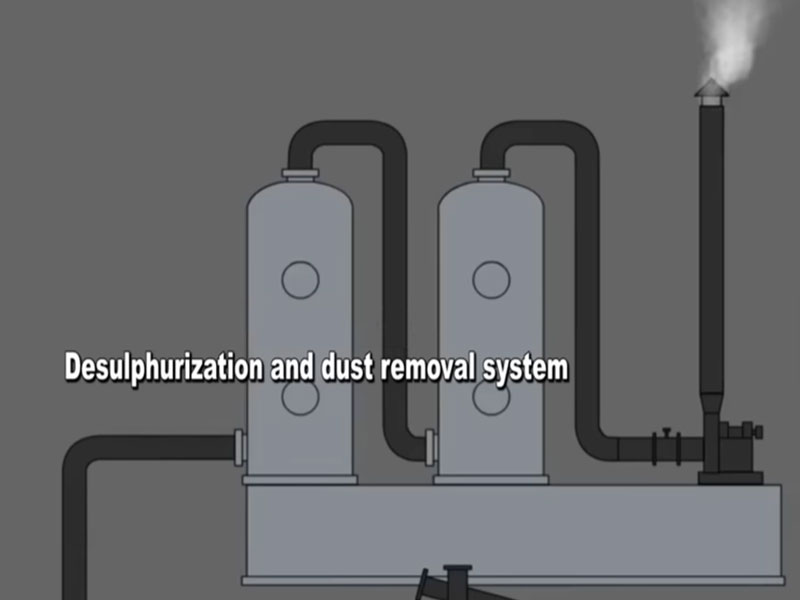
Cyclone dust collectors first remove large dust particles from the flue gas. Then, bag filters filter out small dust particles, ensuring that the dust content in the exhaust gas meets environmental standards.
The gas treatment section typically uses a combination of activated carbon adsorption and catalytic combustion. Activated carbon adsorption towers adsorb toxic and harmful substances in the flue gas. For certain gases that are difficult to adsorb, catalytic combustion devices are used to decompose them into harmless substances at a certain temperature, thereby ensuring clean and environmentally friendly exhaust gases.
Control System
The control system is the “brain” of the waste tyre to oil plant, responsible for controlling and coordinating the operation of all components. It typically employs a PLC control system.
Operators can set parameters (temperature, pressure, feed rate), and the system will automatically adjust equipment operation according to these settings. The control system also has a fault alarm function. If any component of the equipment malfunctions, the system will immediately issue an alarm and stop the relevant operation to prevent accidents.
Furthermore, the control system can record equipment operating data (such as oil yield, temperature, and pressure changes) in real time. This facilitates operator analysis and optimization of the production process.