With increasing environmental awareness and emphasis on sustainable development, sludge disposal methods are constantly evolving. Various advanced sludge treatment technologies have emerged, progressing from simple dewatering and landfilling to today’s diversified treatment methods such as anaerobic digestion, aerobic fermentation, drying and incineration, and pyrolysis carbonization.
More and more wastewater sludge companies are turning to advanced thermal treatment methods, such as pyrolysis and gasification. These methods have shown the potential for effective removal of contaminants.
Pyrolysis Sludge Disposal Method
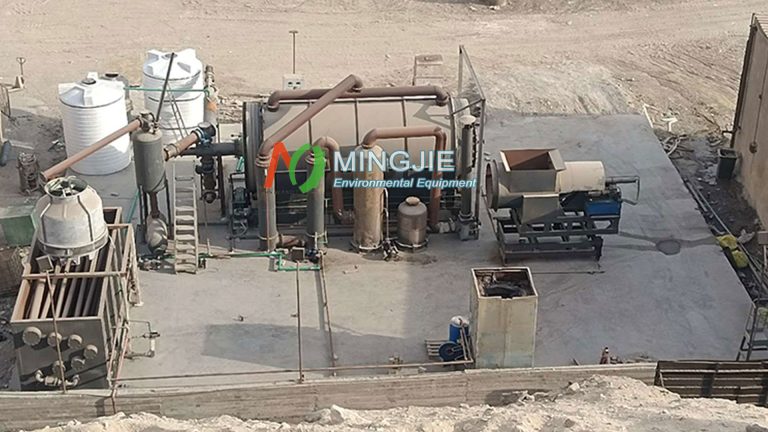
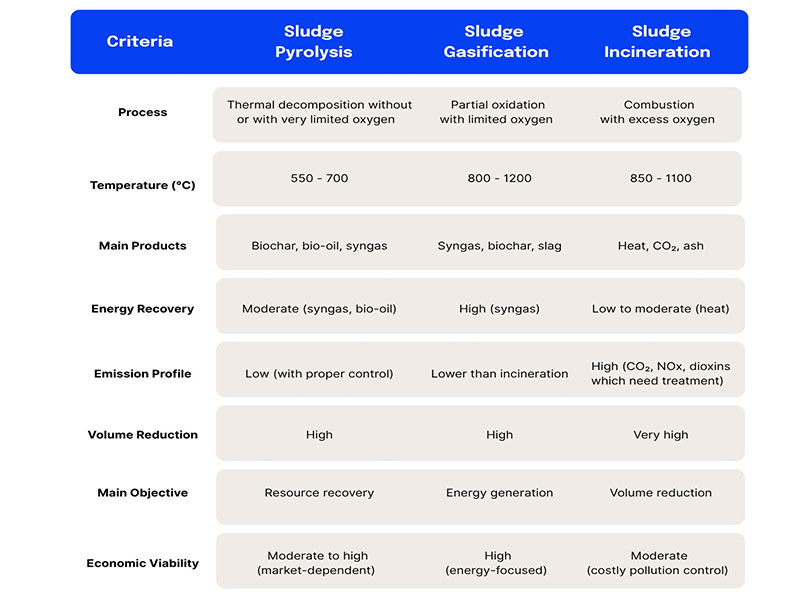
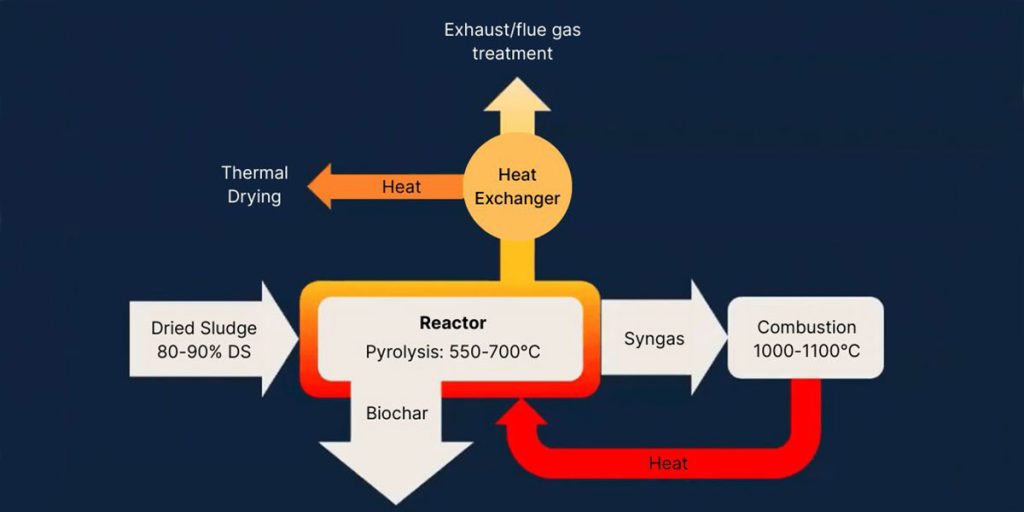
Sludge pyrolysis carbonization is a thermal treatment process for treating dewatered sludge, typically from wastewater treatment plants. This process achieves thermal decomposition of the sludge by heating it to high temperatures (550–700°C) in an anaerobic environment. This controlled pyrolysis process reduces sludge volume and converts waste into valuable byproducts.
Typically, approximately 30% to 60% of the sludge is converted into gas and oil, with the remainder forming biochar. The resulting syngas is typically used for combustion to generate heat, which is then used to maintain the reactor temperature and drive the sludge carbonization process. This integration makes the system more energy self-sufficient.
In sludge pyrolysis system, dewatered sludge is heated in a reactor under anoxic or anaerobic conditions. Pyrolysis produces three main byproducts: biochar, bio-oil, and syngas.
Pyrolysis Sludge Disposal Method can be categorized into slow pyrolysis and fast pyrolysis based on the heating rate and residence time. Slow pyrolysis is ideal when biochar is the primary target product. Fast pyrolysis is suitable for producing bio-oil as fuel or chemical feedstock.
Sludge Gasification
Sludge gasification is a complex thermochemical process. Its core involves introducing a limited amount of air or oxygen at high temperatures to convert the organic matter in the sludge into syngas.
The sludge undergoes a series of pretreatment processes, including drying and crushing, followed by drying, pyrolysis, oxidation, and reduction in a gasifier. This process transfers the chemical energy from the sludge into syngas, while simultaneously solidifying pollutants and heavy metals in inert residue. Ultimately, post-treatment achieves the clean utilization of energy products and the safe disposal of solid waste.
Sludge Incineration
Incineration utilizes high temperatures to oxidize and decompose the organic matter in sludge, converting it into substances such as carbon dioxide, water, and ash. Generally, sludge requires pretreatment before incineration, such as dewatering and drying. The pretreated sludge is then fed into an incinerator and fully combusted under high temperature (above 850℃) and sufficient oxygen conditions.
The heat generated during incineration can be recovered and utilized through waste heat boilers for power generation and heating, achieving energy recovery. The resulting flue gas requires a series of rigorous treatments, ao as to remove harmful substances and ensure compliance with emission standards. The residue after incineration is mainly inorganic matter and can be landfilled or further utilized for resource recovery.
Advantages of Sludge Pyrolysis Carbonization
Compared to traditional technologies such as landfill and incineration, sludge pyrolysis carbonization demonstrates significant competitiveness in terms of environmental safety, resource utilization, and energy costs.
High Degree of Harmlessness
Under a high-temperature, anaerobic environment, the pathogenic bacteria in the sludge are killed at a rate exceeding 99.9%, completely eliminating the risk of biological contamination. Simultaneously, organic pollutants are decomposed or fixed in biochar during pyrolysis, with detection rates far below national standards. For heavy metals, biochar can stabilize and solidify them through adsorption and complexation, with leaching concentrations only 1/10 to 1/5 of those in landfill sludge, effectively preventing soil and groundwater pollution.
High-value Products
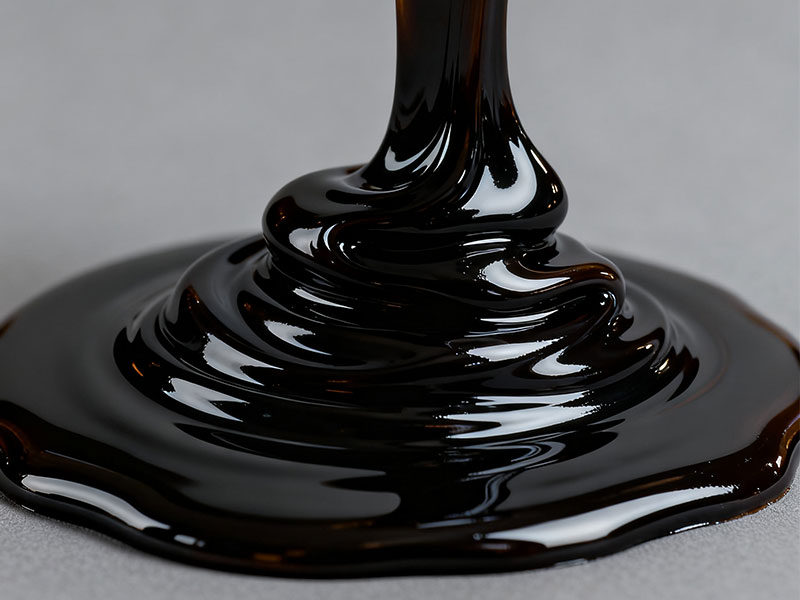
One of the most attractive aspects of sludge pyrolysis carbonization is the utilization of its byproducts. The three main products of sludge pyrolysis are biochar, bio-oil, and syngas. Each has unique application prospects, enhancing sustainability and resource utilization efficiency.
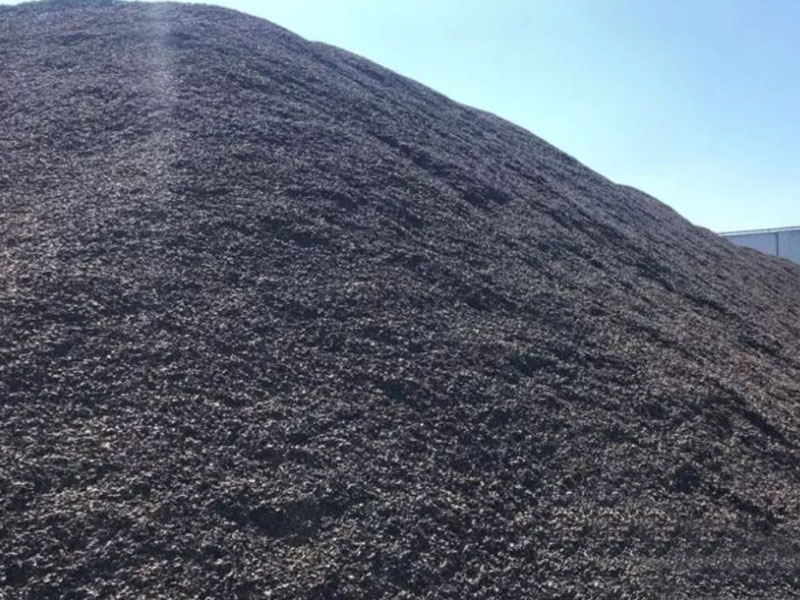



- Biochar: Soil improvement and carbon sequestration.
- Bio-oil: Renewable fuel and chemical feedstock.
- Syngas: On-site energy and electricity generation.
Low Energy Consumption
Compared to gasification and incineration sludge disposal method, pyrolysis carbonization operates in the medium-to-low temperature range. Moreover, it can recover syngas to heat the pyrolysis equipment, significantly reducing external energy input.
Data shows that the energy consumption of pyrolysis carbonization in treating 1 ton of sludge with 80% moisture content is approximately 60%-70% of that of gasification technology and 50%-60% of that of incineration technology. Moreover, the carbon emissions throughout the process are reduced by more than 80% compared to landfilling, which meets the requirements of low-carbon development.