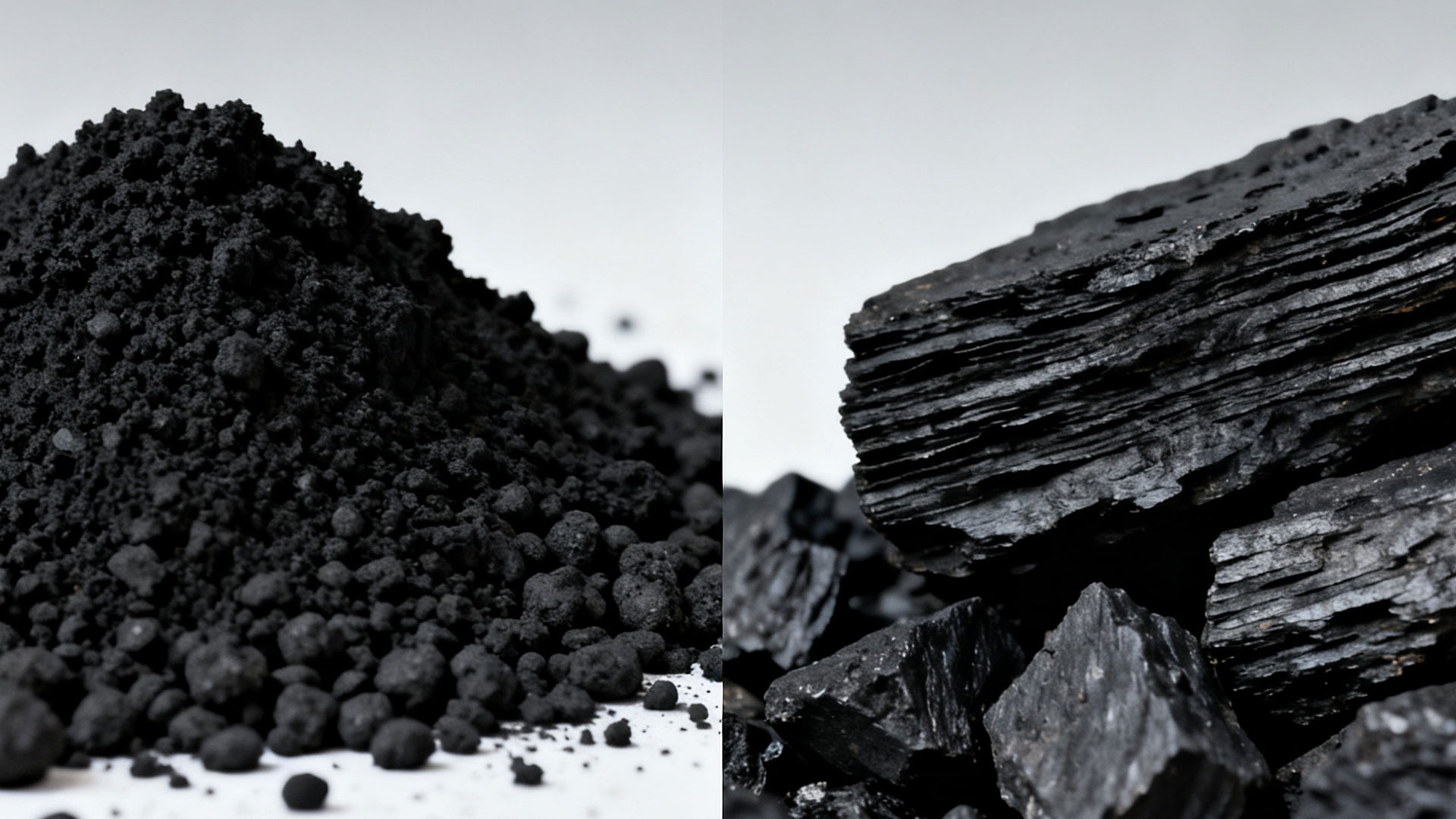
Making biochar and biocoal both use biomass as raw materials, but they differ in their core purpose, production process, and end-use applications.
The appearance of biochar is more diverse, with common forms being powder, blocks, or irregular granules. It is generally pure black with a metallic luster.
Biochar focuses on the “carbon,” aiming to improve soil quality and sequester carbon and reduce emissions. Biochar is a multifunctional carbonaceous material. While it has some fuel value, its functions are more diverse. Beyond fuel, it exhibits unique application value in agriculture, environmental protection, industry, and other fields.
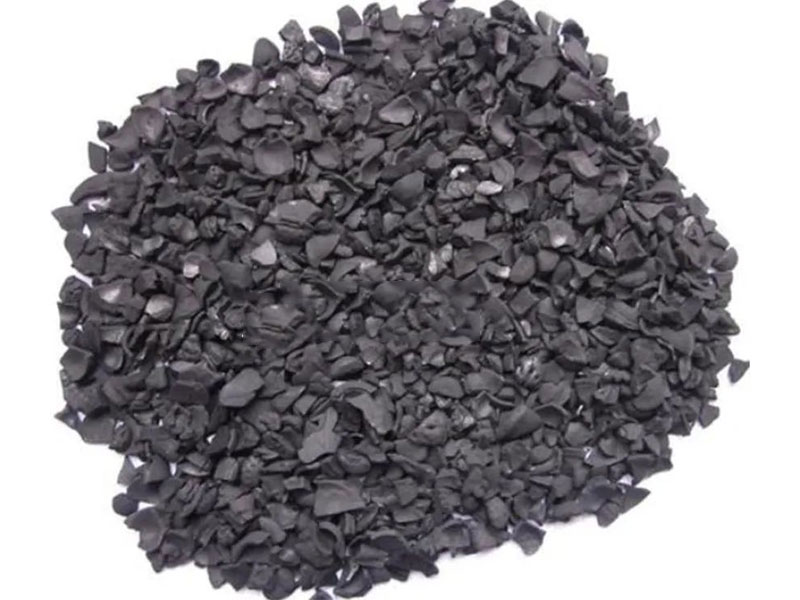
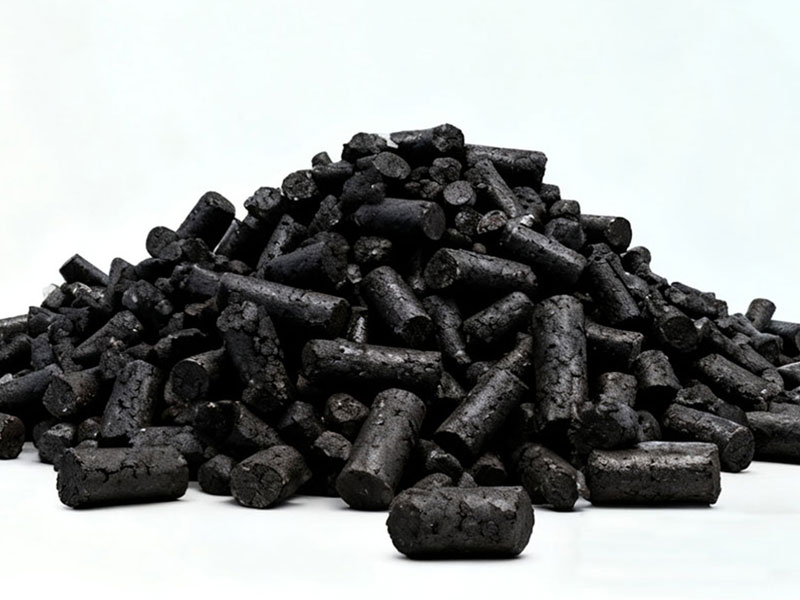


Biocoal typically exhibits relatively regular shapes, such as rods, blocks, or granules. Its color is often black or dark brown, with a low gloss. This is due to its relatively high carbon content and the presence of certain volatiles and impurities.
Biocoal focuses on the “coal,” aiming to serve as an energy fuel and replace fossil coal. Biocoal is primarily an energy product, providing heat and emphasizing its fuel properties.
Different Methods Between Making Biochar and Biocoal
Biochar Production Process
The process for making biochar is primarily based on slow pyrolysis. Temperatures are typically between 300-700°C, with slow heating rates and long residence times to maximize charcoal yield.
Slow pyrolysis involves a slow heating rate and a prolonged pyrolysis time, typically several hours. This method produces a large amount of biochar. Biochar has a well-developed pore structure, a large surface area, and excellent adsorption properties. This makes it suitable for the soil improvement and pollutant adsorption applications.
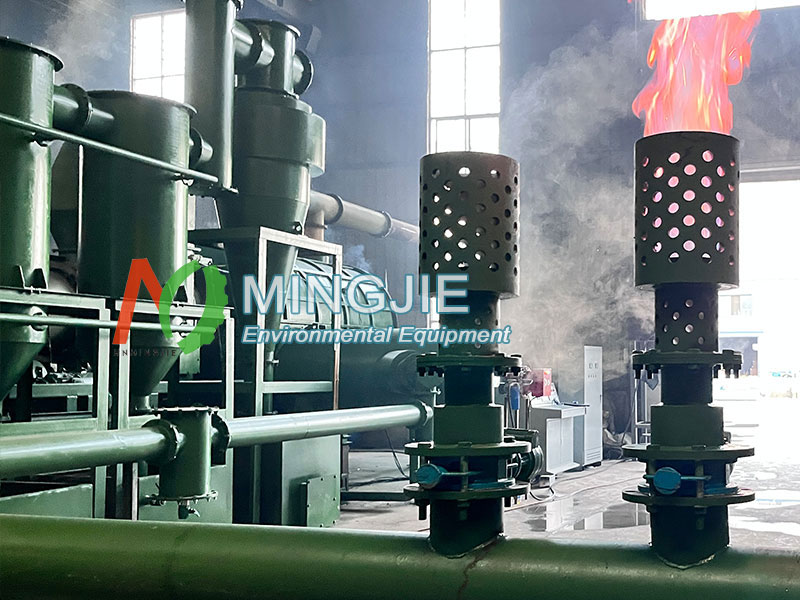

The syngas produced during the making biochar process is recycled to provide energy for the biomass pyrolysis process. The Mingjie biomass carbonization plant uses continuous pyrolysis technology, which can achieve continuous production of biochar and effective energy recovery.
The core value of making biochar lies in its carbon sequestration capacity. Once burned, this fixed carbon is immediately released back into the atmosphere in the form of CO₂, completely losing its significance as a “carbon sink“.
Biocoal Making Method

Biocoal is typically produced using rapid pyrolysis or hydrothermal carbonization. These processes operate over a wide temperature range and with short residence times to maximize oil yield and fuel quality.
During the biocoal production process, biomass is typically pre-treated by pulverization and drying to remove moisture and impurities. Then, through key steps such as forming and carbonization, high-temperature heating in an oxygen-deficient or low-oxygen environment removes volatiles and increases the carbon content. This results in biocoal with excellent combustion properties, enabling stable heat release to meet energy needs.
The forming process is crucial for giving biocoal its specific physical form. A common method is extrusion, where pre-treated biomass is compressed into rods, blocks, or pellets. This increases the biomass’s density, making it easier to store and transport.
Carbonization is the core step in improving biocoal energy density and combustion performance. This process removes a significant amount of volatiles, increases the carbon content, and ensures more stable combustion and higher heat release.
Application Difference Between Biochar and Biocoal

Making Biochar Applications
Biochar, with its unique physical and chemical properties, plays a multifaceted role in environmental protection and agriculture. Biochar making machines have become a powerful tool for improving the ecological environment and promoting sustainable agricultural development.
Making biochar has significant benefits in soil improvement. Its alkalinity can adjust soil pH, creating a suitable environment for plant growth. It also increases soil’s cation exchange capacity, enhancing its ability to adsorb and retain nutrients. Its rich pore structure improves soil aeration and water retention, facilitating plant root growth and respiration.
In wastewater treatment, making biochar also demonstrates powerful adsorption and purification capabilities. Its high surface area and rich pore structure enable it to effectively adsorb harmful substances in wastewater. Microorganisms on the biochar surface can metabolize organic matter, further purifying water quality.
Making biochar plays a significant role in carbon sequestration and emission reduction. Biochar is a highly stable carbonaceous material. When biomass is converted into biochar and applied to soil, the carbon can be stored there for a long time, reducing carbon emissions into the atmosphere.

Biocoal Carbon Emissions and Resource Utilization
Biocoal offers certain advantages in terms of carbon emissions. Its raw materials primarily come from biomass, which absorbs carbon dioxide through photosynthesis during its growth. When biocoal is burned, it also releases carbon dioxide. However, over its life cycle, the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed and released is roughly equal, making it considered a near-zero carbon emission energy source.
However, the combustion of biocoal still produces small amounts of pollutants such as nitrogen oxides. Advanced combustion technology and pollution control equipment are needed to reduce these emissions.
In terms of resource utilization, biocoal can be sourced from a wide range of sources, including agricultural waste and forestry residues. Converting waste biomass into biocoal realizes the resource utilization of waste and improves resource efficiency.
Summary
Although biochar and biocoal are both made from biomass, they differ significantly in their environmental impacts and sustainability. Understanding these differences is crucial for their appropriate selection and application.
By thoroughly studying and utilizing the properties of biocoal and biochar, we can better achieve the coordinated development of energy and the environment.